Real-World Examples of Generative AI Transforming Business Operations

2024 turned out to be a pivotal year for AI/ML development and implementation across industries. According to McKinsey, 65% of businesses actively employ it in at least one area of their operations. Organizations, on average, integrate the technology across two functions, with marketing and sales, as well as product and service development, emerging as the most common use cases. Some enterprises are reaping even greater rewards from their investments in generative AI, delivering measurable societal benefits.
The progress thus far has been highly encouraging, so we decided to take a closer look at generative AI examples and real use cases across industries.
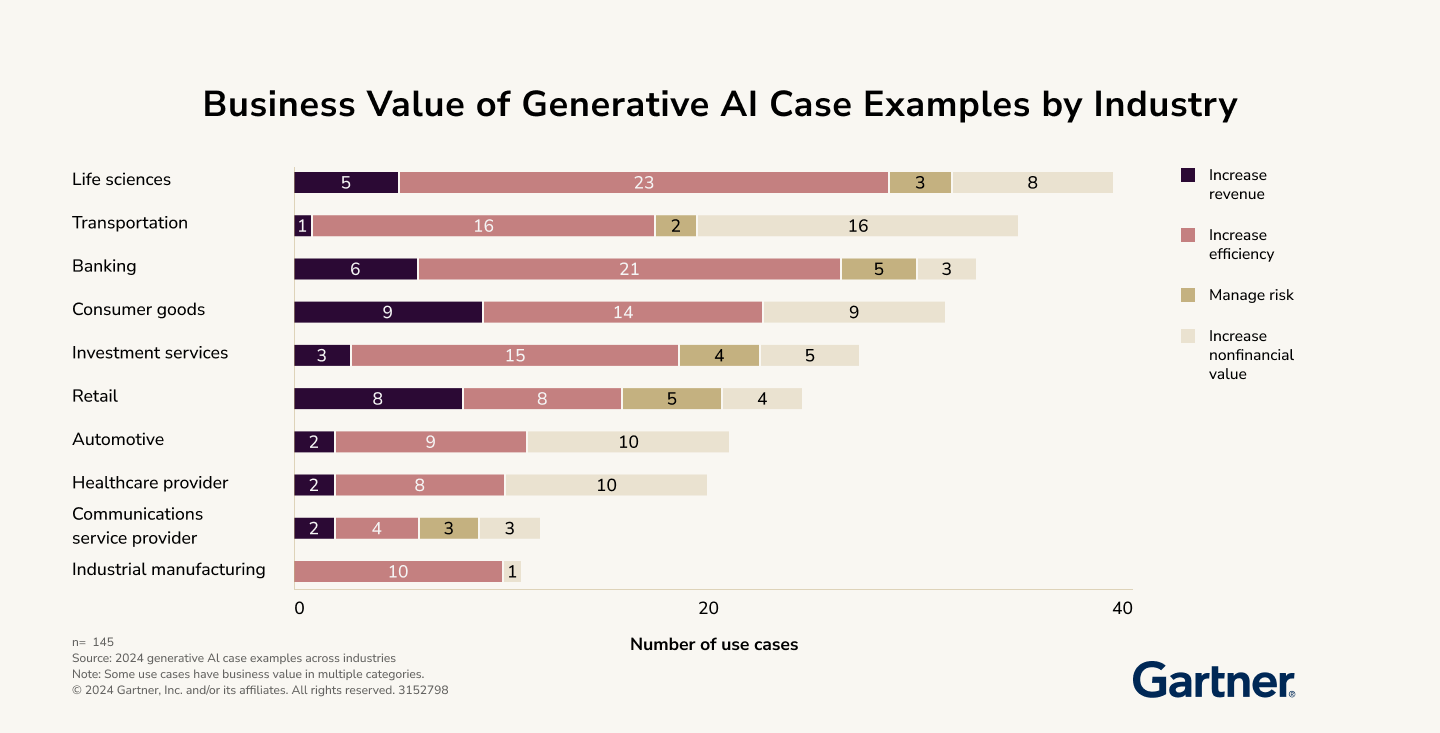
Business Value of Generative AI
Generative AI delivers results that once seemed unattainable. It accelerates coding processes from days to mere minutes, enables unparalleled personalization of products, and detects security flaws almost instantly. This remarkable technology has driven AI's ROI to surge from 13% to an impressive 31% since 2022.
