Reducing Administrative Burden in Healthtech with Generative AI: Automating Medical Documentation

Administrative tasks have long been a pain point for healthcare professionals. From managing patient records and processing insurance forms to navigating prior authorizations and regulatory requirements, the sheer volume of paperwork is overwhelming. According to a study by Google Cloud and The Harris Poll, doctors and nurses in the United States spend an average of 28 hours per week on administrative duties, with insurance staff dedicating an even greater 36 hours. This diversion of time from patient care is not just inefficient—it's a contributing factor to clinician burnout, staffing shortages, and, ultimately, diminished healthcare quality.
But what if there were a way to lift this burden? Enter generative AI—a groundbreaking tool capable of transforming administrative processes across the healthcare landscape.
This blog explores generative AI development and its potential to reduce administrative burdens in health tech, providing real-world examples and unpacking the wide-ranging benefits it offers to healthcare professionals and organizations alike.
Administrative Burden in Healthtech
Before we explore how generative AI can help, it's important to understand the extent of the administrative challenges healthtech professionals face.
Studies estimate that as much as 25-40% of healthcare spending is consumed by administrative costs, driven by inefficiencies in documentation, billing, and compliance. This not only adds financial strain but also limits the time professionals can devote to patients.
For healthcare workers, the consequences are clear:
- Burnout: over 82% of clinicians report feelings of burnout, largely due to time-consuming clerical work.
- Reduced Patient Time: administrative tasks keep providers away from bedside care, impacting patient experiences and outcomes.
- Human Error: the monotony of these tasks increases the likelihood of mistakes, which could jeopardize care quality.
This pressing issue demands innovative solutions—and that's where generative AI comes in.
