Conversational Banking: Application and Examples

Services across domains depend heavily on the quality of customer experience. For finance, interaction with clients represents a massive amount of work as banks have to approach each case individually. But sometimes, communication doesn’t go well or doesn’t happen at all because call centers are busy. Having a client on the other end of the wire who ends up with unanswered questions or unsolved issues doesn't help to play the game.
Does conversational banking mean the end of staying on hold or long lines at the bank to get your problems resolved? Let’s try to figure it out.
What is Conversational Banking?
Conversational banking is a natural evolution of digital and mobile banking. While mobile apps allow basic account management and transactions, conversational banking offers personalized and intuitive experiences without making users sift through apps or websites. It relies on AI, Communications Platform as a Service (CPaaS), and conversational messaging tools. Combined, these technologies empower financial institutions to track customer interactions, learn from them, and deliver personalized support across communication channels.
Technology exists to make our lives more convenient, and in this case, it reached its goal. Conversational AI in banking app development provides financial institutions with an opportunity to satisfy users' needs for hyper-personalization. Finally, each individual can receive one-on-one assistance, whether through text, call, or video chat, using any mobile device. Personalized support is just a message away. There’s no need to visit physical branches unless clients choose to.
Perhaps this is the best part of conversational banking. It allows customers to address their financial needs on their own terms and timelines. From this perspective, technology makes a major step toward redefining what it means to truly serve the customer.
Why Banking Needs Conversational AI
Banks choose how to shape tomorrow’s experiences for their clients. Given the rising customer demands and the proliferation of cyber threats, they better do their best.
Meeting Growing Customer Expectations
The COVID-19 crisis accelerated the shift to digital financial services. At the time (and, perhaps, still) the industry wasn’t ready to deal with pressing customer demands. Clients expect more than quick resolutions; they need instant access to information and services. Above all, financial services users value autonomy — choosing how and when they interact with businesses. Despite the rapid growth of digital banking, there’s a huge gap in digital self-service solutions adoption.
This has driven the BFSI sector to explore advanced tools, including conversational AI.
Conversational AI understands the customer’s intent and context allowing the technology to:
- ensure tailored customer service
- answer complex queries
- solicit user feedback
- recommend products and services
- enable transactions.
The main task of a chatbot is to deliver guidance at critical moments within the customer’s financial journey. But, unlike single-tool solutions like chatbots, conversational banking incorporates a combo of technologies that make digital conversations practical. These range across multiple channels, including:
- messaging platforms
- live customer service systems
- voice-based conversational interfaces.
Ultimately, conversational banking encapsulates both ease and convenience for users. The challenge lies in using AI technologies effectively while maintaining a human-centric touch to deliver genuinely impactful experiences.
Battling Rising Cybersecurity Threats
Financial institutions have made cybersecurity a priority. However, effective threat prevention goes beyond advanced technology and antimalware solutions. It requires fostering a strong cybersecurity culture. Educating teams on threat detection and data protection can be a great first step toward achieving unanimity on safety priorities. Many organizations turned to security awareness programs to reinforce these measures.
Since remote work is now the norm, businesses have a hard time monitoring employee work. Challenges such as these have prompted major players in the financial industry, including Wells Fargo and Fidelity Investments, to transition from traditional call centers to automated systems. This shift has been adopted widely across the sector, with conversational AI playing a pivotal role in streamlining customer service, improving operational efficiency, and enhancing security practices.
Conversational AI in banking alters existing security measures by
- monitoring transactions in real time
- alerting customers to suspicious activities
- identifying emerging fraud patterns
- enabling banks to implement preventive measures.
Let’s say an AI system detects a transaction that deviates from a customer’s typical behavior. It will calculate the likelihood of fraud and notify the customer before any damage is done.
Conversational AI vs. Generative AI
Although these two AI technologies overlap, they serve distinct purposes. They also perform differently in terms of applications and outputs. GenAI focuses on producing a wide spectrum of text and visual content. Trained on diverse datasets, Generative AI models interpret an extensive range of prompts and then generate content accordingly. Meanwhile, conversational AI is engineered to engage with people by mimicking human speech patterns. Its primary goal is to facilitate personalized and meaningful communication. This is why it relies heavily on training with large datasets. It has to learn to encompass common customer questions, responses, and conversational nuances.
Their reliance on context and interaction is what sets them apart. Conversational AI depends on real-time human interactions and contextual cues to function effectively. GenAI operates independently, drawing on its training data to produce content without needing live human input.
However distinct, these technologies can still complement each other in a well-rounded AI strategy. Their synergy can help avoid data bottlenecks that often hinder data flow.