These promising outcomes are primarily linked to pilot agendas, sandbox experiments, and other limited-scale initiatives. However, they've sparked a wave of optimism among business leaders regarding the future of generative AI. IBM Institute for Business Value (IBV) 2024 served 5,000 executives across 24 countries and 25 industries. The research found that confidence in the technology has markedly increased. Over 77% of respondents believe generative AI is market-ready. Furthermore, 62% now perceive GenAI as a tangible, game-changing reality.
Generative AI's impact on profitability is already evident. From 2022 to 2023, its contribution to operating profit nearly doubled, reaching close to 5%, and executives anticipate this figure could rise to 10% in 2025. Embedding generative AI within existing enterprise software workflows is also projected to yield sustainable ROI, reinforcing its strategic importance based on forthcoming research from the IBM IBV.
While generative AI's potential is promising, it's not a panacea. Rather than acting as a replacement for human work, it excels when it complements human efforts, making cultural adaptation crucial for sustained success. The widespread adoption of generative AI hinges more on people's willingness to integrate it than on the technology itself.
So, how should leaders approach traditional AI vs generative AI to ensure a meaningful and enduring transformation? Here are three tips you can try:
- Implement generative AI in low-risk, non-core functions. By prioritizing areas where traditional AI has already demonstrated success, companies can achieve incremental profitability while minimizing risk.
- Apply generative AI to essential business functions. Focus on areas like sales, information security, and supply chain logistics. These critical yet underutilized applications are becoming focal points for enterprises seeking lasting competitive advantage.
- Adopt a platform-based approach to generative AI. It consolidates resources and outcomes across departments or partner organizations. This strategy enables organizations to deploy the technology in high-potential functions like finance, human resources, manufacturing, supply chain, and sales and marketing.
Generative AI Market
The global generative AI market is projected to reach approximately USD 1005.07 billion by 2034. This represents an anticipatory CAGR of 44.20% over the forecast period. For the North American market alone, the value exceeded USD 10.60 billion in 2024, with a CAGR of 10.60% expected in the years ahead. These estimations, based on revenue metrics (in millions and billions of USD), use 2024 as the reference base year for calculations.
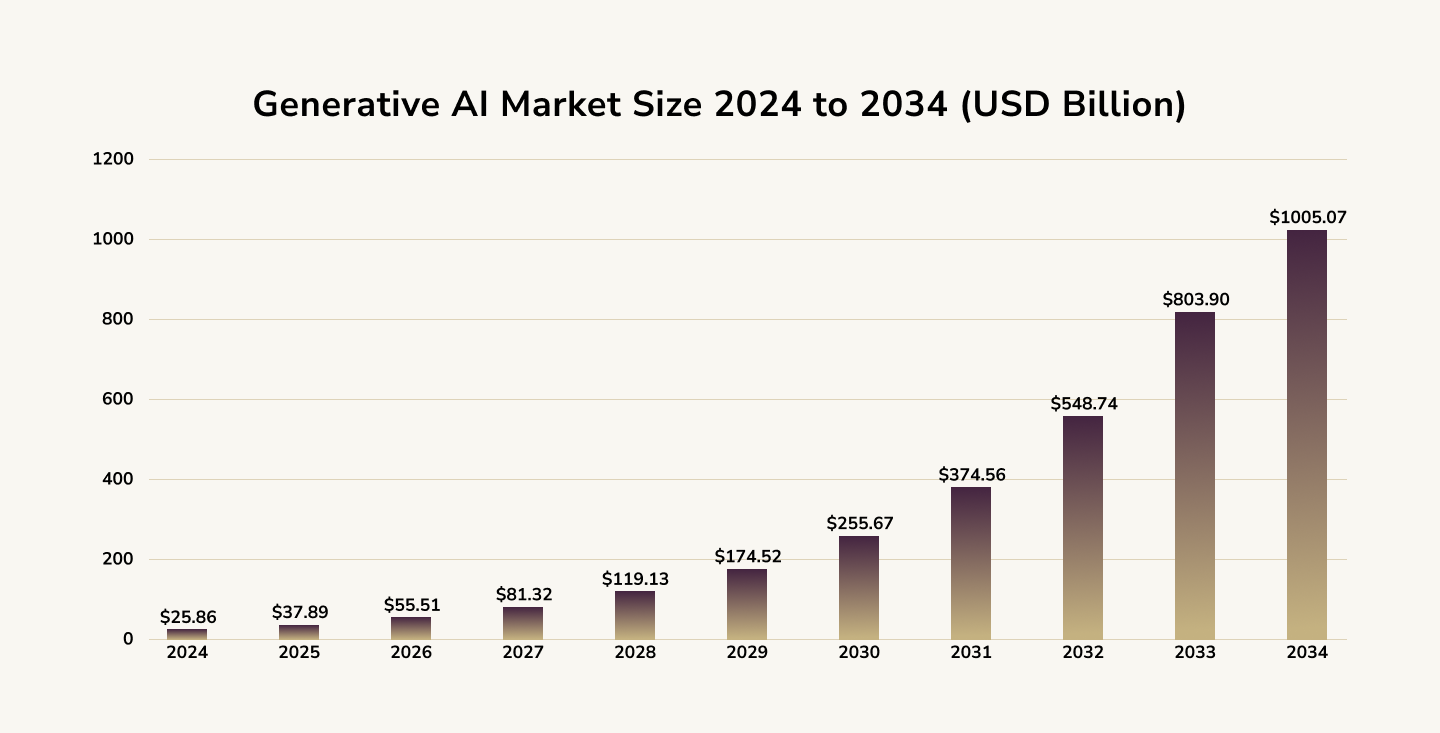