Generative AI in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations are increasingly exploring the potential of generative AI to revolutionize operations and enhance the way stakeholders collaborate and deliver services. However, some remain hesitant, preferring to adopt a cautious, wait-and-see approach.
The future of AI in healthcare administration (particularly in HMS) seems bright, as many organizations are already beginning to take decisive steps. According to a Q1 2024 survey, over 70% of respondents, spanning payers, providers, and healthcare services and technology (HST) groups, reported that they are either pursuing or have already implemented gen AI tools.
The survey, conducted in March 2024 and encompassing 100 US healthcare leaders, follows a related Q4 2023 survey conducted in December 2023 with another 100 US leaders. Comparing responses from both surveys reveals key trends in how the industry is approaching gen AI adoption.
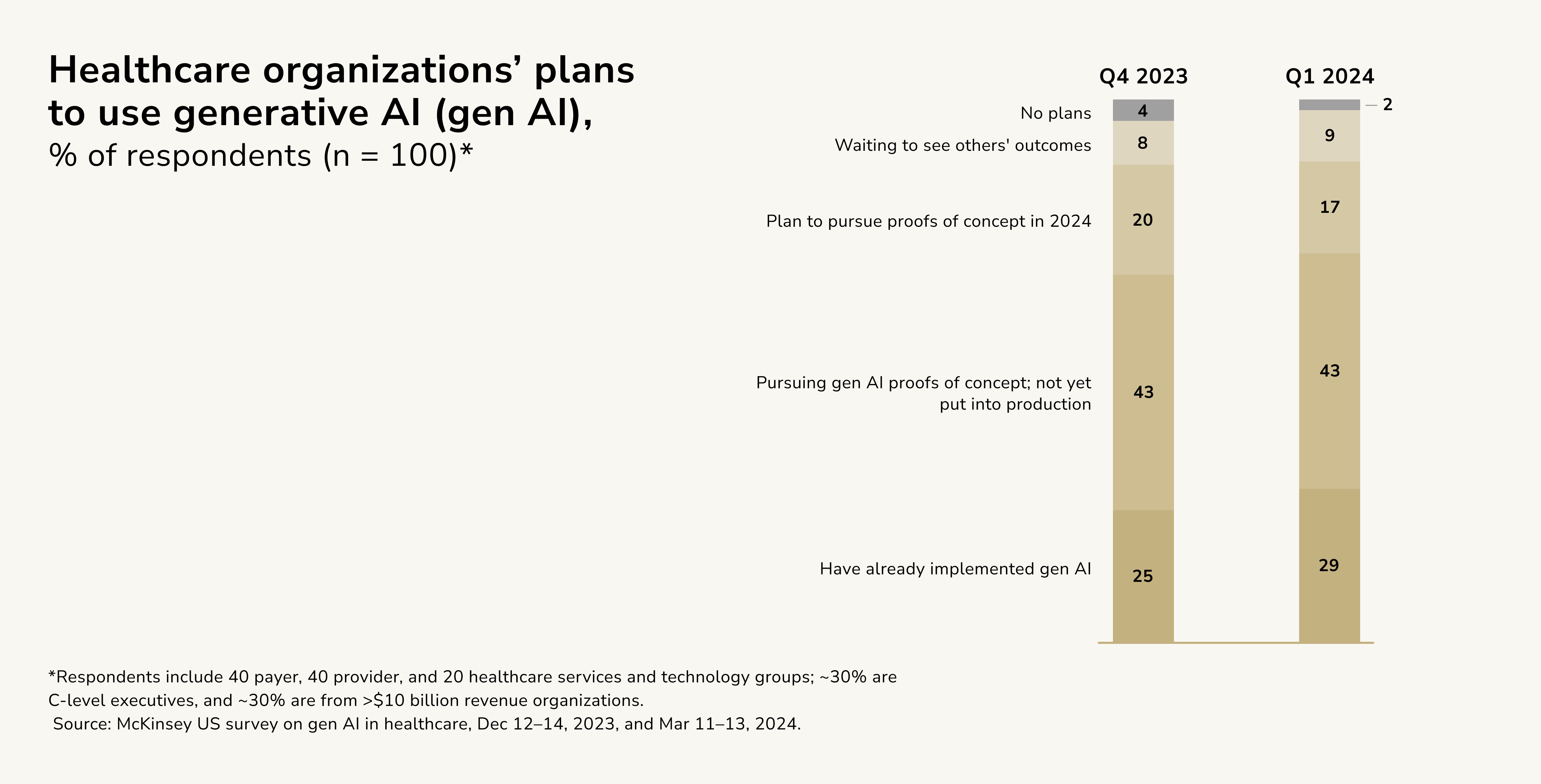
Findings from the Q1 2024 survey indicate that a significant number of healthcare organizations are actively experimenting with gen AI, primarily in the proof-of-concept phase. Leaders are carefully evaluating potential returns, risks, governance structures, strategic priorities, and their organization's overall AI maturity. Nevertheless, despite widespread interest, a notable portion of respondents have no immediate plans to adopt gen AI and continue to observe from the sidelines before committing to action.
Among organizations implementing generative AI (gen AI), 59 percent are working with third-party vendors to create tailored solutions, while 24 percent plan to develop these systems internally. Only 17 percent intend to purchase pre-built gen AI tools. On the other hand, for those yet to adopt gen AI, 41 percent are leaning toward buying ready-made products. This preference could be influenced by their concerns regarding risks (as 57 percent hesitate due to risk factors) and their particular technological requirements (with 29 percent identifying tech needs as a barrier).
