AI in Telemedicine: Examples and Real-World Use Cases

Telemedicine becomes essential when a patient can't physically visit a doctor. Meanwhile, AI can maintain communication and patient health records for ongoing care management.
Consistent care pathways are crucial for maintaining healthcare equality. Rather than replacing human expertise, AI is helping “re-humanize” medicine. This evolution aligns with the shift toward value-based care. The goal is to prioritize the quality of patient outcomes rather than the volume of patients treated.
How else can AI contribute to telemedicine?
What is Telehealth
Telehealth is the use of technology to provide medical services. It helps overcome challenges in healthcare delivery caused by time, distance, and difficult terrain. This approach has come a long way from basic phone consultations to offering comprehensive healthcare remotely. Over time it proved to be a cost-effective solution that improves access in developed and developing countries. It's particularly valuable during emergencies like earthquakes and floods.
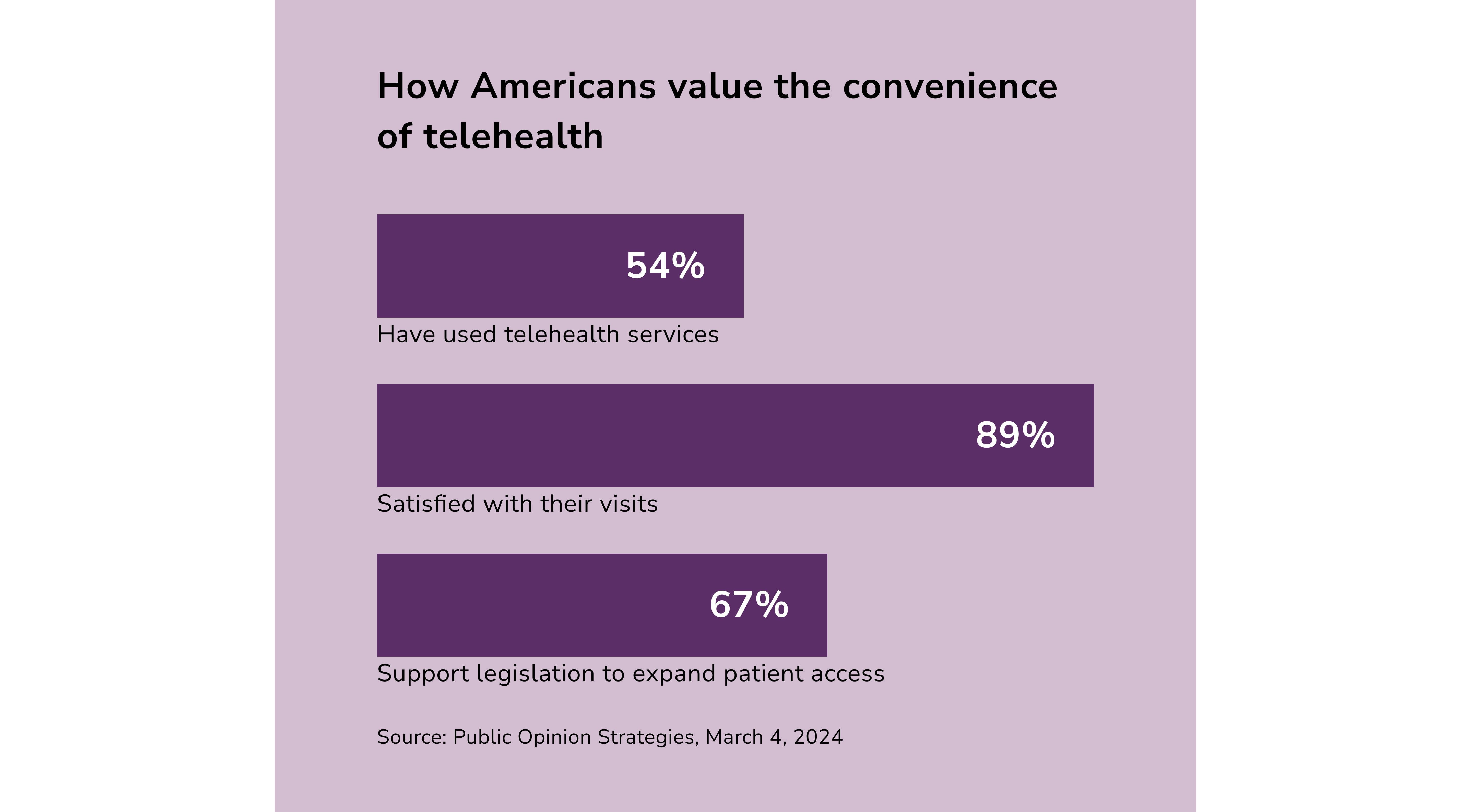
As of today, several factors drive the upsurge in telemedicine in the United States. First, a steadily aging population creates demand for medical care that outpaces the availability of healthcare practitioners. Second, the U.S. faces a critical shortage of qualified healthcare professionals. According to projections from the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC), a more alarming physician shortfall is predicted by 2032. This increased strain on healthcare systems leads to longer patient wait times. It also burdens the already overstretched staff.