Source: Precedence Research
While generative AI demonstrates impressive capabilities in creating new content, it is not without its constraints. Being in its nascent stages, generative AI demands significant investment and a specialized workforce for effective implementation. According to IBM's 2022 Global AI Adoption Index Report, nearly 34% of respondents identified a lack of AI-specific knowledge, skills, or expertise as a critical obstacle to the adoption of AI technologies across industries. Consequently, the shortage of skilled professionals, coupled with the high costs associated with implementation, is expected to act as a barrier to the growth of the generative AI market.
Technology Insights
Generative AI technology is categorized into four main areas: variational auto-encoders, GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), diffusion networks, and transformers. Among these, transformers dominated the market in 2024, capturing over 42% of the revenue share, largely due to the increasing popularity of applications such as text-to-image generation. Transformers are designed to understand the contextual relationships between words in a phrase or text. They use a technique called self-attention, which enables the model to weigh the significance of words relative to their context within a sequence.
Unlike traditional models like Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), which process input sequentially and lack a holistic grasp of context, transformers process sequences with global understanding. A notable example is the transformer DALL-E, which can interpret text instructions and generate corresponding images. Similarly, OpenAI's GPT-3, another transformer-based model, excels at generating text that mimics human writing, from emails to creative content like poems.
Generative AI Examples in Real World: Generative AI Apps
To illustrate the tangible impact of AI, we will explore practical examples of generative AI that are already transforming how people approach their daily work routines.
OpenAI's ChatGPT
One of the most prominent examples of generative AI is OpenAI's ChatGPT, a conversational agent designed to engage users in natural language. Built on the GPT architecture, this AI can generate human-like text responses, making it a valuable tool for customer support, content creation, and education. Companies are integrating ChatGPT into their customer service platforms, where it can handle inquiries 24/7, provide information, and even assist in troubleshooting, thereby freeing human agents for more complex tasks. The implications here are profound; businesses can enhance customer experience while reducing operational costs.
