How AI Helps Detect and Prevent Fintech Fraud

Modern cyber threats challenge the efficacy of fintech security measures, often surpassing traditional fraud detection methods. The increase in online transactions has led to a corresponding rise in scams. Although human oversight remains crucial, it is insufficient against the growing frequency and sophistication of breaches.
Fortunately, advancements in GPU-powered AI, data science, and machine learning models offer promising solutions for combating cyber hazards. This article will explore the role of AI/ML software in enhancing fraud detection capabilities.
What Is Fintech Fraud?
FinTech fraud refers to any fraudulent or deceptive activities targeting financial technologies to illicitly gain money. These can include:
- stealing login credentials to empty bank accounts
- making charges or transferring funds without authorization
- initiating fake investment schemes to deceive individuals into investing
- manipulating stolen personal information to open fraudulent accounts
- exploiting weaknesses in fintech systems to manipulate data or steal funds.
Traditional fraud methods like check forging and credit card skimming still exist. However, fintech introduces novel vulnerabilities pushed by several factors:
- As we rely more on online accounts, they are prime targets for cybercriminals.
- Fraudulent activities can be hard to detect. Rapid transactions and automated systems can obscure them.
- New fintech solutions often have security flaws as they evolve. This makes them vulnerable to exploitation.
- Centralized platforms with vast financial data attract attackers. They usually target high-value information.
Fintech Fraud Stats
Alloy, the company specializing in identity risk management and working with over 500 leading banks and fintech firms, has unveiled its 2024 State of Fraud Benchmark Report.

The report says that, after years of rising fraud, some companies report a drop in attack numbers.
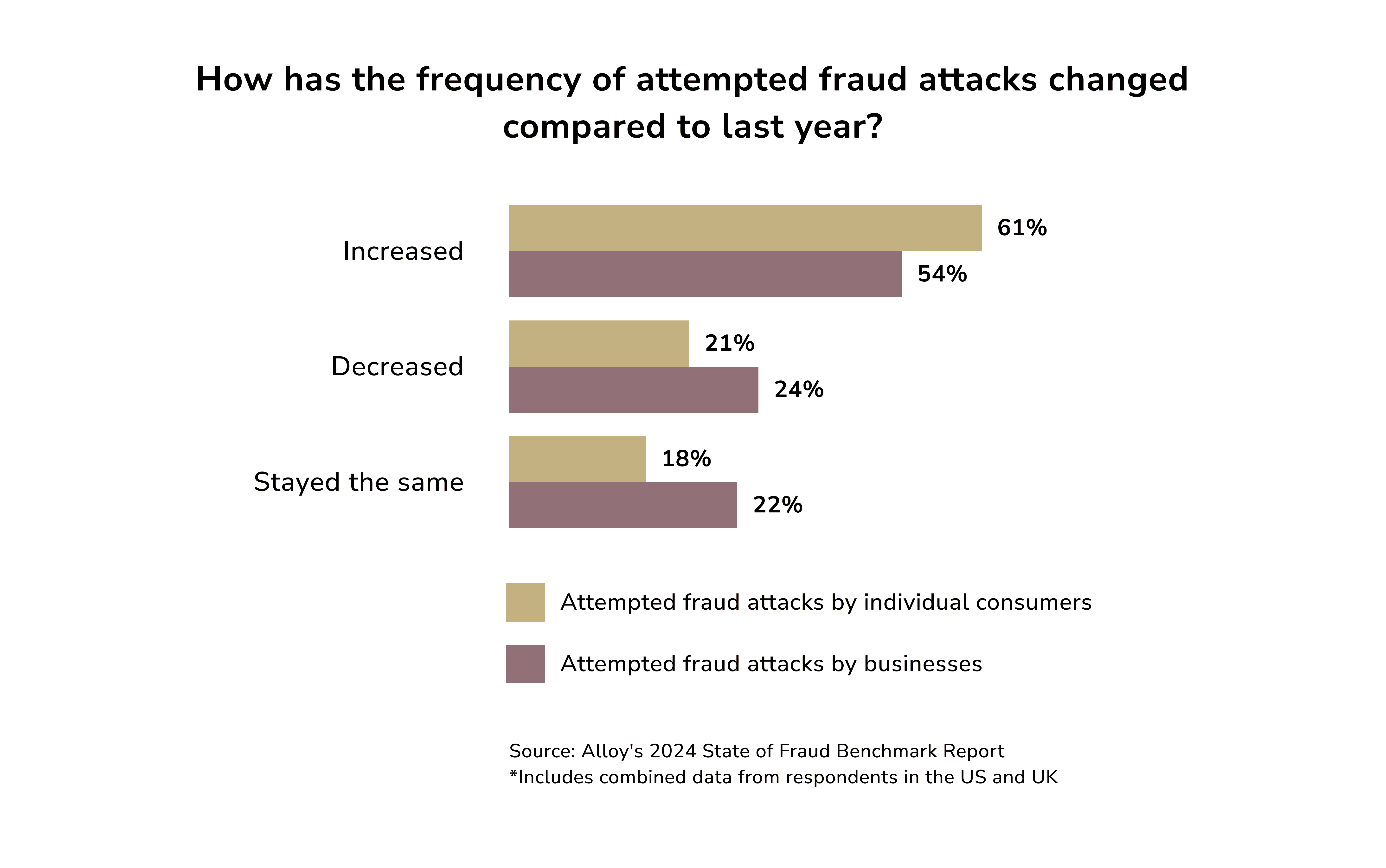
Nevertheless, fraud continues to cause significant financial damage. The report states that 56% of respondents reported losses exceeding €/$ 500,000 in the past year. Also, 25% experienced losses of over 1 €/$ million during the same period.