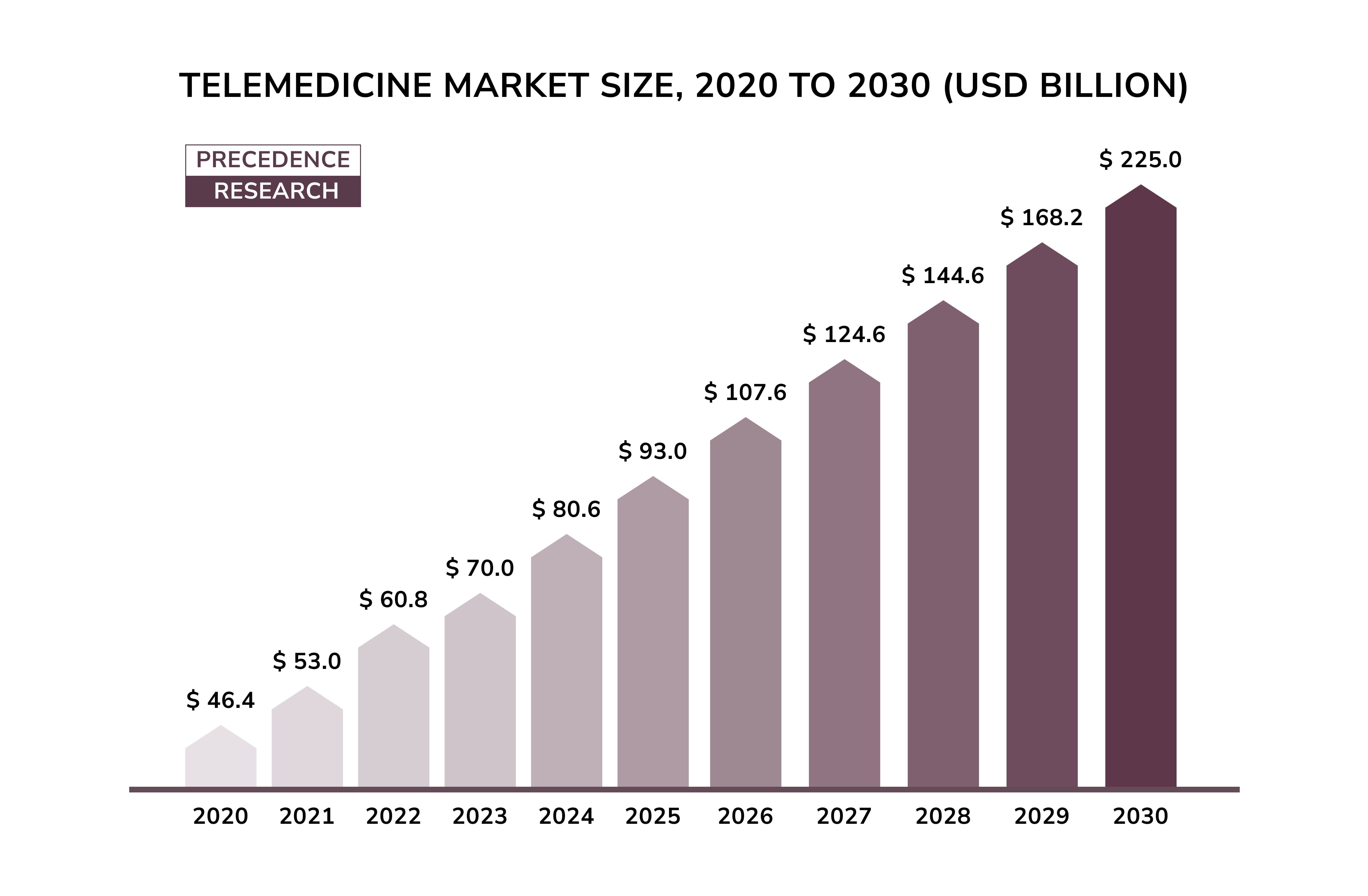
The tech industry played a pivotal role in improving telemedicine. Numerous startups offer multi-purpose platforms - from scheduling appointments to engaging with care providers. Additionally, many health insurance providers now cover telehealth services. Whether intentionally or not, they thus remove another significant barrier to widespread adoption.
The Massive Covid Impact
The telemedicine market skyrocketed when the global pandemic hit the world in 2020. Virtual patient-doctor visits ensured safe access to healthcare during lockdowns. Over 97% of healthcare professionals then incorporated telemedicine into their practices.
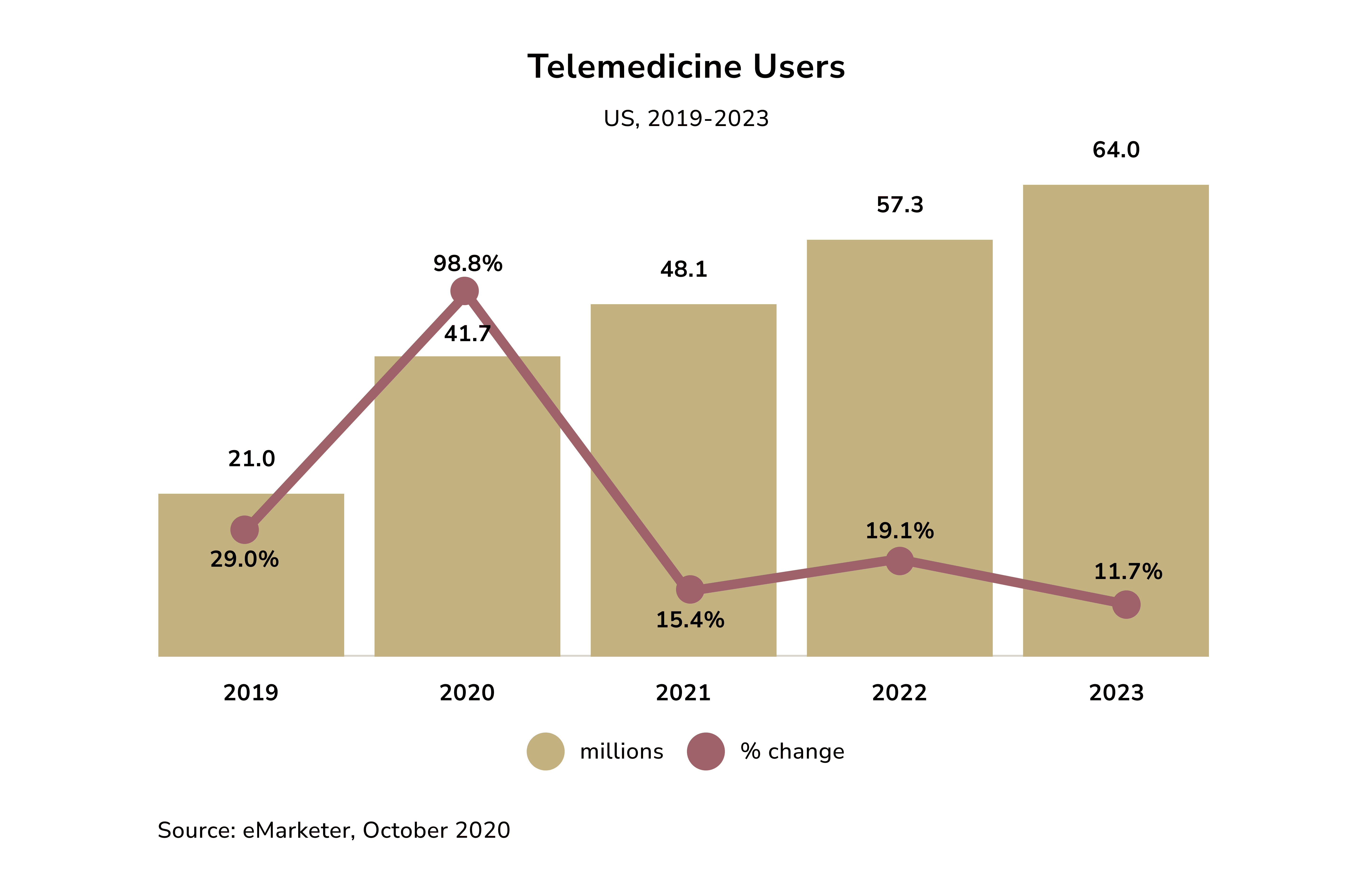
However, its overall usage has declined when lockdowns ended. Trilliant Health’s recent report highlights that doctors and patients prefer in-person visits. Today, behavioral health services dominate telehealth usage. They accounted for 62.8% of all telehealth visits in the fourth quarter of 2022.
Still, experts believe telemedicine will likely stabilize as a key component of healthcare in 2024 and beyond. “Telemedicine adoption has grown exponentially since COVID-19,” said Rini Mukhopadhyay, a forecasting analyst at Insider Intelligence. “Historically, U.S. consumers were slow to adopt telemedicine due to limited insurance coverage and concerns about the quality of virtual care. However, as more consumers become accustomed to the unique aspects of seeing a provider digitally, adoption rates are gradually increasing.”
A remarkable example of AI's impact is its role in diagnostic tools. It helped analyze medical imagery, such as chest X-rays and CT scans, for signs of COVID-19 pneumonia. Infervision and Qure.ai developed AI algorithms to help detect the virus faster. These solutions deliver results in mere seconds. The overburdened healthcare systems can hardly put a price on such tools.
AI in Telemedicine Stats
A survey by MIT Technology and GE Healthcare revealed promising insights. Over 900 healthcare professionals reflected on AI's role in their daily tasks. Most view AI as an extension of their capabilities, not a replacement. Over 80% believe it will improve revenue generation, talent recruitment, and competitiveness.
Virtual doctor visits are now one of the top AI trends that help boost telemedicine adoption. A study reveals that 33% of patients who initially planned an in-person visit chose teleconsultation after AI guidance.
Additionally, AI alleviates the burden of administrative tasks for healthcare providers. It can interact with patients before consultations. Gathering key patient data reduces the documentation workload. While it seems like a small help, for healthcare staff, it's substantial. See, over 50% of doctors experience burnout. This was reported in the I Cry, but No One Cares: Physician Burnout & Depression Report 2023. So, AI can ease the strain by supporting these responsibilities.