DALL-E 2
Another notable application from OpenAI is DALL-E 2, an image generation model that creates stunning visuals from textual descriptions. For instance, a user can input a prompt like "a futuristic cityscape at sunset", and DALL-E will generate a unique image that captures this vision. This capability has far-reaching implications in creative industries such as advertising, game design, and even architecture. Designers can quickly visualize concepts, test aesthetics, and iterate on ideas without the need for extensive manual drawing or modeling.
Note: DALL-E 2 raises questions about authorship and creativity. As artists and creators begin to incorporate AI-generated imagery into their work, it challenges traditional notions of artistic creation, prompting discussions about the role of human intuition and emotional expression in art.
Runway ML
Runway ML is revolutionizing the film and media industry by providing tools that harness the power of generative AI for video editing and content creation. Its applications include real-time video effects, background replacement, and even script writing. Filmmakers can use Runway ML to generate storyboards based on script inputs, enabling them to visualize scenes before committing resources to film.
Note: the platform's ability to produce synthetically-generated content raises critical ethical questions about authenticity and the potential for misinformation. As deepfakes and AI-generated media become more prevalent, the industry must grapple with the implications for trust, representation, and intellectual property rights.
Jasper AI
Jasper AI is a content generation tool that assists marketers and writers in creating high-quality text. By inputting specific keywords or topics, Jasper can generate articles, social media posts, and marketing copy that align with the user's desired tone and style. This capability not only enhances productivity but also democratizes content creation, allowing individuals and businesses with limited writing skills to produce compelling narratives.
DeepArt and Artbreeder
Platforms like DeepArt and Artbreeder utilize generative adversarial networks (GANs) to create unique artworks by blending existing images or transferring styles. DeepArt allows users to apply the style of famous painters to their photographs, effectively transforming them into works of art. Artbreeder, on the other hand, enables users to 'breed' images, combining elements from different artworks to create new compositions.
Generative AI in Healthcare Examples
The use of Generative AI in healthcare enhances patient care, optimizes operational efficiency, and supports medical research. We've researched several compelling real-world examples that illustrate its profound impact.
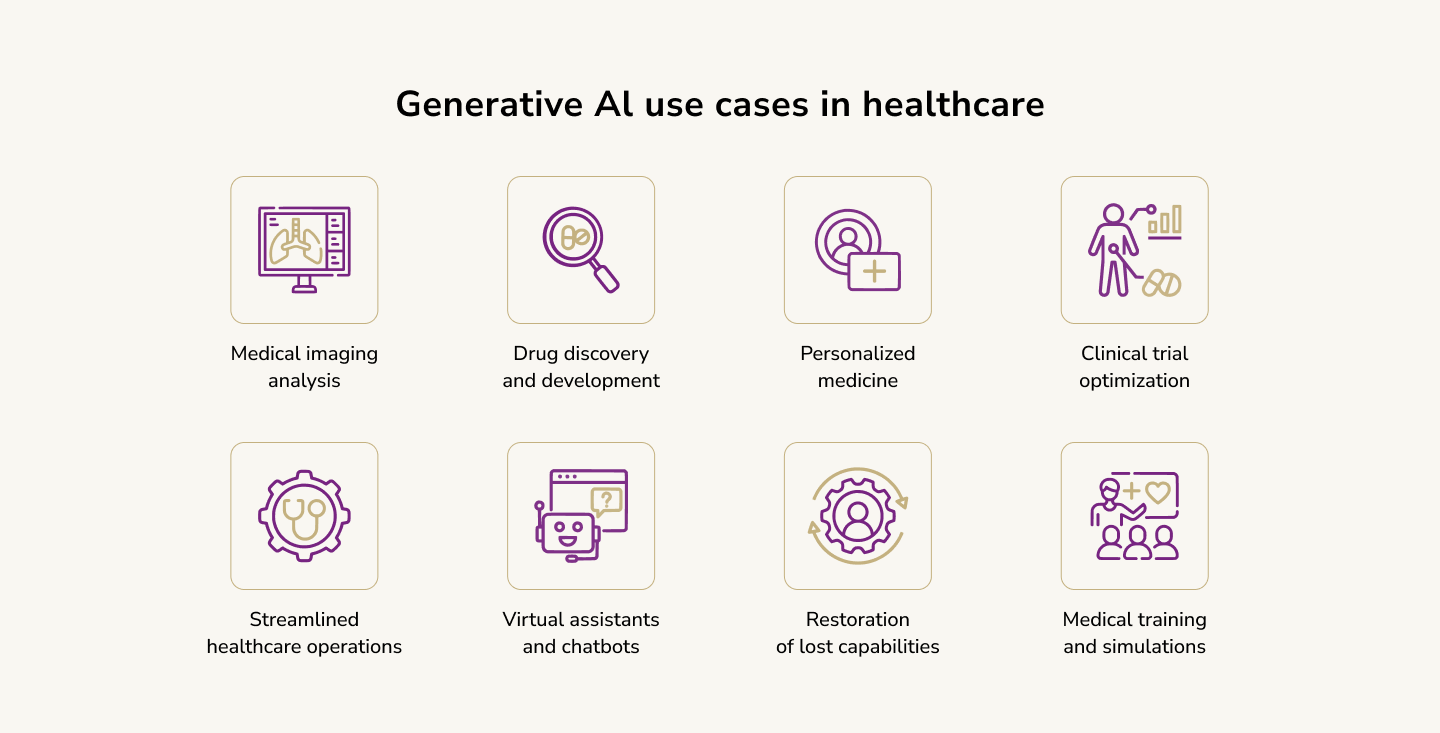
Drug Discovery and Development: Insilico Medicine