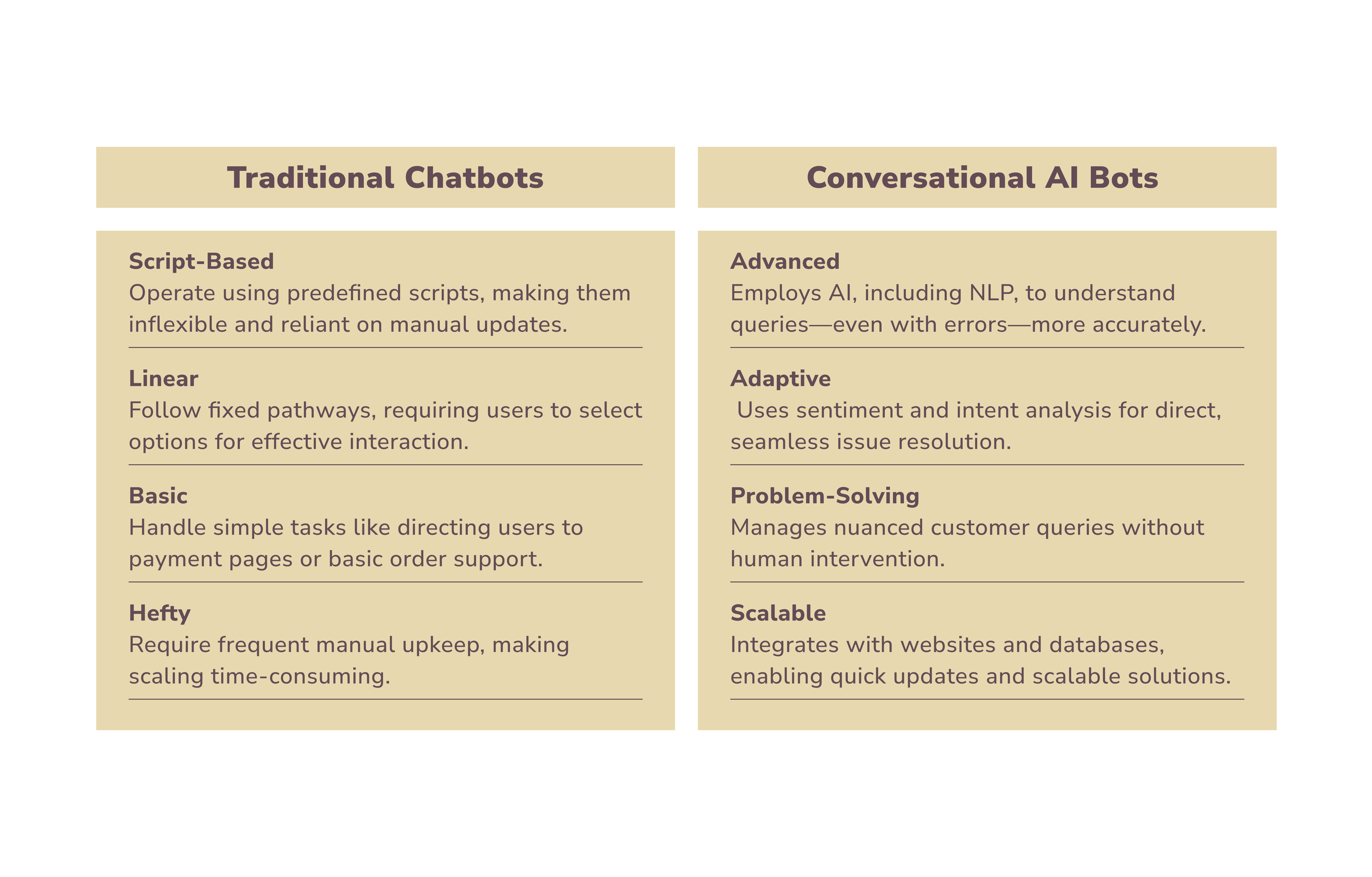
Traditional Chatbots vs Conversational AI Bots
Traditional chatbots are limited in scope: they operate based on predefined rules meaning they can’t handle requests beyond their scripted capabilities. Confined to basic chat interfaces with menu-based structures, they provide standardized responses rather than personalized solutions. This simplicity often falls short of user expectations, especially for those seeking tailored interactions and clear answers to specific questions.
Conversational AI enables the creation of more sophisticated, AI-powered chat systems with broader capabilities. This disparity often leads to the terms “conversational AI” and “chatbots” being used interchangeably. Meanwhile, they’re not. Conversational AI goes beyond chat interfaces. It powers solutions like voice-activated assistants and interactive voice systems, offering support across a company’s platforms, from its website to its mobile app.
How Does Conversational AI in Banking Work?
Conversational AI in banking functions as a virtual assistant available 24/7 within multiple communication channels. Typically, a user can initiate a conversation via:
- the bank’s mobile app
- the bank’s website
- messaging apps (e.g., WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, etc.)
- SMS or RCS.
Customers only have to type or speak their requests to the AI assistant. Powered by NLP, conversational AI swiftly interprets requests, even if they contain typos. It’s not a dialog tree, so there’s no need to stick to predefined keywords or commands.