How AI Can Enhance Telehealth
According to Artificial Intelligence: A Modern Approach by Russell and Norvig, AI encompasses problem-solving, logic, planning, etc. It allows computers to act as “intelligent agents” that mimic human thought. With healthcare accumulating patient data, computational data science strives couldn’t be more timely. Deriving new insights significantly enhances health outcomes. Smarter assistance and diagnosis in healthcare may be just around the corner.
Telehealth's ultimate aim is to balance the mismatch between healthcare demand and supply. AI virtual interactions help achieve exactly that. “By focusing on areas that patients, providers, or systems are invested in addressing, we have set the stage for more rapid adoption and dissemination of AI” - says Rachael Callcut, Associate Professor of Surgery at the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Medical Center.
Telediagnosis of Clinical Conditions
Over the years, medical diagnosis has shifted from relying solely on clinical examinations to being heavily evidence-based. Doctors draw on their experience and skill to interpret this evidence. AI appears to be a worthwhile helper in this process. This is particularly relevant in fields like oncology. Understanding this disease progression is invaluable for predicting risks.
A prominent example of telediagnosis is teledermatology. Diagnosing melanoma, for instance, traditionally depends on the doctor’s expertise. Yet, a recent study revealed that AI outperformed most dermatologists in diagnostic accuracy. The AI’s accuracy had a median score of 0.86 compared to the dermatologists’ 0.79.
The study also marked the value of deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs) in classifying skin lesions from images. This AI system, trained with only pixel data and disease labels, matches expert performance in identifying melanoma. These results promise a breakthrough in breast and cervical cancer diagnosis.
A study published in Nature highlights similar achievements. Using CNN researchers explored its ability to diagnose skin conditions. The CNN was trained on 129,450 clinical images encompassing 2,032 diseases. The results were remarkable. CNN achieved a 97.1% sensitivity (true positive rate) and a 78.8% specificity (true negative rate). It once again outperformed dermatologists.
Another prominent example is Wound Viewer, an AI-driven wound assessment device. During clinical validation, 150 patients presented various wound types. The device captures wound images remotely via sensors. Algorithms then analyze characteristics like area, depth, volume, etc. As a result, the device achieved a 97% accuracy rate.