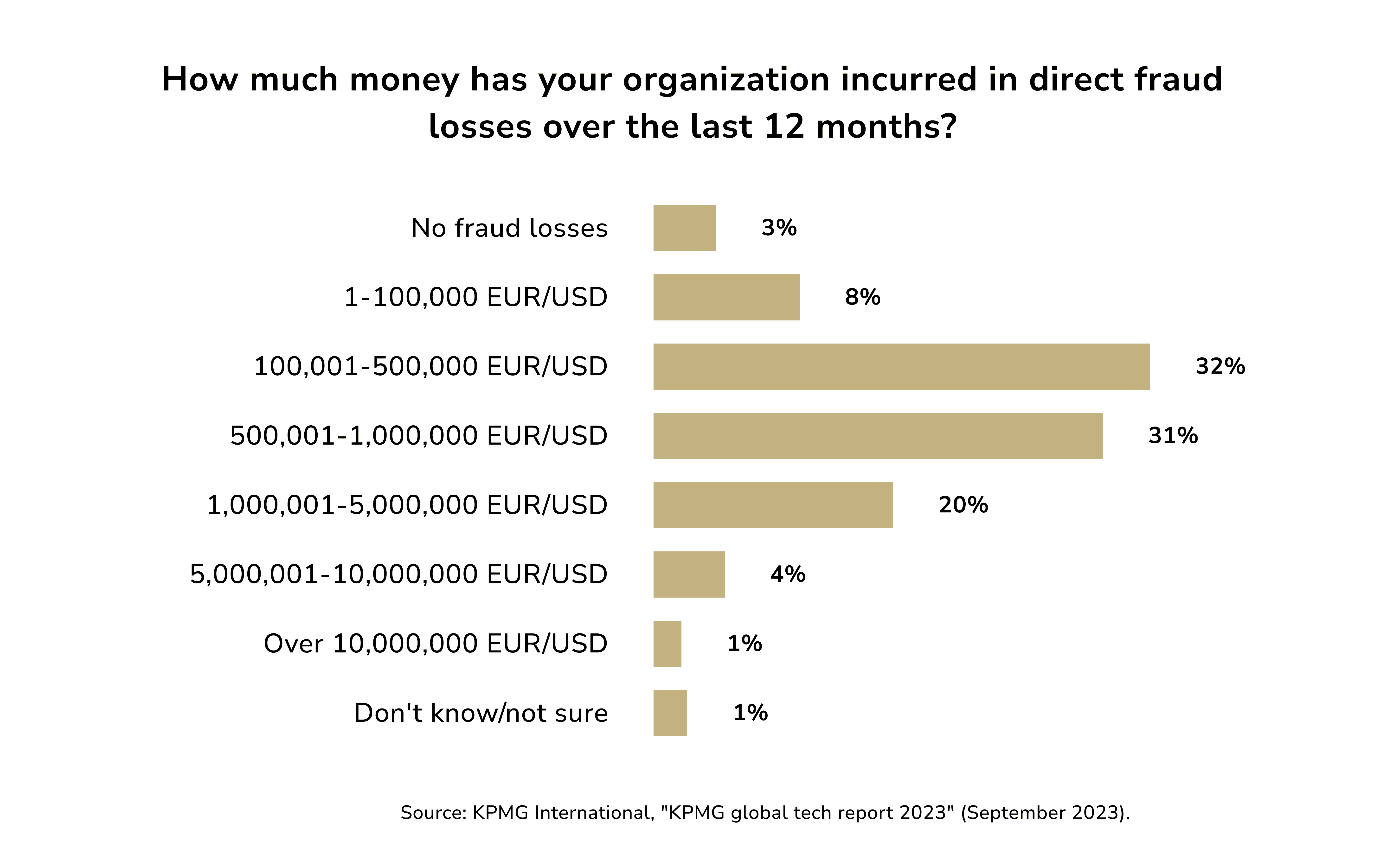
Fintech companies face an average annual loss of $51 million due to fraud (“The FinTech Fraud Ripple Effect,” a PYMNTS & Ingo Money report). A Javelin study revealed that identity fraud alone caused $20 billion in damages in 2022.
The good news is new fraud prevention tools work. Businesses that invested in them saw positive results. Last year, 24% of large fintechs and 43% of mid-sized banks reported fewer fraud attempts on their accounts. Interestingly, 37% of large fintechs and 60% of mid-sized banks used new fraud tools. This suggests that external tech might be reducing their fraud rates. In 2024, 75% of companies will invest in identity risk solutions to prevent fraud.
Importance of Fraud Detection in Fintech
Fraud doesn’t just result in a direct financial loss. It sets off a chain reaction that incurs additional costs for the financial system and everyone involved. This includes everything from regulatory fines and damaged workplace culture to diminished customer trust. All of this collectively harms the perceived security of the financial system.