The AI responds promptly, handling tasks like balance inquiries instantly. It may propose financial recommendations based on the client’s banking history and profile. If an inquiry is more complex, it may raise additional questions to better understand customer concerns. What makes this technology (and AI in general) so fantastic is that it learns from interactions. It goes through evolution, resulting in a smarter system adept at predicting user preferences.
Top Use Cases of Conversational AI for Banking
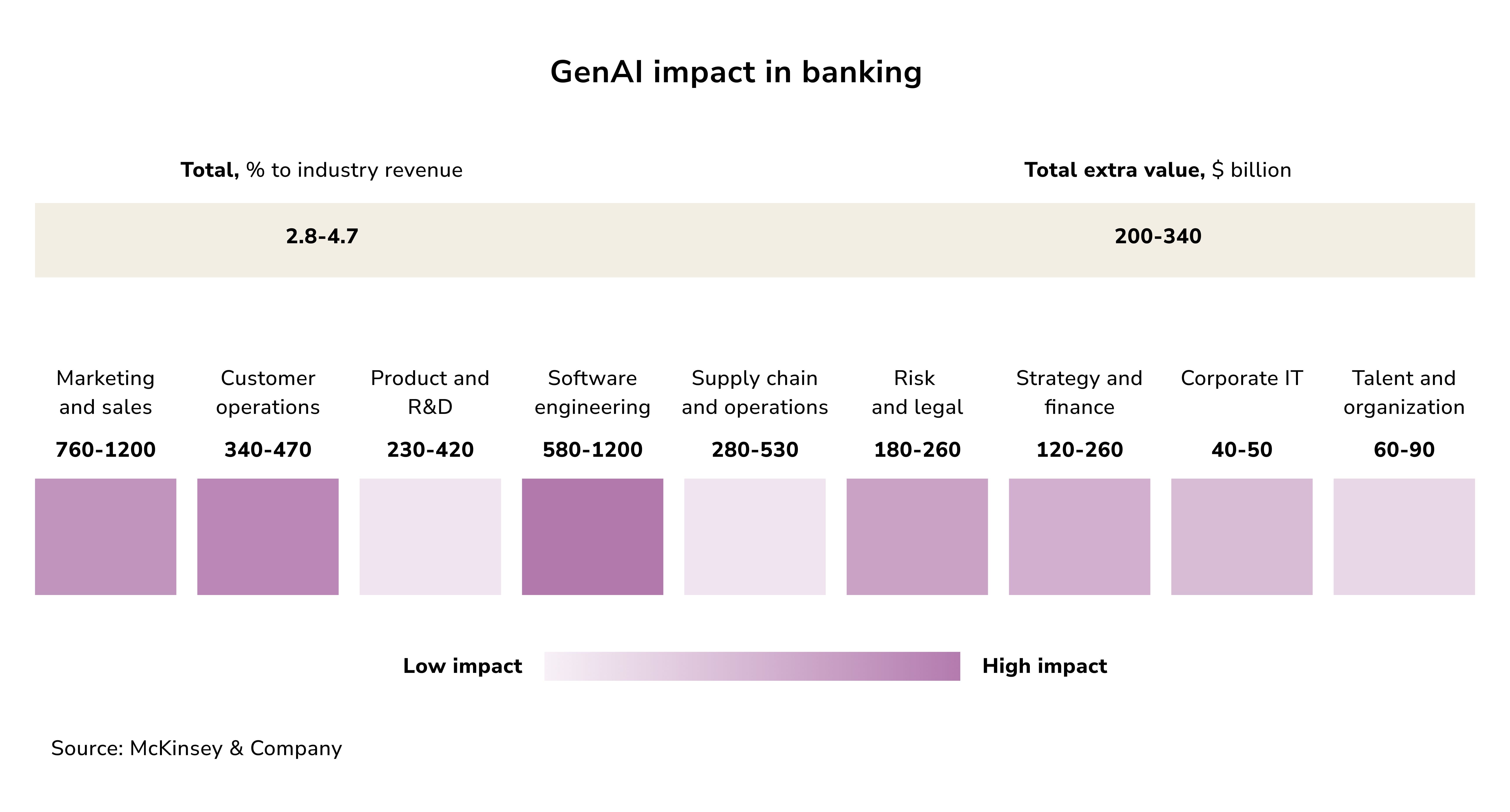
Projections indicate GenAI could contribute between $200 billion to $340 billion annually in revenue and cost savings. This potential boost to the industry’s annual revenue (from 2.8% to 4.7%) is predominantly driven by the application of conversational banking chatbots.
What are those applications, and what value do they bring to businesses?
Optimizing Internal Communications for Global Teams
Language barriers often hamper global communication in multinational banks. The outcome? Slower than needed decision-making, misunderstandings, and disrupted workflows across key communication channels.
AI chatbots bridge these gaps with real-time written translation, vocal interpretation, multilingual support, contextual understanding, etc. Besides, chatbots can seamlessly integrate with tools like Microsoft Teams, Skype, and Slack. Their scalability ensures they can grow alongside your user base.