Remote Patient Monitoring and Management
AI-based remote patient monitoring devices make progress in chronic disease management.
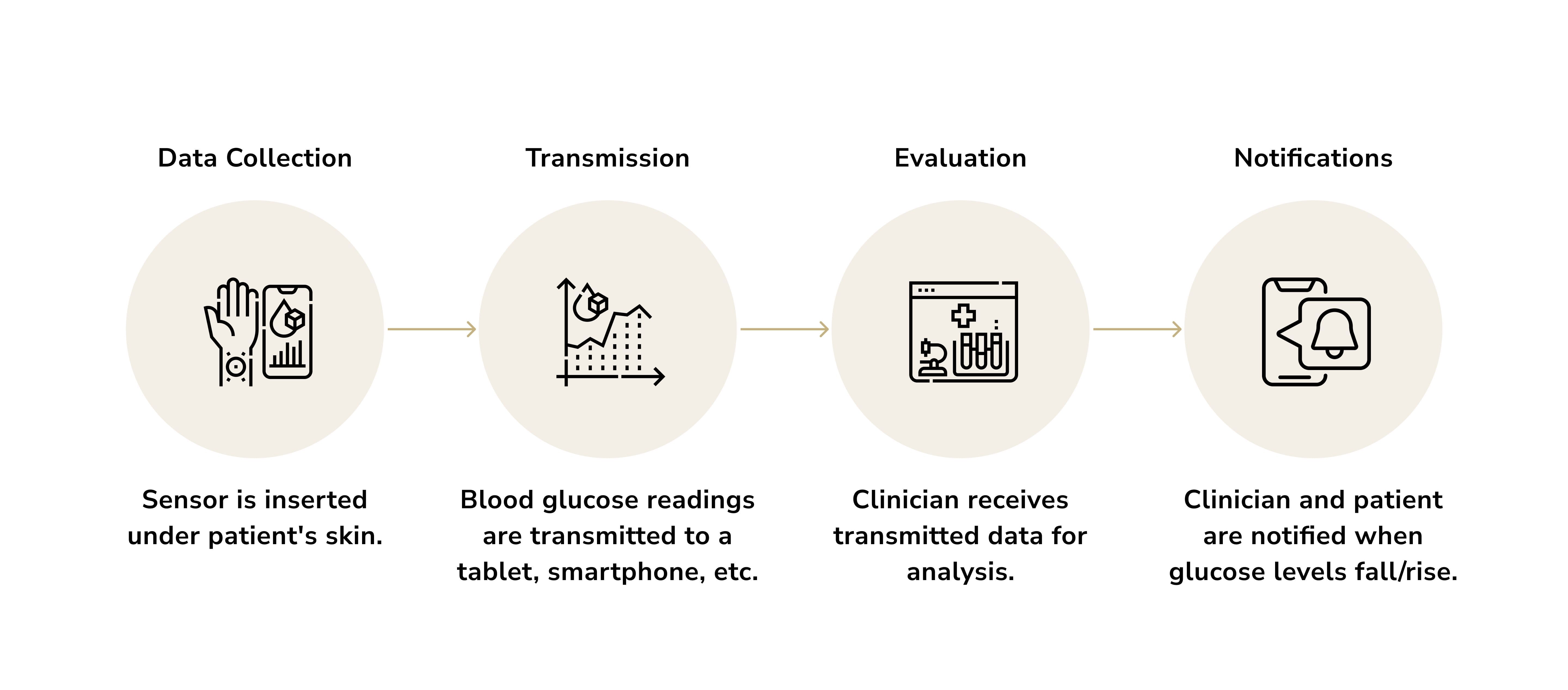
Researchers at the University of California conducted a study in which smartwatches tracked heart rate and step counts. This data was then used to train a deep neural network capable of approximating R-R intervals. When validated against gold-standard 12-lead ECG readings, the algorithm demonstrated impressive accuracy. Smartwatches successfully identified atrial fibrillation (AFib), a potentially dangerous irregular heartbeat linked to strokes. It reached 97% accuracy in detecting AFib and 98% in ruling it out in healthy individuals.
AI-driven smart wearables and RPM solutions represent a transformative force in healthcare.
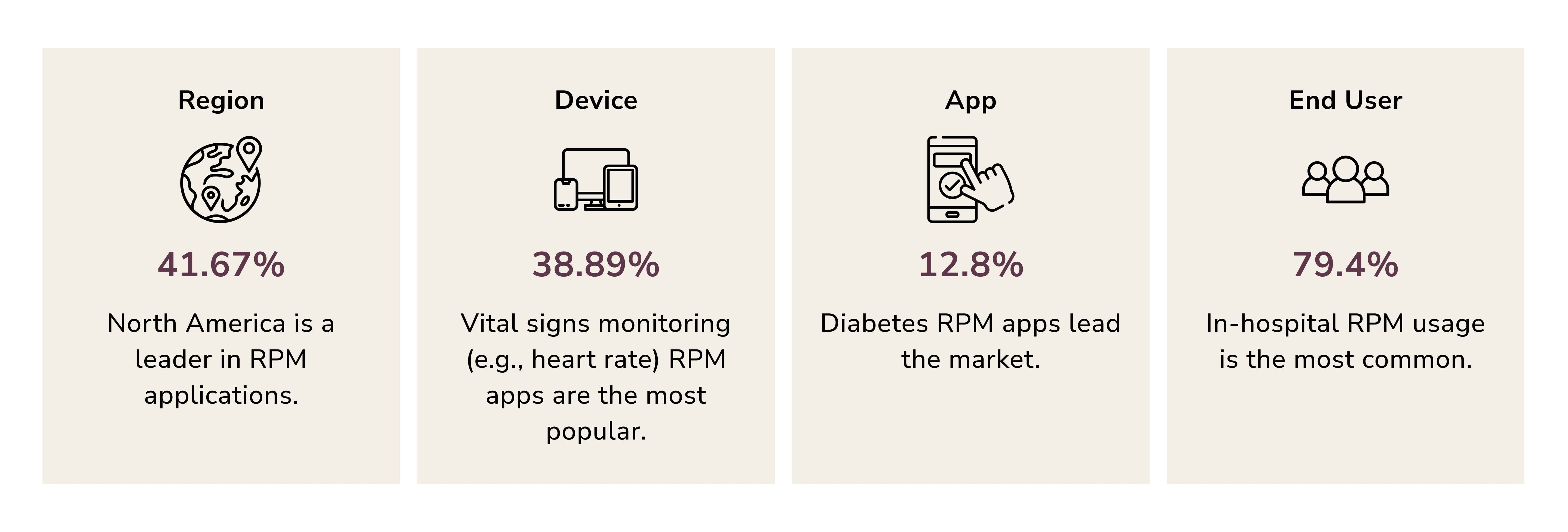
Despite the advancements, manual oversight remains crucial. Human intervention ensures accuracy and provides a safety net. It is likely to exist alongside AI systems in the foreseeable future.