Here’s how fintech fraud affects businesses:
- Financial loss: a fraudster gaining access to a company’s payment system could make unauthorized withdrawals or transactions, leading to direct financial losses. Businesses often have to bear the cost of chargebacks from fraudulent activities.
- Increased operating costs: fighting fintech fraud requires costly security measures. These include advanced fraud detection systems and staff training. They raise overall operating expenses.
- Regulatory and compliance issues: fraud can trigger regulatory scrutiny, fines, and sanctions. This strains resources and increases compliance and reporting demands.
- Reputational damage: fraud can tarnish a fintech company's reputation. This makes it harder to attract and retain customers. Losing trust in the company can require costly PR and customer service efforts to rebuild it.
- Operational disruption: fraud can divert resources from regular operations. It may disrupt service delivery and efficiency. For example, a security breach requiring system shutdowns can lead to downtime, affecting sales and services.
- Delayed innovation: a fintech's focus on security can slow down innovation. Resources for new products or better services often involve security and fraud prevention.
A strong fintech sector is vital for economic growth. Unchecked fraud can destabilize the financial system. That is why AI security systems in finance aim to do more. They must protect users from unauthorized access, identity theft, and fraud. Effective fraud detection is vital. It keeps the fintech sector stable and drives economic growth.
Types of Financial Fraud
Let’s briefly discuss some of the most widespread financial frauds.
Account Takeover
Account takeover (ATO) is an identity theft and cybercrime where an intruder unlawfully access a user’s online account credentials. This form of fraud involves unauthorized parties successfully accessing and manipulating someone's account information.
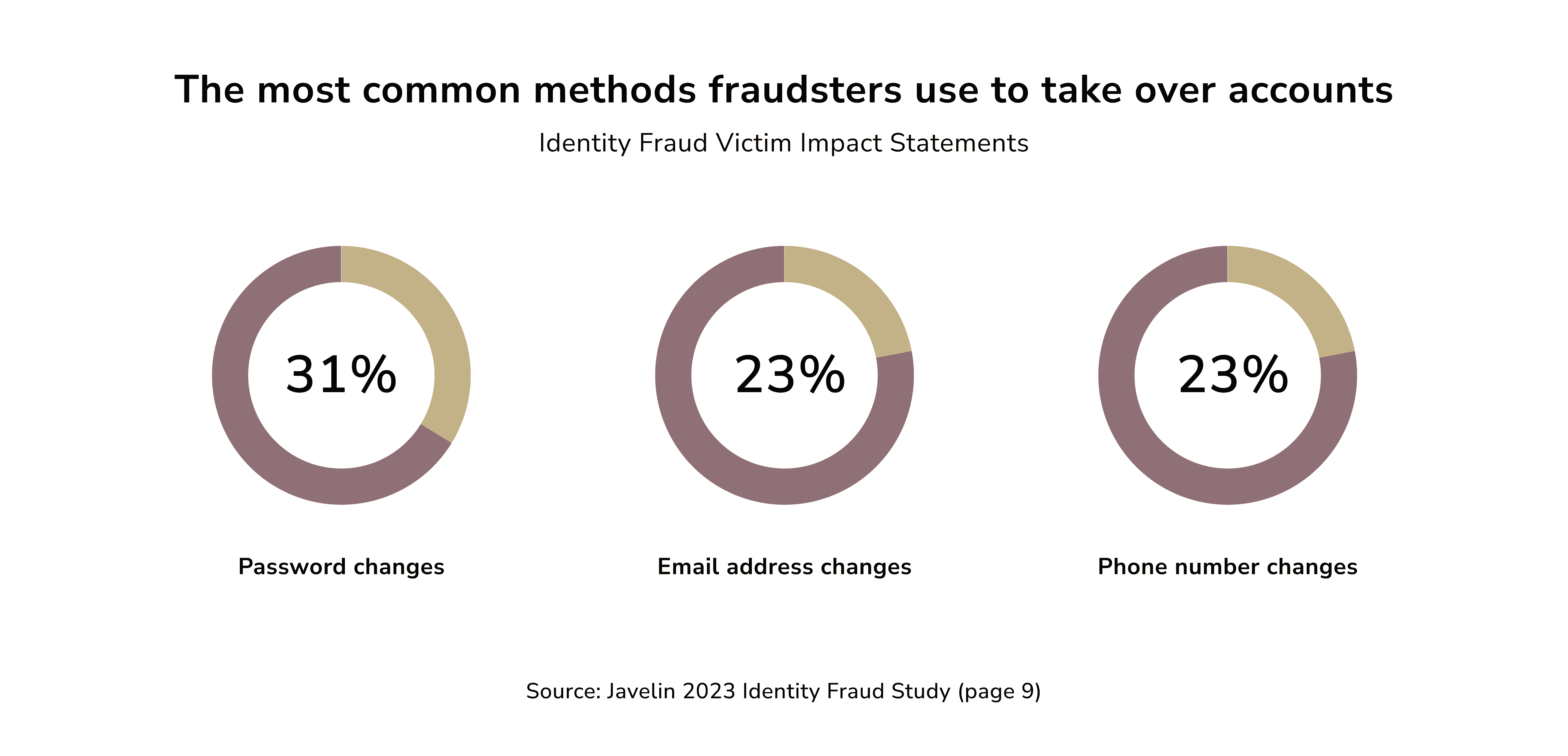
Identity Theft
Identity theft is the most frequently reported issue among consumers. In these cases, cybercriminals access a customer's account and change key credentials, like passwords.