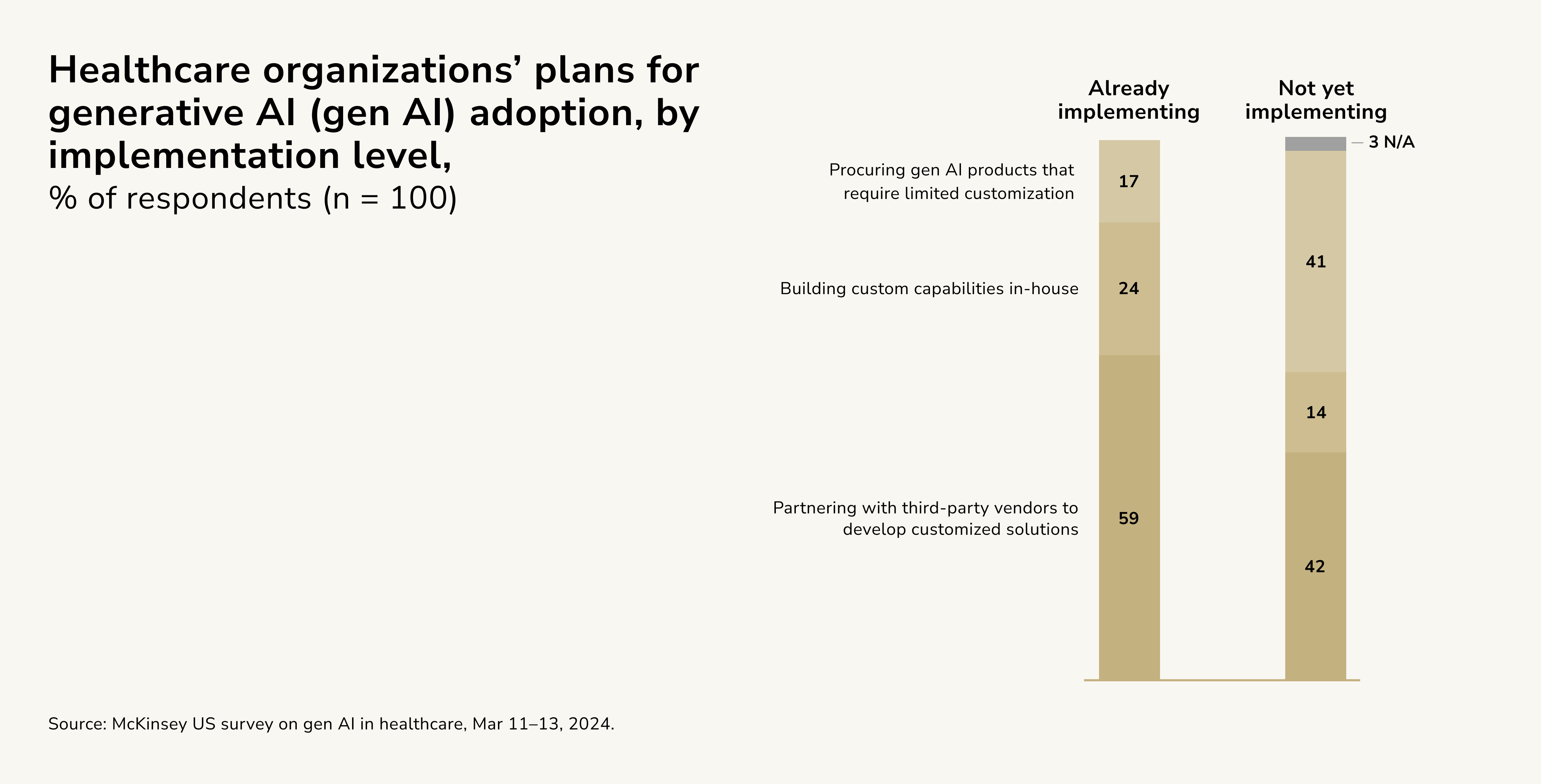
Generative AI in Healthcare Administration
Among various applications, the ability to enhance clinician and clinical productivity is widely regarded as one of the most impactful benefits of Generative AI. Beyond this, the technology is also expected to bring advancements in areas like streamlining administrative processes. This broadening interest demonstrates a shift from purely clinical applications to more comprehensive approaches that enhance overall interactions in patient care.