GenAI-assisted Administrative Workflows
Generative AI is mainly used to provide patients with round-the-clock service. But it can also be helpful to the administration itself. It can assist with scheduling, coding diagnoses, drafting referrals, and handling insurance communications. Streamlining these processes is an essential step toward reducing administrative burdens. According to Dushyant Sahani, Professor and Chair of Radiology at the University of Washington Medical Center, "using AI for smarter scheduling opens up more slots, which empowers referring physicians to schedule more patients or more effectively match patients with specialists.”
The benefits of GenAI are linked closely to its ethical deployment. Yes, tools that automatically document patient records come in handy. However, human oversight is necessary to ensure patients’ data integrity. The clinician’s review is still vital before any AI-generated note becomes a permanent part of a patient’s medical history
The challenge now is to ensure GenAI makes healthcare inclusive and accessible. It should empower rather than exclude those without digital skills or resources.
Organizations should leverage AI to bridge gaps rather than widen them. Then all sectors of society can benefit from these advancements.
Tele-ICU and Tele-Stroke Programs
Tele-ICU programs use AI to connect specialists with ICU teams. This is possible due to video conferencing tools with screens, cameras, and call buttons. This setup ensures seamless communication between on-site medical professionals and remote specialists. Doctors engage with patients virtually and document their findings. Meanwhile, AI algorithms help on-site teams make informed decisions during critical moments of care.
Telestroke works similarly. It is instrumental in rural regions where specialized stroke care is often unavailable. Neurologists rely on WebRTC and AI-driven technologies to examine patients remotely. These tools provide a detailed analysis of neurological indicators. This way specialists can make accurate diagnoses and swift recommendations for treatment.
A great example is the CLEW tele-ICU solution. Two Israeli hospitals, Sheba and Sourasky Medical Center implemented it in 2020. At the time, the system performed two primary functions:
- expanding ICU capacity by optimizing resources
- treating COVID-19 patients while protecting frontline workers.
With the help of ML, CLEW forecasts respiratory failure. This fosters timely interventions to improve clinical outcomes. Both hospitals established field ICUs equipped with telemedicine tools. This is to stay ready for potential surges in ICU admissions.
AI-Powered Telemedicine Examples and Real-World Use Cases
Telemedicine’s core mission is to make healthcare accessible to everyone, especially to individuals with mobility challenges or those living in remote regions. Well, it’s about time it delivers on its promises. Replacing one-size-fits-all treatment approaches with high-quality patient care is long overdue.
Where does AI stand in this?
Patient Well-Being
With AI telemedicine tools, patients can avoid hospital visits (if not urgent). Instead, they can rely on monitoring devices to keep track of vital indicators. Statistics say individuals value such comfort.
Take Binah.ai. The platform allows for monitoring heart rate, respiratory rate, and oxygen saturation. All they need is everyday devices like smartphones, tablets, or laptops. What’s more, organizations can use Binah.ai’s SDK to upgrade preliminary assessments. These non-invasive health assessments via facial video streams once again reduce the need for a face-to-face visit. Patients can easily monitor their health from virtually anywhere. This breakthrough makes healthcare accessible no matter the distance. This is precisely why telehealth was invented in the first place.
Early Interventions Support
AI telehealth tech approaches each case individually. It promotes early interventions and reduces the chances of adverse side effects.
Kaiku's algorithms for instance alert care teams when intervention is necessary. The platform extends from oncology to fertility treatments and preventive healthcare. Currently, over 30 hospitals and clinics across Europe rely on Kaiku Health. It alleviates healthcare workers’ administrative burden while improving patient care.
Hello Heart AI empowers better hypertension (high blood pressure) management. The way it works is as follows:
- A user installs a mobile app.
- The app connects to blood pressure monitoring devices.
- Patients routinely measure and record their readings.
The app supports data sharing with healthcare providers. They, in turn, check the indicators and assess risks.
Manageable Chronic Conditions
Managing chronic conditions like diabetes, heart disease, and asthma requires constant vigilance. AI-driven telehealth platforms make this challenge more manageable.
A leader in telehealth services, Teladoc, has greatly progressed in this regard. They use AI and ML for primary care, mental health support, and chronic condition management. The platform enhances symptom assessment via predictive analytics. It identifies potential health risks and personalizes patient interactions.
The company collaborates with employers, hospitals, and health systems to amplify its reach. Teladoc also plans to incorporate generative AI tools through Nuance’s voice-enabled medical scribe app. It will integrate OpenAI’s GPT-4 to further streamline service delivery.
Patient Engagement
Patient engagement encourages individuals to take on an active role in their healthcare journey. This approach is important for three reasons:
- It fosters adherence to treatment plans.
- It improves health outcomes.