Note: Anomaly detection serves as the initial safeguard against fraud. It involves finding data points that deviate from typical patterns in a dataset. The goal is to uncover rare events that may indicate fraud. AI can spot abnormal activities by recognizing a customer's usual behavior. This includes changes to passwords or contact info. To prevent identity theft, it alerts the customer. It also uses security measures like multi-factor authentication.
Synthetic Identity Fraud
Synthetic identity theft uses an actual Social Security number (SSN). To create a false identity, it pairs it with fake details, like a name, birthdate, address, email, and phone number. Fraudsters can obtain an SSN by either stealing it themselves or buying it from the dark web. The genuine SSN is then used alongside made-up personal information in a method known as identity compilation.
TransUnion says US lenders face nearly $3 billion in losses from synthetic identities (TransUnion (NYSE: TRU) analysis, 2023).
ACH Fraud
The ACH system is a national network. It lets financial institutions exchange batches of electronic credit and debit transactions. This fraud occurs when malicious actors get bank account details. They then use them to withdraw funds through ACH transactions. Another form of ACH fraud takes advantage of the extended processing times. For instance, a fraudster might use an empty account to fund an investment account via ACH. By the time the fintech company learns of the lack of funds, the fraudster has already cashed out the investment account.
Money Muling
Money muling is an escalating issue within financial crime, posing a significant risk to the global economy. This activity involves individuals who, often unknowingly, act as intermediaries in illegal money transfers. Criminals enlist these individuals to hide illegal funds. They use their bank accounts to conceal the money's true source.
Social Engineering
Social engineering is when malicious people trick victims. They aim to get confidential information, like account passwords, or to transfer funds. These transfers are often irreversible, especially when done through real-time payments or cryptocurrency. For example, a hacker might target a company's payroll system. They could do this by sending an email that looks like it was from the payroll provider. The email would have a subject like "Urgent Security Update Required." The email directs the recipient to a fake website to enter their account details. Once the hacker has these details, they access the account and the company’s funds.
Note: Once you withdraw cryptocurrency, it goes into an immutable ledger (the blockchain), making the transaction irreversible. That is why most resources for learning fraudulent techniques are focused on the crypto space.
Bust-out Fraud
A bust-out starts with the person building the card issuer's trust and creating a solid credit profile. This is done to open multiple accounts and secure higher credit limits. Once trust is established, the individual moves to phase two. They make transactions with no intention of repaying the debts.
Individuals aiming to commit this type of fraud often open several accounts over time, typically reaching around ten. They then max out these accounts and default on them simultaneously.
Presentation Attack
A presentation attack is when a fraudster uses another person's biometrics, like a fake fingerprint or photo, to impersonate them and access their online accounts. For instance, they might use a high-quality image or deep fake tech to replicate the person's appearance. The fraudster uses a fake likeness to fool the facial recognition system during login. This grants access to the victim's account. With this access, the fraudster can steal funds, make unauthorized transactions, or commit other fraud on the victim’s account.
How Fraud Detection with AI Works
Fintech fraud detection systems use AI for:
- pattern recognition
- anomaly detection
- data verification
- behavior analysis
These strategies let algorithms set their own rules. They can learn from new data and become more accurate over time.
Mastercard and Fintech Nexus surveyed financial institutions about their AI usage. The survey shows that "increased fraud detection" is the main reason (63%) for AI investment. It highlights the industry's commitment to protecting customers from transaction fraud, making fraud detection and prevention one of the most crucial AI technology trends. Also, "fewer false positives" was a secondary priority. It aimed to balance strong security with a seamless customer experience.
AI-driven fraud detection and prevention models function through a series of stages.
- Initially, they collect, process, and classify historical data. It includes both "good data" (legitimate transactions) and "bad data" (fraudulent ones).
- Data engineers provide the algorithm with varied examples of bank fraud patterns. This makes the model adaptable, versatile, and tailored to specific business needs.
- With each new transaction, the system's data pool grows. Self-learning and adaptive analytics allow the machine to update with new info. It can adapt to new fraud tactics and find new fraud types.
Machine Learning
ML uses algorithms to detect online fraud. They are trained on historical data to find suspicious activities. These algorithms examine past fraud incidents and genuine transactions. They use this to create risk rules. The rules can block or allow actions like logins, identity verifications, or purchases.
Labeling fraudulent and non-fraudulent instances to train ML models is essential. This reduces false positives and improves risk rules' accuracy over time. The system evolves by learning new fraud tactics. It becomes better at stopping fraud before it affects your business.