Insilico Medicine, a biotechnology company, utilizes generative adversarial networks (GANs) to design novel drug compounds. In a notable achievement, the company developed a promising drug candidate for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in less than 18 months, a process that typically requires several years. By analyzing vast datasets of existing compounds and biological data, Insilico's AI systems can propose new molecular structures that are more likely to succeed in clinical trials, thus potentially revolutionizing the speed at which new therapies can be brought to market.
Personalized Treatment Plans: Tempus
Tempus, a tech company specializing in precision medicine, employs AI algorithms to analyze clinical and molecular data from cancer patients. By generating insights into how different patients might respond to various treatments, Tempus helps oncologists craft personalized treatment plans. The AI-driven recommendations can significantly improve outcomes, enabling healthcare providers to select therapies that are more likely to be effective for specific genetic profiles.
Medical Imaging and Diagnostics: Zebra Medical Vision
Zebra Medical Vision has developed AI algorithms that analyze medical imaging data, such as X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs. Their technology can detect a wide range of conditions, including cardiovascular diseases and cancers, often with a level of accuracy comparable to that of human radiologists. Furthermore, the algorithms can generate synthetic images to augment training datasets, allowing for better model performance in detecting rare conditions. This capability not only enhances diagnostic precision but also helps in the early detection of diseases, which is critical in improving patient outcomes.
Virtual Health Assistants and Chatbots: Buoy Health
The use of AI in telemedicine has long been anticipated. For now, the market is focused on virtual solutions. Buoy Health employs a generative AI-powered chatbot that interacts with users to assess symptoms and provide personalized health information. By asking a series of questions, the chatbot can generate tailored advice on the next steps, whether it's self-care, scheduling an appointment, or seeking immediate medical attention. This approach not only enhances patient experience but also reduces unnecessary visits to emergency rooms, optimizing healthcare resource utilization.
Clinical Documentation and Administrative Tasks: Nuance's Dragon Medical One
Nuance's Dragon Medical One is a voice recognition and NLP tool that assists healthcare professionals in creating clinical documentation. Basically, it uses AI in the hospital management system to facilitate routine tasks. By generating notes and reports from spoken language, the system dramatically reduces the time clinicians spend on documentation. In studies, it has been shown to save physicians up to 2 hours a day, resulting in increased productivity and more time for direct patient interaction.
Generative AI for Retail Examples
Advanced algorithms and ML help retailers create innovative solutions that enhance customer experience, streamline operations, and drive sales.