- It strengthens the patient-provider relationship.
Integrating AI into telehealth platforms supports these benefits.
A notable example is Healthily, an AI-driven app focused on self-care. It offers features like symptom checking, health assessments, and goal tracking. It also comprises a library of medically verified articles on health conditions. The app's mission is to educate users, promote self-care, and support health tracking.
Sensely promotes patient-doctor communication. It leverages conversational AI and virtual assistant technology. It also optimizes interaction for insurance providers, pharmaceutical companies, and hospitals.
Mental Health
AI-driven risk models help match patients with the right clinician at the right time. All a patient has to do is provide data.
Behavioral health startups began to flourish in 2020 when the pandemic severely worsened the global mental health state. This pushed the telemedicine market to its unseen-before height. Many of them focus on developing AI-enhanced mental health tools. One standout is Utah-based startup Videra Health. It offers an AI-powered, FDA-registered digital platform for patient-doctor communication. The platform works as follows:
- A patient checks in by responding to traditional healthcare assessment questions. Alternatively, they can share video, audio, text, or hybrid responses.
- AI analyzes these interactions, summarizing them into clinical insights for care teams and operational leaders.
- Healthcare professionals then identify urgent mental health concerns facilitating earlier intervention.
Past diagnoses, medical history, frequency of healthcare usage, and social determinants of health are all valuable in decision-making. AI will generate a comprehensive risk score for each patient and identify the most urgent ones.
This approach enables providers to move beyond the traditional first-come, first-served system. AI prioritizes cases based on clinical necessity rather than putting patients into a waiting queue solely based on when they scheduled an appointment. A patient with a history of suicide attempts might be flagged as requiring immediate attention. Clinicians can then adjust schedules (in case their appointment was requested after someone with less severe symptoms).
Virtual Triage
AI in the triage process has demonstrated substantial improvements in both predictive precision and risk evaluation.
For instance, research incorporating AI models such as Logistic Regression (LR) and XGBoost highlighted significant advancements when the chief complaint was utilized as a key predictive factor.
AI-based triage process looks as follows:
- The system first gathers basic patient information, like demographics and risk factors. Then, it explores primary symptoms, suitable for individuals of all ages, from newborns to adults.