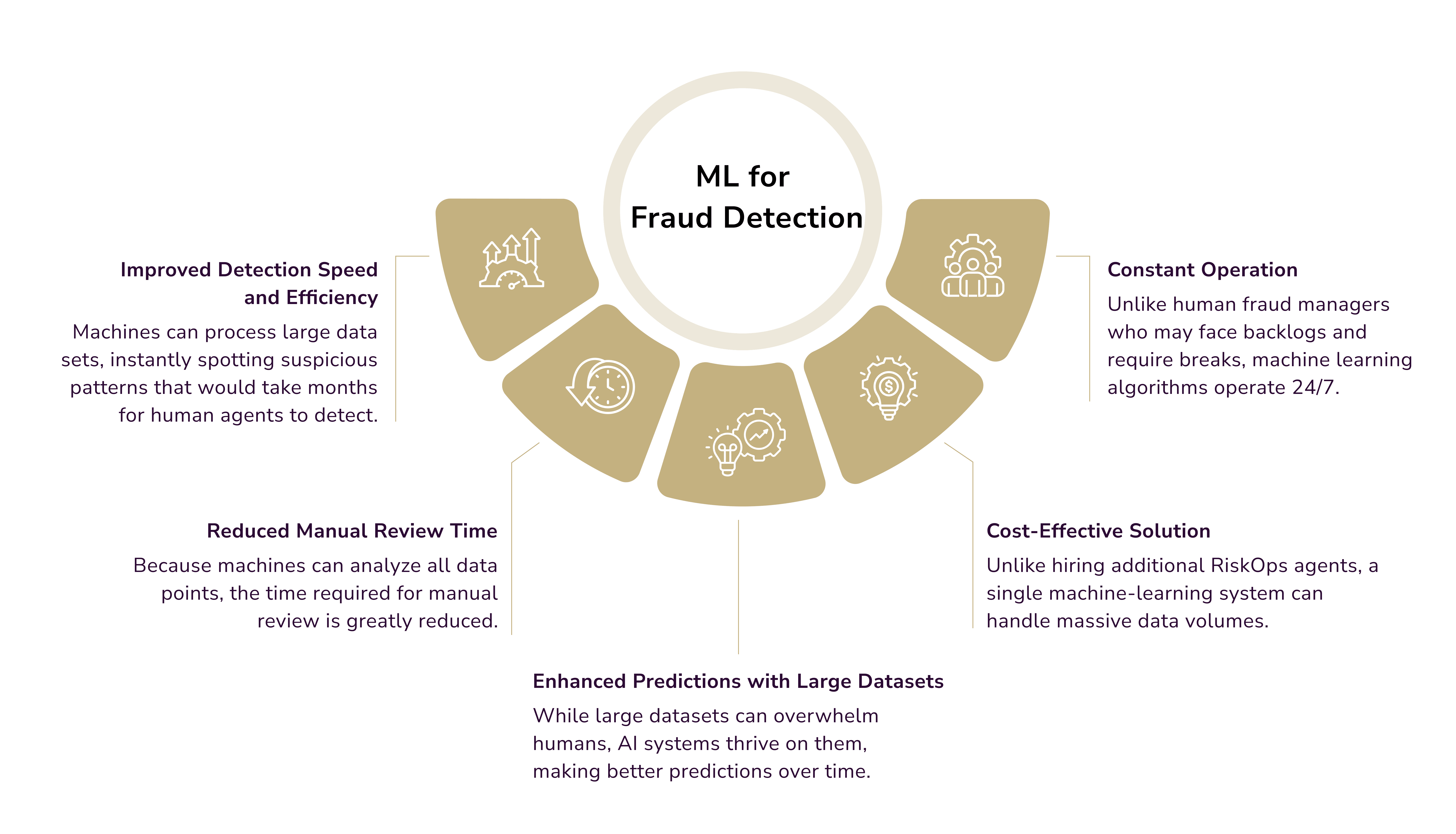
Note: Not all fraud prevention solutions utilizing machine learning offer the same benefits. Blackbox machine learning operates on a “set it and forget it” basis, where decisions are automated and not transparent. This system is ideal for small businesses. They don't need custom risk rules. Whitebox machine learning, on the other hand, explains its risk rules. This transparency helps identify risks. It lets fraud managers improve their fraud prevention strategies.
Behavioral Analytics
AI can track customer behavior trends over time to find anomalies. Behavioral analytics studies patterns in customer interactions. It aims to find predictable behavior profiles. It can reveal the typical times users log into apps, their everyday transactions, their devices, and their keyboard habits. If a customer makes large, unusual purchases, the AI can mark them as suspicious.
Here are some behavioral indicators that can help identify fraud early:
- Unexpectedly large transactions: a customer suddenly starts making significant purchases.
- Unusual buying patterns: buying the same item repeatedly or making multiple transactions of the same amount.
- Geographical location changes: a user logs in from a high-risk country or region.
- Suspicious login activity: multiple password changes or repeated failed login attempts.
- Uncommon interaction behaviors: irregular typing patterns or unusual touch gestures.
- Changes to user details: a customer updates their shipping address, phone number, payment method, etc.
Biometric Authentication
Biometric verification uses unique biological traits to confirm a person's identity. Common traits include facial features, voice patterns, irises, and fingerprints.
There are two primary approaches to biometric verification:
- Unimodal: This method relies on a single unique trait for authentication. It is faster and smoother for users. But, it is more vulnerable to cyber-attacks like spoofing, where hackers can access sensitive data.