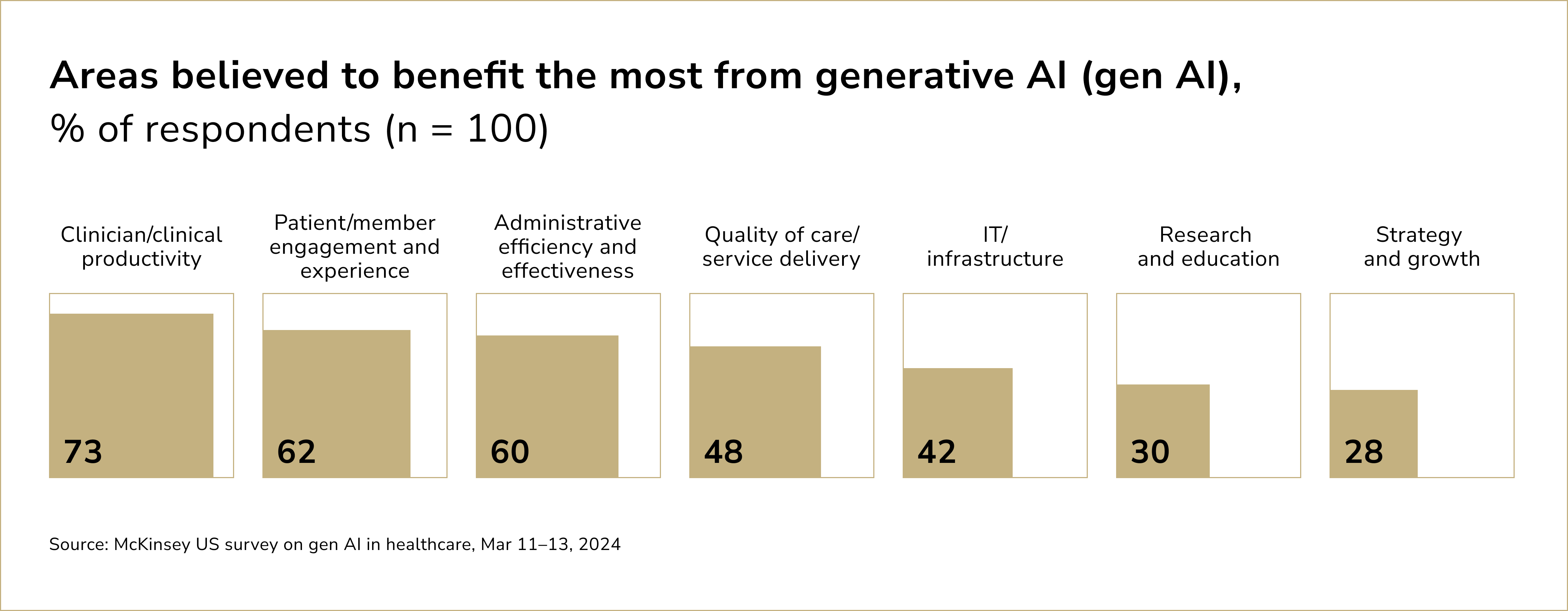
According to 56% of physicians, AI's greatest potential lies in reducing administrative demands through automation. Processes that traditionally required hours of manual effort can now be completed in a fraction of the time. Automating clinical note creation enables healthcare professionals to dedicate their time to more critical activities, such as engaging with patients and making accurate clinical decisions, ultimately boosting overall efficiency and productivity in the healthcare ecosystem.
Generative AI also enhances the precision and quality of medical documentation. Minimizing errors commonly caused by human fatigue or oversight ensures that healthcare providers have access to accurate, up-to-date, and interoperable information. This improvement not only reduces the likelihood of medical errors but also facilitates better collaboration among care teams, enabling seamless continuity of care and fostering more effective patient outcomes.
Automating Clinical Documentation
Generative AI can draft, edit, and summarize clinical documents such as bedside shift reports, discharge summaries, and patient histories. For example, HCA Healthcare partnered with Google Research to create a tool that generates nurse handoff reports. Rather than merely summarizing patient charts, the AI identifies critical details and key events, creating highly focused summaries. This pilot alone received a 90% approval rating from nurses, who found it helpful enough to replace traditional processes.
Streamlining Prior Authorizations
Prior authorization processes—a significant administrative bottleneck—are ripe for automation. Highmark Health has used generative AI models to streamline and automate 30% of its prior authorizations, reducing staff costs by 85%. This means faster approvals, fewer delays in patient care, and lower administrative expenses.
Enhancing Health Record Navigation
A major frustration for medical staff is the difficulty in navigating extensive electronic health records (EHRs). Generative AI tools alleviate this by summarizing dense data and highlighting critical information. Meditech, for example, developed an AI model that uses the SBAR format (Situation, Background, Assessment, Recommendation) to simplify nurse handoff summaries. These tools allow clinicians to quickly access actionable insights without wading through overwhelming data.