Key business benefits:
- improved collaboration between diverse teams
- translation-related cost savings
- clearer communication leading to higher productivity
- reduced compliance risks and financial errors.
Enhancing Employee Expertise and Retention
The banking sector is burdened by the process of onboarding and training employees. High turnover rates, complex regulations, and disconnected training resources hinder learning outcomes. Additionally, many programs are rushed, generalized, or fail to include progress tracking and refresher courses.
AI-powered chatbots address these inefficiencies by acting as central hubs for onboarding and training processes. They provide personalized learning paths, track progress, and suggest materials tailored to individual strengths and knowledge gaps. For instance, Dutch AMRO Bank reduced attrition by 40% with an AI virtual assistant, while SouthState Bank transformed its intern program using ChatGPT.
Key business benefits:
- faster onboarding and skill-building for employees
- reduced turnover through targeted development
- greater expertise and employee satisfaction.
Improving Customer Query Resolution
AI chatbots can handle repetitive queries while freeing up human agents for more complex issues. These tools access vast knowledge bases to provide quick, accurate resolutions and offer two effective approaches:
- Pre-screening and responding to queries automatically, reducing agent workload.
- Self-service tools that allow customers to independently resolve their concerns, regardless of language or location.
For example, Morgan Stanley uses GPT-4 technology to enable advisors to find answers efficiently, leading to faster and more accurate service.
Key business benefits:
- faster response times for customer queries and technical issues
- reduced workload for support teams.
Assisting in Code Development
GenAI assists with fintech software development. By suggesting the next lines of code or helping draft the first versions, AI let’s developers focus on refining their work. Giants like Goldman Sachs and Wells Fargo are already leveraging generative AI, with Goldman Sachs reporting a potential 30-40% increase in developer productivity and projected savings of up to $100 million.
Key business benefits:
- increased coding efficiency
- significant cost reductions.
Personalized Financial Guidance
As far as personalization in banking goes, communication definitely plays a key role in it. Conversational AI tools generate helpful insights into customers’ financial goals, investment preferences, risk tolerance, repayment history, etc. With this information, banks can deliver personalized recommendations on investment products and retirement planning tailored to each individual. These customized solutions improve engagement, pushing higher conversion and retention rates.
Key business benefits:
- increased customer loyalty
- rise of repeat business and lifetime customer value (CLV).
Continuous Support for Transactions
Ensuring routine banking tasks are handled efficiently is yet another task AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can handle easily. Customers can check account balances, transfer funds, adjust credit card limits, and pay bills without expert intervention.
These smart tools interpret customer intent accurately, providing relevant solutions or forwarding complex inquiries to human agents when necessary. Additionally, these bots can access integrated knowledge bases to offer immediate support for out-of-scope queries. A great example is Bank of America’s Erica, an AI-powered assistant that proactively offers financial advice based on users' spending patterns while educating them about financial literacy.
Key business benefits:
- reduced number of missed deadlines
- enhanced customer satisfaction score (CSAT).
Simplified Document Collection and Sharing
Documentation is an integral part of banking, yet it often creates bottlenecks. From loan applications to activating additional services, customers frequently face delays due to complex paperwork. Conversational AI simplifies this process by automating document sharing and follow-ups.
For instance, chatbots can send users required forms or a checklist of documents, followed by timely reminders for any missing paperwork or upcoming deadlines. They can even collect approvals and digital signatures remotely, significantly reducing the time and effort involved.
Key business benefits:
- eliminated roadblocks
- lowers the customer effort score (CES).
Streamlined Customer Onboarding
Customer onboarding is a pivotal process that decides the likelihood of long-term customer retention and satisfaction. Conversational AI makes this process seamless and efficient, helping users transition quickly and easily.
For example, a new credit card customer may use a chatbot to quickly find information about terms, hidden charges, loyalty programs, or cashback offers.
Key business benefits:
- frictionless onboarding
- faster time-to-value
- strengthened bank-client relationships.
Query Analysis and Intent Detection
Financial service brands often experience sharp spikes in incoming traffic, particularly during peaks like tax season or investment periods. This is where conversational AI steps in with its sentiment analysis and intent prioritization features to streamline queues and seize otherwise missed opportunities.
With customers now engaging across multiple digital touchpoints, such as social media, financial brands are inundated with high volumes of incoming inquiries, all seemingly urgent. This makes it easy for support agents to lose track of critical queries amidst the noise.
Conversational AI algorithms address this by filtering actionable messages from the overflow, analyzing their sentiment and urgency objectively, and systematically prioritizing them.
Key business benefits:
- seamless query handling
- maximized responsiveness.
Examples of Conversational AI in Financial Services
Some of the world’s most successful banks are leading the way in adopting conversational AI.
Watsonx Assistant by IBM
Watsonx Assistant is a powerful, cloud-based conversational AI developed by IBM. It caters to multiple industries, including banking, and allows businesses to craft AI-powered chatbots for improving customer interactions. With this tool, financial institutions can deliver prompt, accurate answers and empower self-service for their clients.