- Multimodal: It uses two or more unique traits for authentication. This offers better security. It takes an extra step. But, the added complexity makes it much harder for fraudsters to bypass the system.
Big Data Analytics
Big Data helps quickly find fraud. It does this by consolidating, mapping, and normalizing large datasets for analysis. It helps organizations to find strange trends, detect cyber attacks, and uncover security breaches.
Use cases for fraud detection with Big Data analytics include:
- Finding unusual patterns or business problems where fraud might occur.
- Detecting anomalies across channels by comparing data from various sources, like social networks, databases, and call centers, to find discrepancies.
- Predicting suspicious activity before it impacts an organization’s assets or goods.
- Analyzing internal processes to pinpoint areas prone to fraud, allowing for the development of tailored business strategies.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is essential for analyzing large volumes of language-related data. NLP can interpret text by examining patterns like causal, numeric, and temporal info. It can find keywords linked to fraud. Techniques like word embeddings, which numerically represent text, enable NLP to consider context and word order. They capture word meanings. It generates text signals that help spot anomalies in conversations.
AI-Enabled Fraud
AI, similar to other technologies, can be exploited for malicious purposes. Fraudsters can leverage AI to execute more convincing scams at a significantly faster rate.
Generative AI and large language models (LLMs) boost productivity. They do this by understanding the meaning and context of text and numbers. However, cybercriminals can also exploit GenAI for malicious purposes. Using advanced AI prompts, they can bypass security measures. The AI can produce error-free, human-like text. This helps create convincing phishing emails. The dark web hosts various tools like FraudGPT that leverage GenAI for cybercrimes.
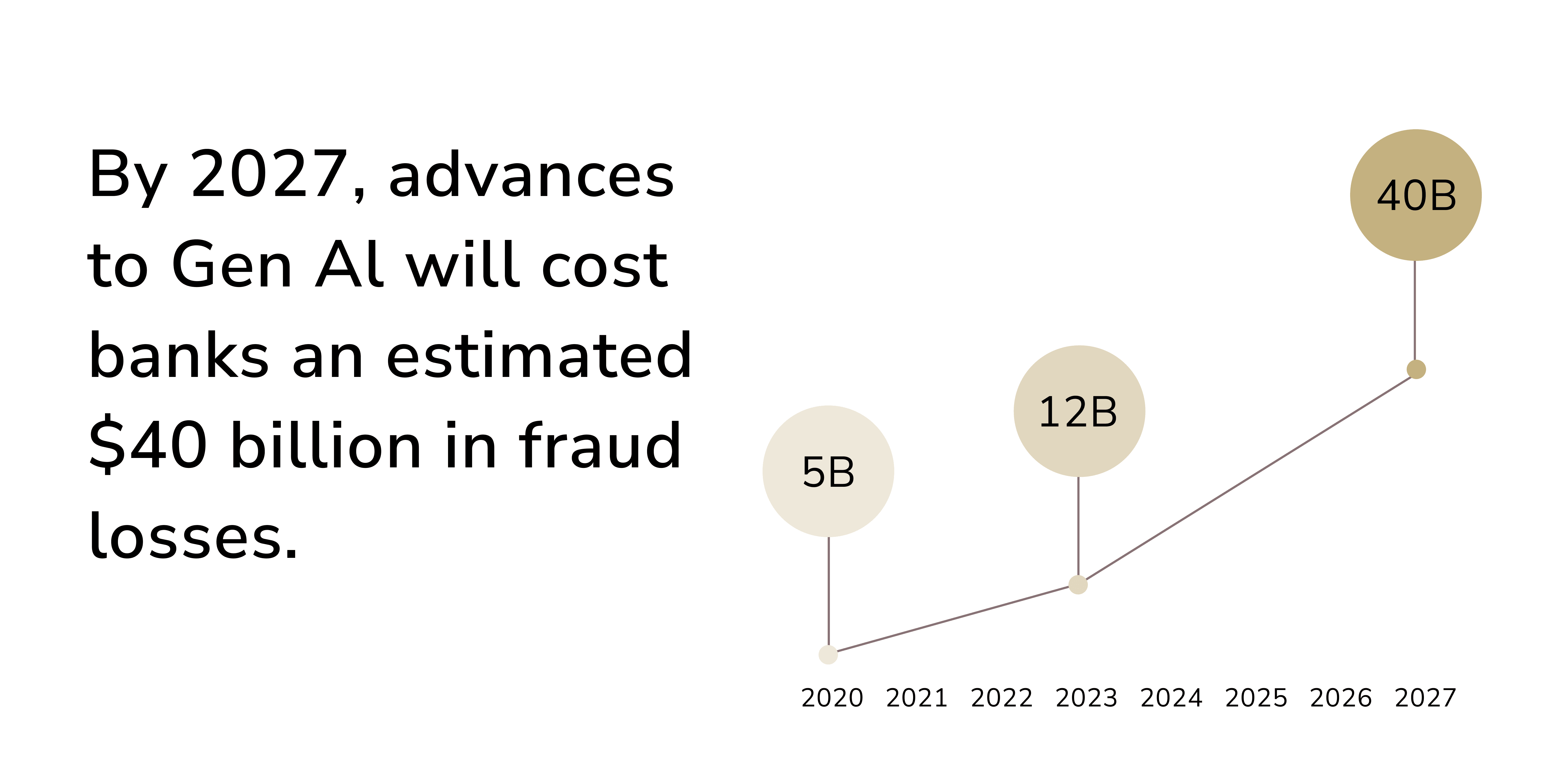
Voice authentication, a security measure used by some banks, is also vulnerable to generative AI. Attackers can clone a customer's voice with deepfake tech. They do this by obtaining voice samples, often via spam calls that elicit responses.