Personalized Shopping Experiences: Stitch Fix
Stitch Fix, a leading online personal styling service, utilizes generative AI to refine its recommendation system. By analyzing vast datasets of customer preferences, purchase history, and even social media activity, Stitch Fix's algorithms generate personalized clothing suggestions tailored to individual tastes. The AI not only predicts which items customers are likely to buy but also creates new styles based on emerging fashion trends.
Note: this smart approach not only enhances customer satisfaction but also reduces returns, a significant cost issue in the retail industry. The ability to generate personalized recommendations at scale illustrates the power of generative AI in making shopping feel uniquely curated for each individual.
Virtual Try-Ons: Sephora and L’Oreal
The beauty industry has embraced augmented reality (AR) fueled by generative AI to enhance customer engagement. Companies like Sephora and L’Oreal have developed virtual try-on applications that allow customers to visualize how makeup products will look on their skin before making a purchase. Using generative AI, these applications analyze facial features and skin tones to create realistic renderings of products in real time. In a world where consumers demand instant gratification and personalized experiences, virtual try-ons exemplify how generative AI can bridge the gap between digital and physical retail.
Inventory Management: Walmart
Walmart, the retail giant, has integrated generative AI into its inventory management systems to optimize supply chain operations. By forecasting demand patterns using generative algorithms, Walmart can predict which products will be in high demand across various regions. This predictive capability allows the retailer to adjust inventory levels dynamically, minimizing overstock and stockouts.
For instance, during seasonal shifts or unexpected sales spikes, generative AI helps Walmart fine-tune its inventory, ensuring that shelves are stocked with the right products at the right time.
Dynamic Pricing: Amazon
Amazon has long been a pioneer in leveraging data for competitive advantage, and its use of generative AI for dynamic pricing is a prime example. The e-commerce giant employs algorithms that analyze various factors, including competitor pricing, demand fluctuations, and customer behavior. These algorithms can generate real-time pricing adjustments that maximize sales and profit margins.
For example, during peak shopping seasons like Black Friday, Amazon can dynamically lower prices on certain items to attract more buyers while simultaneously increasing prices on high-demand products.
Content Generation: Nike
Nike has embraced generative AI to enhance its marketing efforts, particularly in creating engaging content for social media and digital platforms. By analyzing customer interactions and preferences, Nike's AI systems can generate tailored marketing messages, promotional emails, and even product descriptions that resonate with target audiences. This not only saves time and resources but also ensures that content remains fresh and relevant.
For instance, during product launches, Nike can use generative AI to create specific campaigns that highlight features appealing to different segments of their customer base.
Generative AI in Marketing Examples
Generative AI empowers brands to enhance customer engagement, optimize content creation, and personalize experiences.
The New York Times and AI-Generated Newsletters
The New York Times has integrated generative AI to craft personalized newsletters tailored to the unique interests of its subscribers. By analyzing reader behavior and preferences, the AI generates content that resonates with individuals, thus increasing engagement rates. This strategic use of generative AI boosts loyalty and aids in retaining subscribers in a competitive digital landscape.
Coca-Cola's AI-Driven Advertising
Coca-Cola has utilized generative AI to create dynamic advertisements that adapt in real time based on consumer behavior and context. By employing AI algorithms to analyze data trends, Coca-Cola designs campaign visuals and messaging that resonate with specific demographics, locations, or even cultural phenomena. This ensures that the brand remains agile in responding to shifting consumer sentiments.
Hootsuite and AI-Driven Post Creation
Hootsuite has integrated generative AI tools that assist brands in creating engaging social media posts. By utilizing language models, Hootsuite's platform can generate content that aligns with brand voice and audience preferences, crafting everything from catchy captions to full blog posts. This enhances creativity by providing a steady stream of ideas, enabling marketers to maintain a consistent presence across multiple platforms.
Netflix and Content Recommendations
Netflix employs generative AI algorithms to curate and personalize viewing recommendations, but its application extends to content creation as well. The platform uses machine learning models to analyze viewer preferences and trends, helping to inform the development of new series and films. For instance, AI-generated insights might suggest a specific genre mix or character type that audiences are gravitating towards, allowing Netflix to produce content that is more likely to resonate, thus maximizing viewer retention and satisfaction.