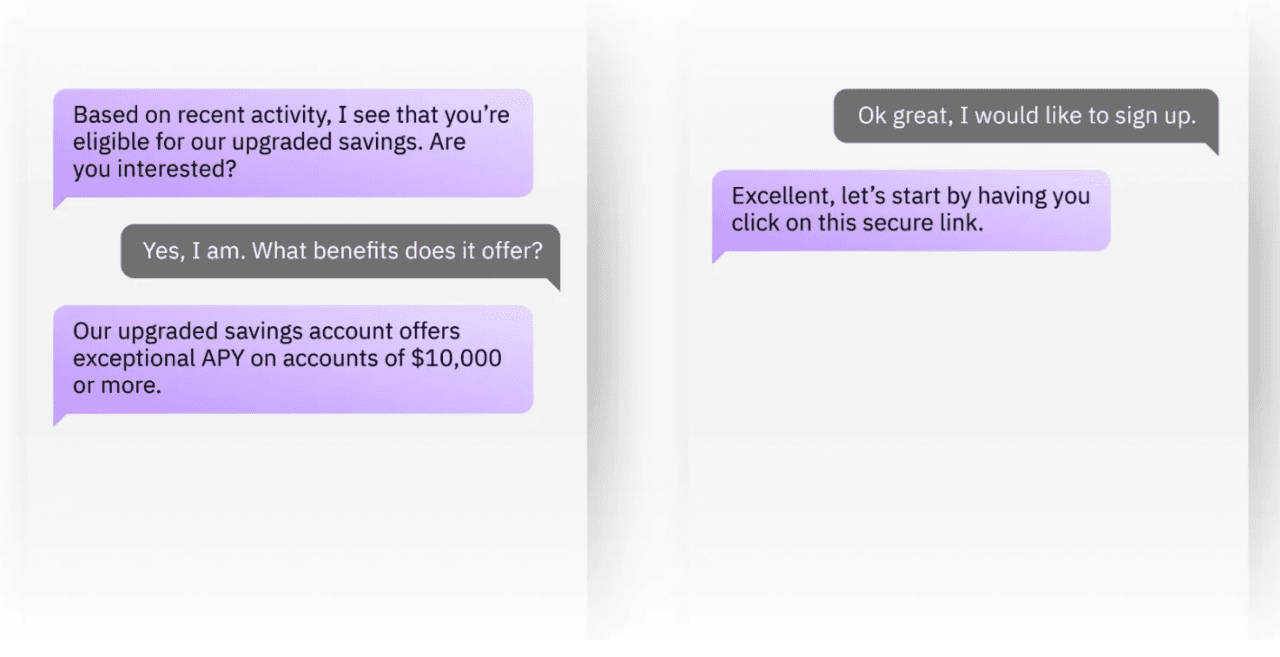
Erica by Bank of America
Erica, the virtual finance assistant from Bank of America, operates within their mobile app and offers over 90% efficiency, completely free.
How does Erica support customers? It delivers personalized suggestions on topics ranging from credit and banking to investing and retirement planning. Erica can also check account balances, share tailored market insights, provide advice, and notify users of account changes.
KAI by Kasisto
KAI is a conversational AI platform explicitly designed for the financial services industry. Developed by Kasisto, KAI integrates generative AI to enhance customer engagement. Its component, KAI Answers, leverages the KAI-GPT language model to provide relevant, accurate responses drawn from existing content sources at financial institutions.
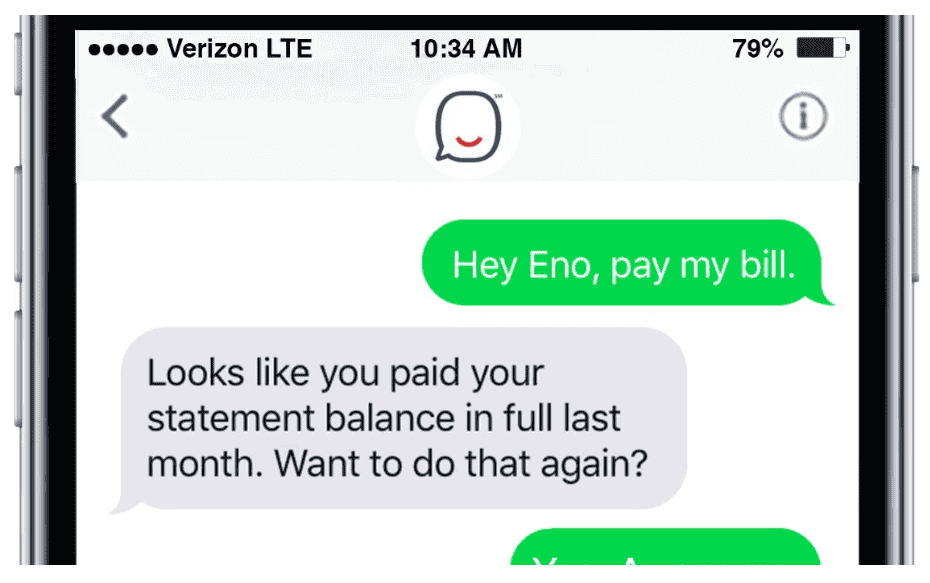
Eno by Capital One
Eno, Capital One’s conversational AI, is the first text-based AI assistant created by a U.S. bank. Branded as “AI with EQ”, Eno understands and responds to both text and emojis.