- Based on this preliminary data, AI generates a series of questions. These replicate the diagnostic reasoning used by clinicians. It evaluates symptom severity, duration, triggering elements, and related conditions.
- It then suggests the next steps. These may range from self-care advice to seeking professional consultations or directing patients to urgent or emergency care. Some AI tools also offer educational articles for home management.
Nota bene: we need to stress that AI tools should not dictate final healthcare decisions. They should serve more as an extension - not extinction - of the healthcare industry as we know it. Today, it assists and supports decision-making, not replacing or enforcing it.
Medical Imaging Analysis
AI tools are now widely used to analyze medical imaging, including X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Combined with human intelligence, these tools make faster, more accurate diagnoses.
“When we combine AI-based imaging technologies with radiologists, what we have found is that the combination of the AI technology and the radiologist outperforms either the AI or the radiologist by themselves”, says Michael Brady, Professor of Oncological Imaging at the University of Oxford.
Researchers at Houston Methodist have designed an AI tool to analyze mammograms Due to its speed and precision, doctors can predict breast cancer risks more effectively. Published in Cancer (August 29, early online release), the study highlights how the AI processes patient data into diagnostic insights 30 times faster than humans, with an impressive accuracy rate of 99%.
“This tool reviews vast amounts of patient records in record time, allowing us to assess breast cancer risk faster and more effectively using mammogram data. This innovation could significantly reduce the number of unnecessary biopsies,” explains Dr. Stephen T. Wong, chair of the Department of Systems Medicine and Bioengineering at Houston Methodist Research Institute.
Hence, we can state that AI tools
- speed up the diagnostic process
- enable timely treatment decisions
- help radiologists manage high patient volumes.
AI in Healthcare Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
Chatbots powered by AI lend a hand in managing patient inquiries. For instance, they can provide preliminary medical advice and manage appointment scheduling.
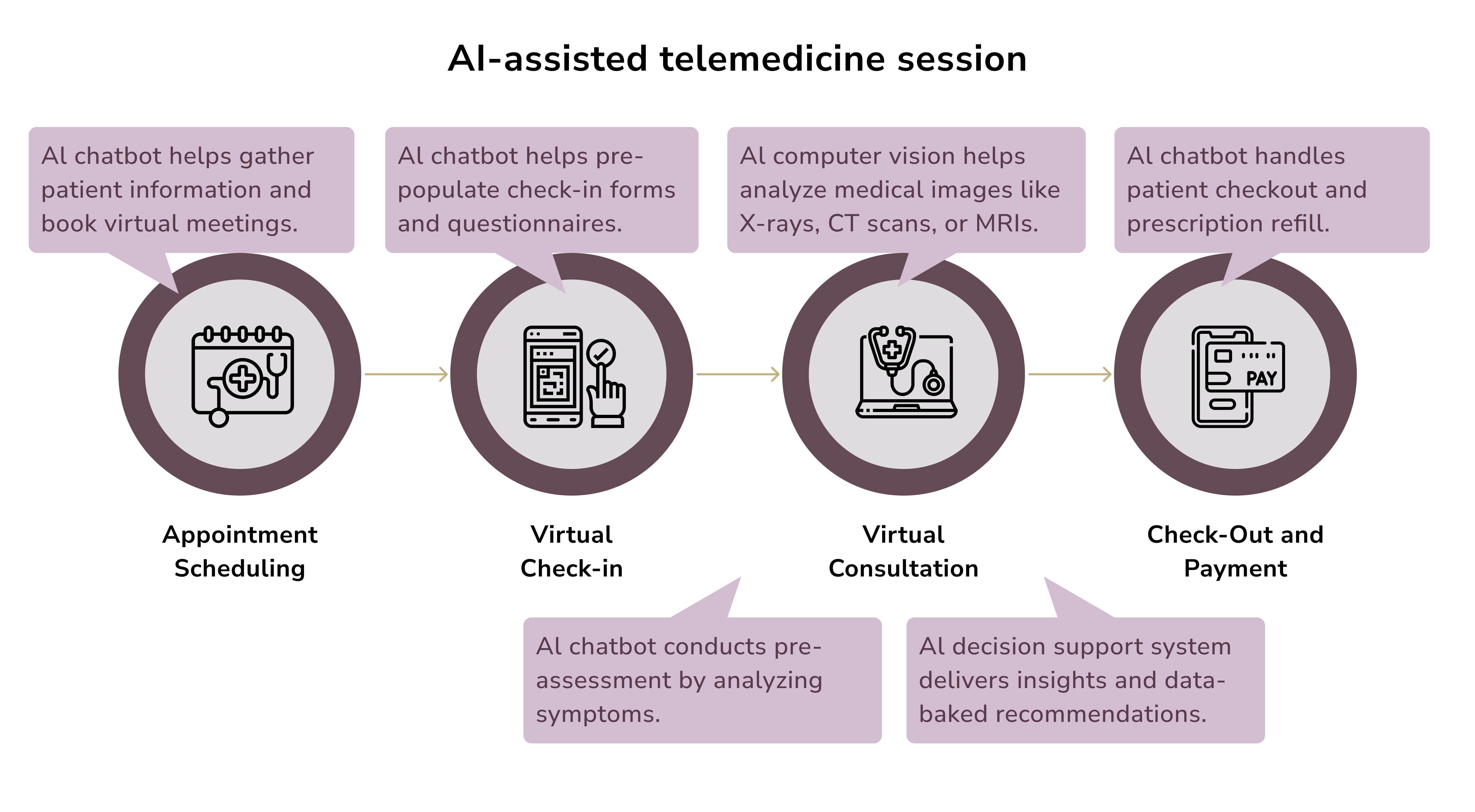
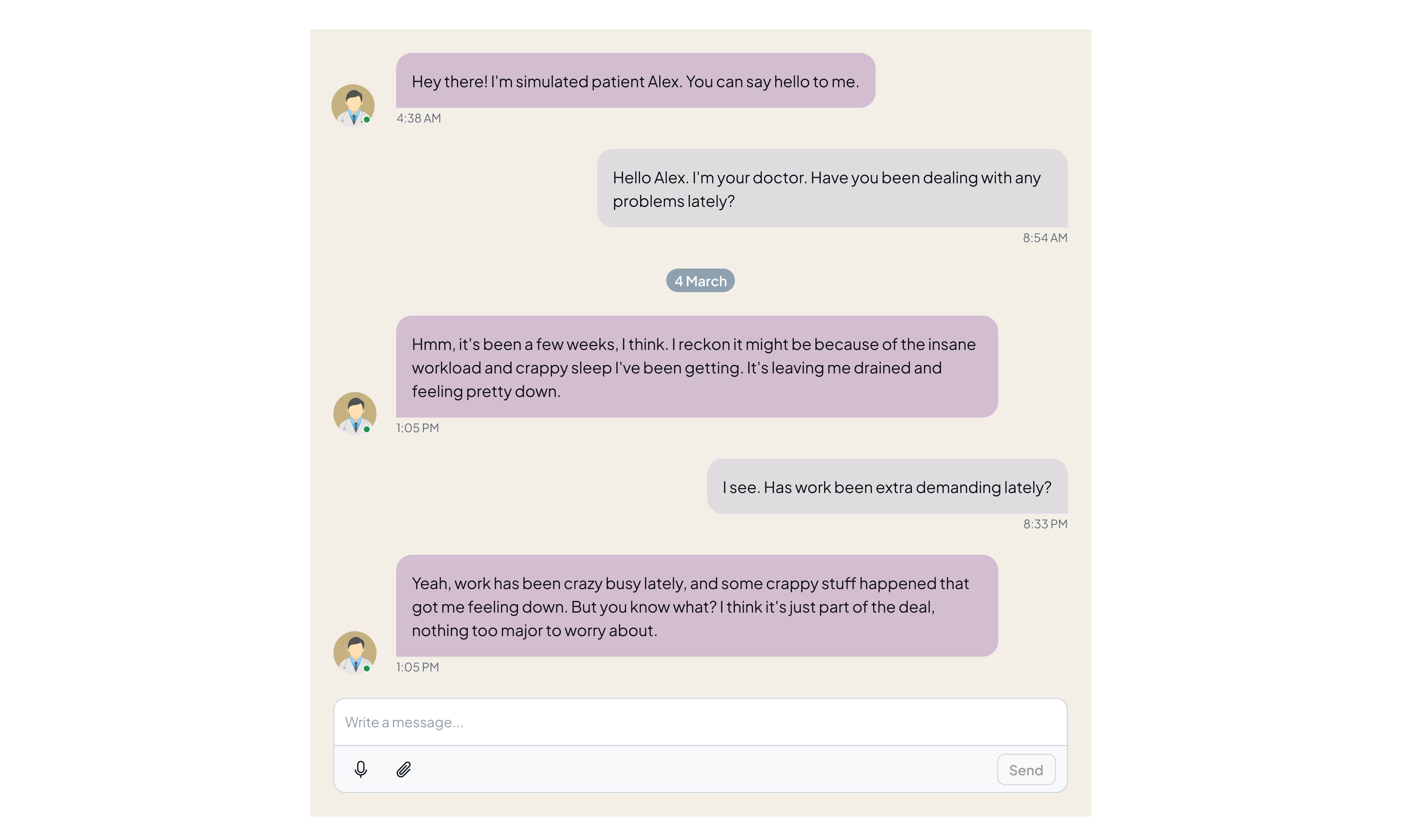
A noteworthy example is AVA built on LLMs and ML by Videra Health. AVA adjusts its questions in real-time to provide personalized support during assessments. Clinicians use it to detect changes in a patient’s condition.