Addressing GenAI Misuse
Fraud detection systems have a powerful ally in the form of generative AI, specifically large language models. LLM-based assistants that use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) can now support manual fraud reviewers. It helps access policy documents. This speeds up the work and streamlines decision-making to find fraud.
LLMs are being used to predict a customer's next transaction. This helps payment firms to assess risks and block fraud.
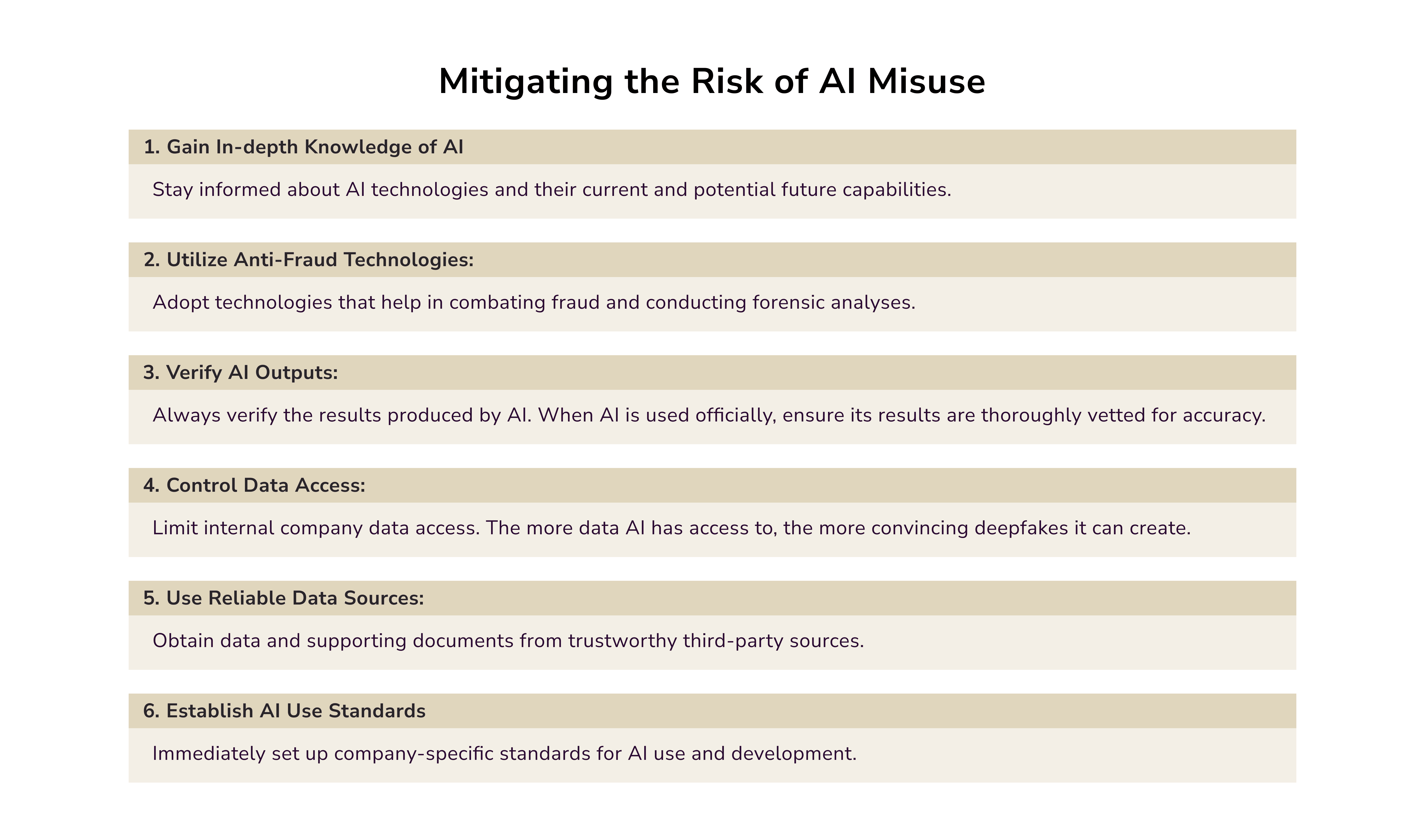
Another critical use of generative AI in fraud prevention is creating synthetic data. This data boosts the volume and diversity of records used to train fraud detection models. It helps AI stay ahead of new fraudster tactics.
AI Fraud Detection: Real-World Use Cases
GenAI combined with ML is especially useful in threat detection. Let’s see how finance industry giants resort to AI software development for funds safety.
- Mastercard's Decision Intelligence uses AI to assess cardholder spending. It gauges the risk of fraud in real time. It blocks suspicious transactions before they are completed. Similarly, Mastercard has upgraded its Decision Intelligence solution. It is now called Decision Intelligence Pro. This tool checks the relationships between entities in a transaction to assess risk.