For example, to check your balance, you can either text “balance” or use the dollar sign emoji “$.” Eno will instantly reply with your account information.
Beyond basic inquiries, Eno also provides proactive features such as generating virtual card numbers for secure online shopping, tracking expenses, and sending real-time spending alerts.
Amex Bot by American Express
Deployed on Facebook Messenger, American Express’ AI chatbot helps users connect their cards with their Messenger accounts. This integration allows the bot to track purchases and provide real-time sales notifications, along with personalized recommendations based on user activity. The Amex Bot enhances contextual, effortless financial interactions for cardholders.
Ceba by Commonwealth Bank of Australia (CBA)
CBA’s Ceba is a conversational AI chatbot introduced in 2018 to handle a wide array of banking tasks, including card activation, answering common questions, and facilitating payments.
Ceba has successfully managed 15.5 million interactions and earned recognition as a two-time Gold Winner at the APAC Stevie Awards. Designed to improve customer satisfaction, Ceba operates 24/7 and handles 60% of inquiries, empowering staff to focus on more complex and creative responsibilities.
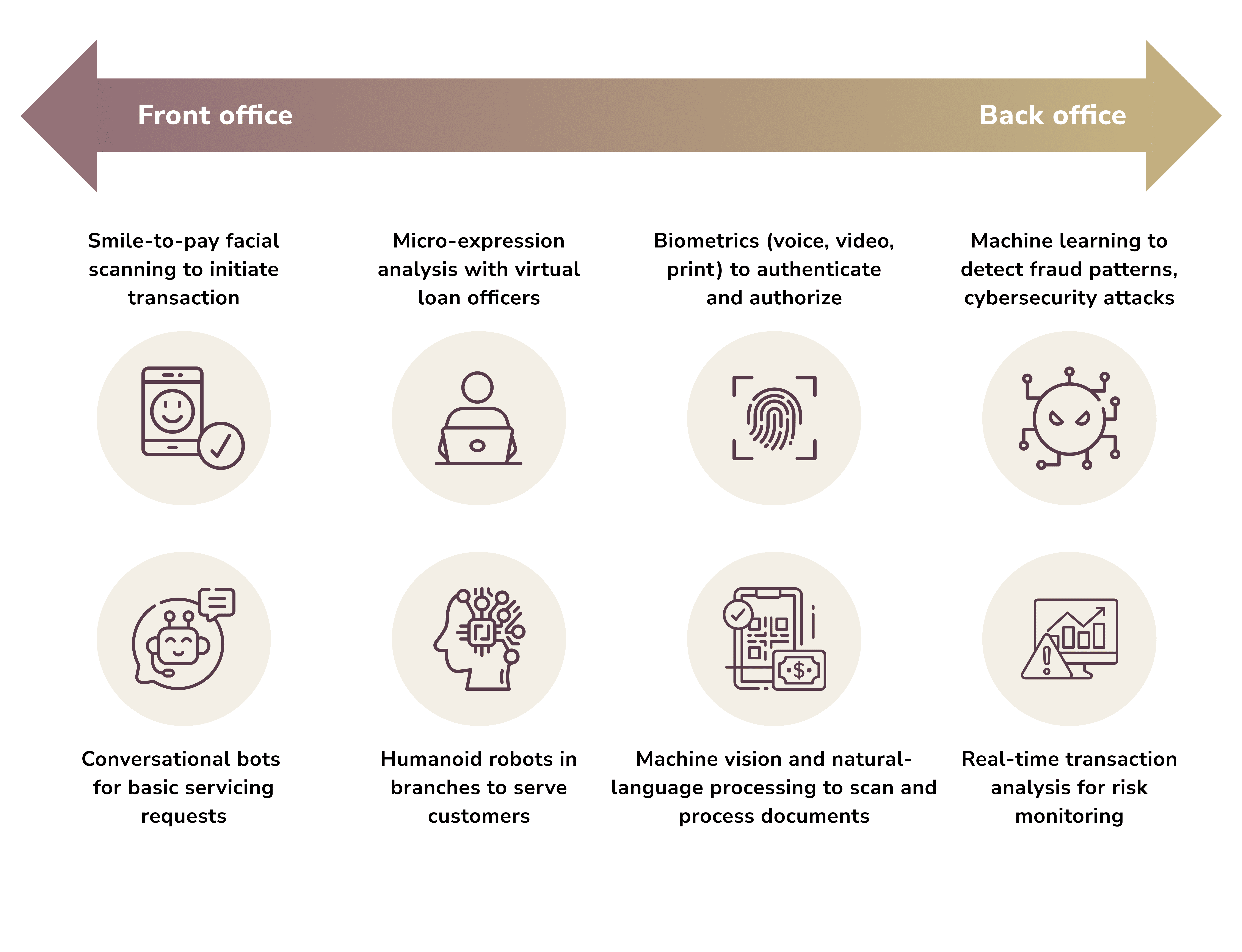
Advantages of Conversational Banking
Let’s analyze the three most evident pros of conversational banking.