Generative AI Examples in Banking
As the financial sector embraces technological advancements, the incorporation of generative AI tools is helping institutions streamline operations, enhance customer experiences, and fortify security protocols.
Personalized Customer Interactions: Erica
One of the most significant applications of generative AI in banking is the use of chatbots stretching the boundaries of conversational banking. Banks like Bank of America leverage AI-powered chatbots, such as Erica, which utilize natural language processing and generative AI to provide tailored financial advice. Erica can analyze user data and generate customized insights. For instance, it helps customers manage expenses, offers savings strategies, and even provides alerts about unusual spending patterns.
Fraud Detection and Risk Management
Generative AI plays a pivotal role in enhancing fintech fraud detection and prevention mechanisms. HSBC has implemented generative AI algorithms to analyze vast datasets and identify anomalous patterns that typically precede fraudulent activities. By generating predictive models based on historical data, these systems can dynamically adjust to emerging threats, reducing the incidence of false positives while effectively flagging genuine risks.
Content Generation for Marketing and Communication
In the competitive landscape of banking, effective communication is paramount. Banks like Wells Fargo utilize generative AI to create marketing content automatically. Through the analysis of customer profiles and behavior, the AI can generate personalized marketing emails and social media posts that resonate with specific demographics. This level of personalization enhances engagement and improves conversion rates, allowing the bank to maintain a competitive edge in a crowded marketplace.
Automated Compliance and Reporting
Compliance with regulations is an ongoing challenge for financial institutions, but generative AI is making this task more manageable. For instance, JPMorgan Chase employs generative AI for compliance monitoring, which streamlines the process of generating reports and ensures adherence to complex regulatory standards. By using AI algorithms to analyze transaction data, the bank can automatically produce compliance reports with minimal human intervention, reducing the risk of human error and freeing up valuable resources for more strategic initiatives.
Risk Assessment in Lending
Generative AI is revolutionizing the lending process by refining risk assessment methodologies. ZestFinance, a financial technology company, utilizes generative AI to analyze alternative data sources, such as social media activity and online behavior, alongside traditional credit scores. This comprehensive approach allows lenders to assess borrower risk more accurately, enabling them to make informed lending decisions. Consequently, more individuals with thin credit files can access loans, promoting financial inclusion and economic growth.
Financial Forecasting and Strategy Development
In a rapidly changing market, the ability to forecast trends is invaluable. Goldman Sachs has integrated generative AI into its financial modeling processes to simulate various market scenarios. The technology generates multiple potential outcomes based on historical data and market indicators. Thus, financial forecasting with AI results in reliable and robust investment strategies.
Generative AI in Education Examples
AI helps personalize learning, enhance content creation, and foster critical thinking in the educational landscape.
Personalized Learning Platforms: Knewton and Smart Sparrow
Knewton's adaptive learning technology leverages GenAI to create personalized learning experiences for students. By analyzing data from student interactions, Knewton adjusts the learning path based on individual strengths and weaknesses. Similarly, Smart Sparrow offers adaptive e-learning platforms that tailor content to meet the needs of each student. These systems generate real-time feedback and learning resources, allowing educators to provide differentiated instruction effectively.
Intelligent Tutoring Systems: Carnegie Learning
Carnegie Learning has developed an AI-powered tutoring system, MATHia, which provides students with personalized math instruction. This platform employs GenAI to assess student performance and adaptively generate problems based on their understanding and progress. The system offers hints, feedback, and step-by-step guidance, promoting conceptual understanding and catering to diverse learning styles.
Automated Content Generation: ScribeSense
ScribeSense is an AI tool that assists educators in creating customized learning materials, quizzes, and assessments. By analyzing curriculum standards and student needs, ScribeSense generates relevant content that aligns with specific educational goals. This ensures that students encounter engaging and pertinent materials tailored to their learning objectives.