- American Express has adopted generative modeling techniques to combat credit card fraud. In 2023, it further improved its fraud prevention with synthetic data generation. AI monitors for anomalies linking them to known frauds. This helps Amex stay competitive.
- Visa, a top payments processor, has launched the VAAI Score solution. Launched in May 2024, this tool detects enumeration attacks in card-not-present transactions. Visa's reach has helped reduce the 33% of accounts that are fraud victims within five days of a fraudster gaining access to their payment info.
- Revolut, a prominent UK-based neobank, has also stepped up its anti-fraud efforts. It launched an AI scam detection feature to protect consumers. It stops scams by intercepting them at the point of transaction. This prevents any money from being sent to the scammer.
- PayPal has used Generative AI and ML to improve its fraud detection systems. This strategy nearly halved PayPal's loss rate from 2019 to 2022. Its yearly payment volume surged from $712 billion to $1.36 trillion. In addition, PayPal's AI quickly adapts to new fraud patterns, protecting customers better.
- JP Morgan Chase uses AI analytics to boost its risk management and fraud detection. The bank uses ML to analyze transactions. It looks for unusual patterns that may signal fraud. This mitigates financial risks and upholds its reputation as a strong bank.
Best Practices in Fintech Fraud Prevention
Financial institutions must adhere to basic security measures combined with advanced technologies to safeguard consumer funds.
Leverage AI Algorithms
An effective fraud prevention solution should offer comprehensive features to detect and prevent fraud. This includes real-time data analysis, learning from new information, and adapting tactics as fraudsters evolve. AI-based fraud prevention software provides a robust defense by continuously monitoring transactional patterns.
Unlike traditional systems that use static rules, Generative AI learns and adapts from the data it processes. This allows it to identify new types of fraud as they arise, often without needing manual intervention. This adaptability is essential for keeping ahead of evolving fraudulent tactics.
Employ Machine Learning Models
Generative AI is particularly useful for creating synthetic datasets based on real data. This is crucial in fraud detection, where limited examples make it hard for machine learning models to learn effectively. Generative AI strengthens detection tools by generating synthetic samples that mimic real-life cases. This approach adds robustness to the deception model, enabling it to spot patterns and similar attacks that traditional methods might miss.
Implement Continuous Monitoring Systems
Generative AI excels at inspecting large datasets in real time. This is vital for high-volume industries like finance and eCommerce. AI can quickly process this data. It can then identify and block suspicious activities as they occur. This reduces potential economic losses. It distinguishes ‘normal’ behavior from historical data and immediately flags deviations. This is a more effective method than previous systems.
Utilize Biometric Authentication
Biometric authentication uses unique physical characteristics like fingerprints, facial scans, or voice recognition to secure accounts and prevent identity theft. These features are difficult to replicate, making unauthorized access challenging. Regulatory frameworks must swiftly adapt to the evolving landscape of fraud in fintech.
Regularly Update AI Systems
AI systems need frequent updates and training with current data. This is necessary to stay ahead of evolving fraud tactics. Fraudsters keep making more advanced techniques. So, AI models must be improved to stay effective. This involves ongoing training. It also requires adding new fraud detection patterns to the AI.
AI-Powered Risk Management for Fraud Prevention
The role of finance is evolving beyond number crunching and traditional data analysis. AI risk management is changing the fight against identity theft and fraud. So, finance leaders today have more responsibilities. They must push forward using AI in fintech to combat digital hazards.
This approach uses a cutting-edge framework. It integrates fraud detection with ML and real-time analytics. Organizations can use advanced algorithms to analyze transaction data. It helps them find anomalies and fix potential risks before they happen.
Digital Footprinting
Digital footprinting is the practice of analyzing data from people's online activities. This process is vital for assessing cybersecurity risks and preventing identity theft. Organizations can enhance fraud prevention by studying user behavior and spotting threats.
This approach is also significant in educating users about their online presence. It promotes safer digital practices and raises awareness about identity theft risks. In short, digital footprinting is vital. It helps build a robust cybersecurity framework that adapts to the ever-changing digital world.
Real-time Analytics
Real-time analytics allows organizations to monitor transactions and user behavior instantly. This skill is key for quickly detecting and preventing fraud. It allows for effective data analysis and machine learning. Real-time analytics uses advanced algorithms. It spots anomalies and learns from past data to improve its predictions. Processing large volumes of transactional data in real time helps businesses spot fraud. It reveals unusual patterns that indicate fraudulent activities.
Improved Risk Assessment
In today's fast-changing world, we must combine tech and data. It's key to robust fraud prevention. AI and ML can enhance risk assessment, improving fraud detection across organizations. These advanced systems, focused on data quality, reduce false positives. They ensure accurate assessments and promote a proactive culture in organizations.
Embracing AI for Fintech Security
AI is constantly evolving. One of its primary goals is to reduce false positives by making algorithms more precise without affecting UX. The best AI cybersecurity solutions are lightweight. And we know how to deliver those. If you want to start your AI product development journey, drop us a line, and we will contact you asap.

Andriy Lekh
Other articles