1. Boosting Efficiency and Cutting costs
When tasks that used to require human intervention can finally be automated, operational efficiency will rise. Chatbots and voice bots reduce service bottlenecks and minimize call waiting times in contact centers. According to McKinsey, generative AI-powered chatbots could cut human-assisted contact volumes by up to 50%. This number, though, depends on an organization’s automation level.
AI optimizes back-office tasks (e.g., payment processing, claims handling, etc.) through payment bots and Robotic Process Automation (RPA). This means companies can drastically lower their operational budgets.
2. Simplified Loan Processes
Conversational AI in financial services automates major steps of loan processing. It gathers and verifies data through natural language interactions, providing real-time assistance during the loan application process. By answering applicant queries and offering guidance, it accelerates approvals. AI analyzes financial data for quicker pre-approval,s streamlining credit assessments as conversational.
For instance, Lendesk Technologies developed an employee-facing solution to support Canadian mortgage professionals. The AI-based assistant delivers instant, precise answers about over 7,000 mortgage options. The tool helps advisors save time without sacrificing service quality.
3. Automating Account Services
When it comes to automation, nothing beats AI. Conversational banking offers unparalleled convenience in managing accounts and conducting transactions:
- Customers can inquire about balance, recent transactions, and statement information effortlessly.
- Fund transfers and payments are simple to manage with natural language commands.
- Real-time notifications about suspicious activities empower users to act swiftly by disputing charges or blocking cards.
- Adjusting subscriptions or scheduling repayments becomes easier with instant confirmations.
- Automated reminders about due dates, transactions, or account activity help customers stay on top of their finances.
Challenges Facing Conversational Banking
The finance industry is heavily regulated, so it always meets multitudes of obstacles when adopting new technologies or approaches to using it.
Protecting Data Privacy and Security
A key challenge in adopting conversational AI within the banking sector is safeguarding data privacy and security. Banks handle sensitive customer information, making compliance with strict data protection regulations like GDPR and CCPA essential. However, AI systems can be targets for cyberattacks or breaches, risking the exposure of personal data and diminishing customer trust. Ensuring the implementation of robust encryption methods and effective AI governance helps improve customer information protection.
Navigating a Complex Regulatory Landscape
The financial industry operates under rigorous regulations, adding complexity to deploying conversational AI solutions. These systems must align with a broad range of legal and financial standards. For instance, automated AI interactions may inadvertently conflict with requirements for transparency or fair treatment. Issues such as unintentionally biased outputs or inaccurate financial guidance must be closely monitored. Achieving regulatory compliance adds another layer of difficulty to the development and implementation of conversational AI technologies in banking.
Overcoming Technical Shortcomings
Despite recent advancements, conversational AI still faces technical hurdles, particularly in natural language understanding (NLU). AI-driven chatbots often struggle with understanding colloquialisms, industry-specific jargon, and nuanced contexts in customer interactions. Such limitations can lead to suboptimal user experiences, with irrelevant responses or unresolved inquiries. Enhancing AI algorithms is an ongoing priority to improve both the relevance and accuracy of these systems, especially in the highly intricate domain of financial services.