Administrative Efficiency: Aeries Software
Aeries Software leverages AI to streamline administrative tasks within schools. By automating attendance tracking, grading, and communication with parents, Aeries frees up educators to focus more on teaching and less on paperwork. The use of GenAI in these systems ensures that data management enhances accuracy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Enhanced Engagement through Gamification: Kahoot!
Kahoot!, a game-based learning platform, utilizes GenAI to create interactive quizzes and learning games tailored to various subjects. The platform analyzes student performance data to recommend specific game formats and topics that could enhance engagement and understanding. Students can participate in real-time competitions, fostering a collaborative environment that motivates learners through gamified experiences.
Generative AI in Manufacturing Examples
By leveraging advanced algorithms and machine learning models, manufacturers are now able to create complex designs, optimize processes, and predict equipment failures with remarkable accuracy.
Generative Design in Aerospace: Airbus
One of the most notable applications of generative AI in manufacturing can be found in the aerospace sector, particularly with a company like Airbus. Generative design software utilizes algorithms to explore numerous design alternatives based on specified parameters such as weight, strength, and cost.
For instance, Airbus adopted Autodesk's generative design software to develop a cabin partition that is not only lighter but also structurally sound. The resulting design was 45% lighter than traditional models, leading to significant fuel savings over the aircraft's lifespan and a smaller environmental footprint.
Supply Chain Optimization: Siemens
Siemens, a global industrial giant, is harnessing generative AI to enhance supply chain resilience and efficiency. Through predictive analytics and machine learning, Siemens can simulate various supply chain scenarios, allowing for optimized inventory levels and reduced lead times.
By leveraging AI-driven insights, Siemens has improved its decision-making processes—enabling the company to respond swiftly to disruptions, such as those seen during the COVID-19 pandemic. The ability to forecast demand accurately means that Siemens can maintain production continuity, reduce waste, and better align its manufacturing processes with market needs.
Predictive Maintenance: General Electric
General Electric (GE) has pioneered the use of generative AI in predictive maintenance across its manufacturing facilities. By analyzing vast amounts of operational data from machinery, GE's AI models can predict when equipment is likely to fail, allowing for proactive maintenance scheduling. This approach minimizes downtime and extends the lifespan of critical machinery.
For instance, GE's Digital Wind Farm initiative uses AI to optimize the performance of wind turbines based on historical and real-time data, increasing energy output while reducing operational costs. By anticipating issues before they arise, GE not only enhances efficiency but also contributes to the sustainability of energy production, demonstrating the transformative power of AI in traditional manufacturing settings.
Custom Product Development: Adidas
Adidas has embraced generative AI to revolutionize custom product development, particularly in its 4D printing technology. Utilizing algorithms to generate lattice structures for shoe midsoles, Adidas can create footwear that offers personalized support and comfort. This process not only accelerates product development cycles but also allows for the creation of shoes tailored to individual customer preferences.
By integrating customer feedback and preferences into the design process, Adidas exemplifies how generative AI can foster innovation while enhancing consumer engagement. This shift toward mass customization represents a significant departure from traditional manufacturing paradigms.
Future of Business Operations with Generative AI
Envisioning the future, Impressit anticipates several key transformations that will redefine how organizations operate. One of the most profound impacts of GenAI will be on decision-making processes. Traditionally, businesses have relied heavily on historical data analysis to inform strategies. However, GenAI can synthesize vast amounts of data, identifying patterns and generating predictive models with unprecedented accuracy.
The future of customer engagement will also be deeply intertwined with GenAI capabilities. By harnessing natural language processing (NLP) and sentiment analysis, businesses can create personalized experiences at scale. Chatbots and virtual assistants will evolve to understand and anticipate customer needs, delivering tailored solutions and proactive support.
GenAI’s ability to automate repetitive tasks will free human resources to focus on higher-value activities. With intelligent automation, businesses can streamline operations across various functions—be it supply chain management, human resources, or finance. GenAI can generate reports, compile data, and even draft communications, significantly reducing time spent on mundane tasks.

Roman Zomko
Other articles