Virtual AI asssitatns can
- enhance patient engagement
- improve access to critical information
- ensure higher patient satisfaction
- allow healthcare staff to handle more complex cases by offloading routine tasks.
Florence chatbot functions as a “personal nurse” on Facebook Messenger, Skype, or Kik. For instance, it reminds patients to take medications. Users only need to enter the medication title, dosage, and the specific times to take it. Additionally, Florence can locate the nearest pharmacy or a clinic in case of emergency.
How Impressit Can Help You with AI Telehealth Solutions Development
Impressit specializes in developing custom AI and ML software solutions to help businesses automate operations, boost performance, and create exceptional user experiences. Targeted toward medtech startups, clinics, wellness enterprises, and other healthcare-focused organizations, we address the unique requirements of each client.
Impressit is well-rounded in software development for healthcare including GenAI integration. Here’s a short list of what we create/provide in the domain:
- medical software, from EHR systems to diagnostic tools;
- healthcare technology consulting services;
- secure, scalable, and user-friendly solutions;
- customized EHR/EMR solutions fully compliant with HIPAA standards;
- HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solutions;
- mHealth apps for providers of all sizes;
- healthcare-specific CRM systems tailored to industry demands.
AI In Telemedicine: The Future of the Market
The future of telemedicine depends on its ability to balance convenience with quality. For AI to maximize its potential, it must complement, not burden, medical professionals. Forecasts predict immense market growth. So, AI does present a pathway to more empathetic, efficient, and effective healthcare systems.
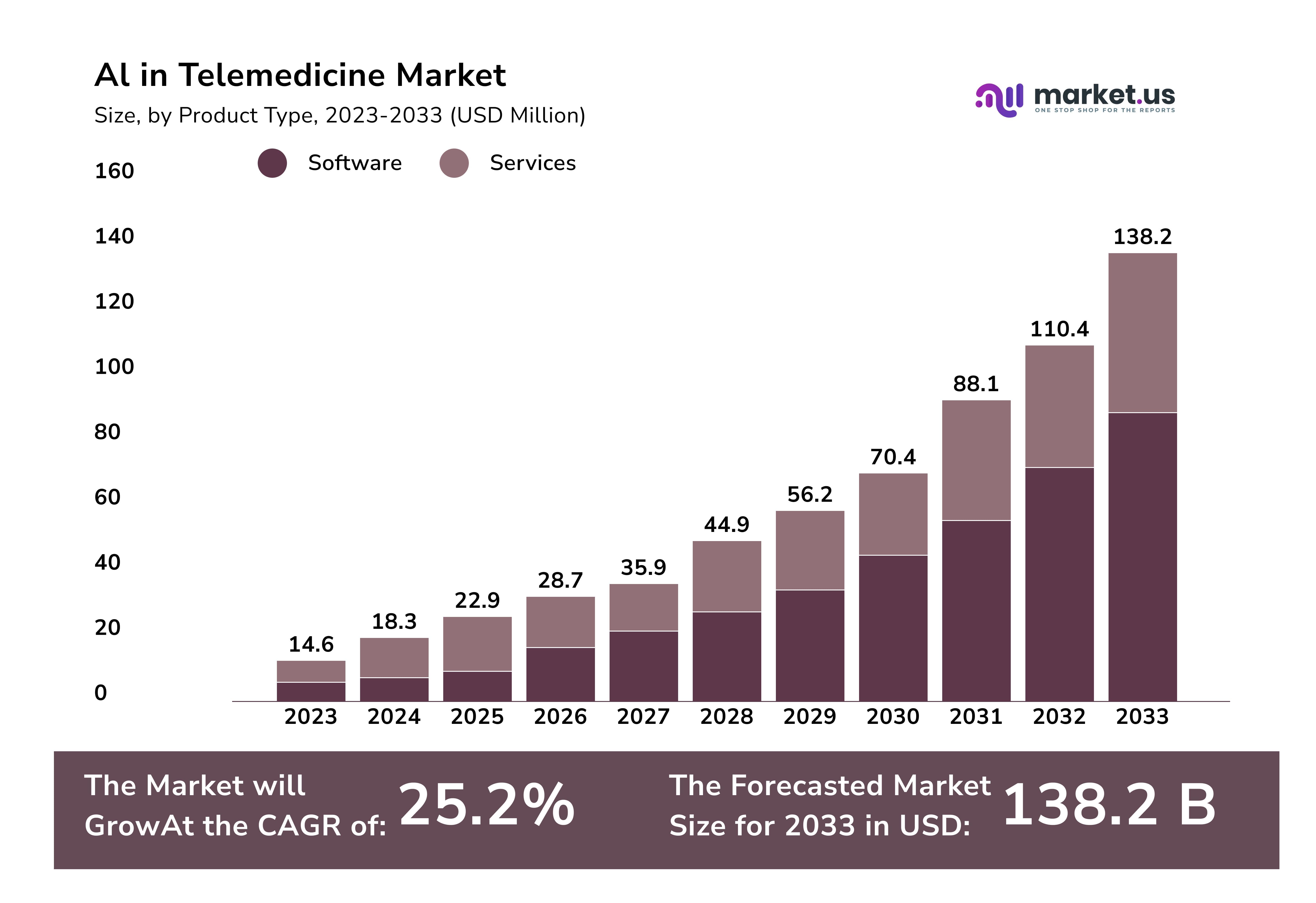
Despite its enormous potential, AI is not without its pitfalls. AI’s task-oriented design prioritizes quick answers over absolute accuracy. Furthermore, adoption complexities still deter its full implementation. Given past resistance to change within the healthcare sector, it may take longer than forecasts say.

Victoria Melnychuk
Other articles