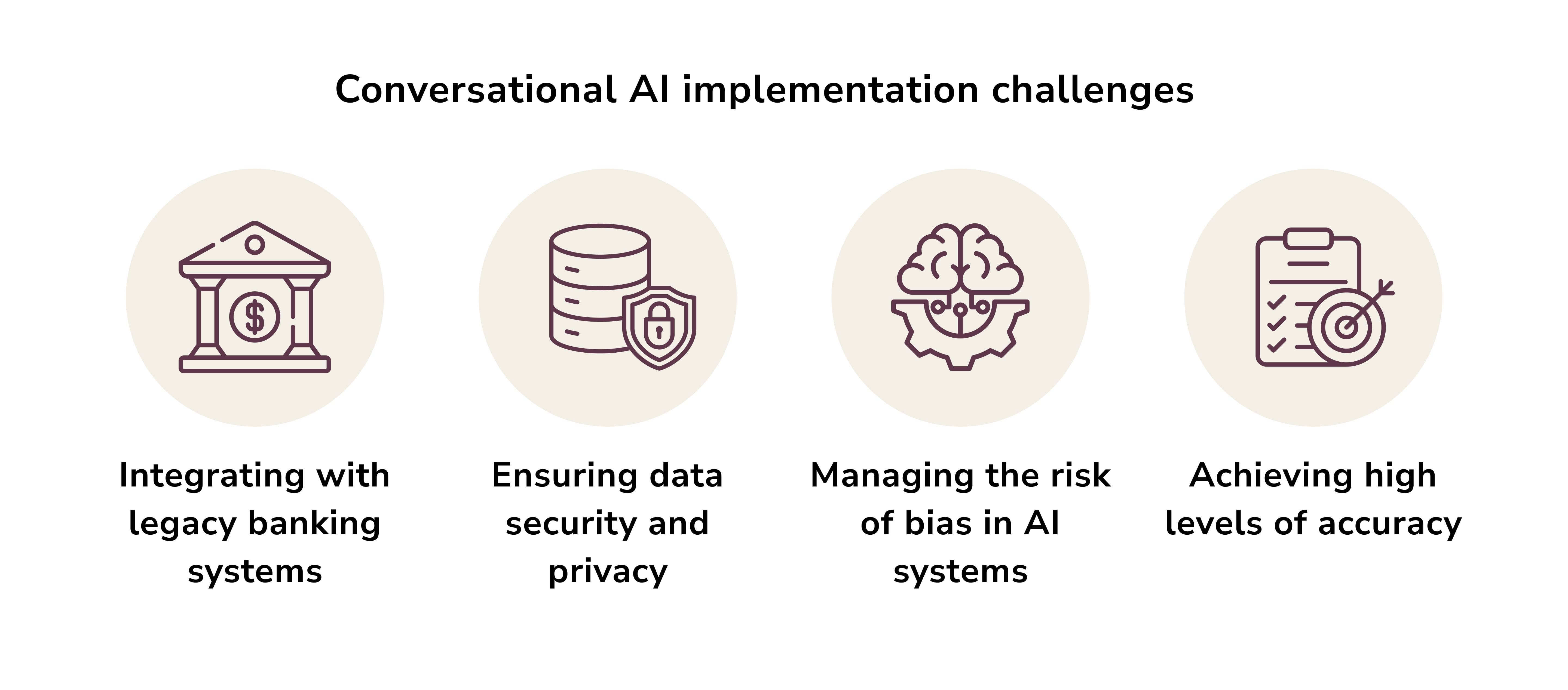
Building Customer Trust and Acceptance
Many customers remain hesitant to use AI for managing their finances, particularly when trust and accuracy are paramount. While conversational AI can streamline service delivery for routine queries, customers often prefer human support for complex or sensitive financial matters. To address these concerns, banks must integrate seamless experiences that combine the efficiency of AI with the empathy of human interactions. Building customer confidence in AI requires consistent reliability, transparency, and effective communication.
Limitations of Using Off-the-Shelf AI Chatbots in Banking
Implementing ready-made chatbots may seem like a quick and convenient solution for banks, but these options often come with significant drawbacks, including:
1. Limited Future Flexibility
While pre-built chatbot solutions can be deployed rapidly, they may not adapt well to a bank’s evolving business needs. This can result in additional costs and delays when adjustments or new solutions are required. Furthermore, these chatbots may include features that aren't fully relevant or lack key functionalities, restricting their application across multiple use cases.
2. Vendor Dependencies
Banks that rely on third-party chatbot vendors remain tied to the vendor’s product roadmap, making customizations both challenging and time-consuming. Every new feature or capability may require complex negotiations, leaving the bank with less control over its operations.
3. Heightened Security Concerns
Using third-party chatbots introduces cybersecurity and data privacy risks. For example, deploying a chatbot that operates in an external cloud environment could expose banks to potential data leaks, as sensitive information traverses between the bank’s internal systems and the vendor’s cloud infrastructure.
4. Added Need for Technical Expertise
Highly customizable off-the-shelf solutions often require a dedicated IT team for installation and maintenance. Banks without these resources may struggle to manage technical issues, software updates, or any operational disruptions caused by the chatbot, further increasing expenses.
5. Training and Onboarding
Adopting third-party chatbots necessitates allocating resources to train employees and ensure user adoption runs smoothly. Organizing workshops, onboarding sessions, and troubleshooting staff concerns can divert time and funds away from other essential business activities.
6. Operational Delays
Although third-party chatbots integrate relatively easily with existing systems, the process can still involve unforeseen complications, requiring additional effort and extending timelines.
The Alternative? Build Custom Chatbots
To minimize these risks and ensure long-term scalability, banks can opt for custom AI chatbot solutions. Custom-built chatbots provide greater flexibility, enhanced security, and tailored functionality that aligns with an organization’s specific needs and priorities. Besides, investing in personalized solutions helps maintain control over operations while avoiding the pitfalls associated with ready-made options.
We understand the challenges that fintech companies face. So, if you decide to develop AI banking software, our expertise is at your service.

Roman Zomko
Other articles