Chatbots for Pre-Appointment Tasks
AI-powered chatbots are increasingly handling pre-appointment administrative functions, such as gathering patient data, answering routine queries, and scheduling follow-ups. This not only reduces the workload for administrative staff but also improves patient satisfaction by offering immediate, accurate responses.
Generative AI Use Cases in Healthcare
The best way to explain the use of GenAI in healthcare is to see it in action.
HCA Healthcare and Nurse Handoffs
HCA Healthcare, one of the United States' leading healthcare organizations, has partnered with Google Cloud to integrate generative AI into its workflows. This initiative aims to streamline time-intensive tasks, such as clinical documentation, enabling physicians and nurses to dedicate more time to patient care.
Launched as a pilot program in 2023, the initiative involved approximately 75 emergency room physicians across four HCA Healthcare hospitals. These physicians began utilizing Google's AI technology to efficiently document key medical details from patient interactions. The project represents a collaborative effort between HCA Healthcare, Google Cloud, and Augmedix, a healthcare technology company specializing in ambient medical documentation.
Using a hands-free device, physicians access an Augmedix application that facilitates the creation of accurate and timely medical notes directly from clinical conversations.
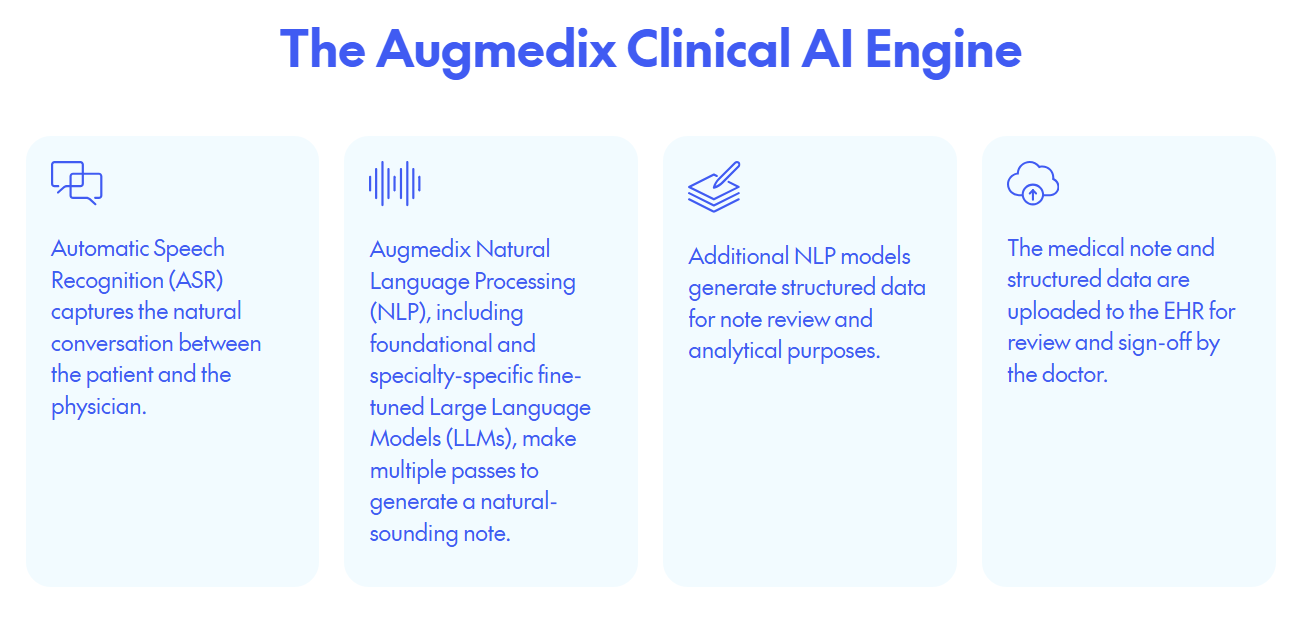
Source: Augmedix
Powered by Augmedix's proprietary platform, the process combines natural language processing with Google Cloud's generative AI capabilities and advanced medical speech-to-text technology. This system instantly converts spoken data into structured medical notes. Physicians then review and approve these drafts before they are seamlessly integrated into the hospital's electronic health record (EHR) system in real time.
Meditech and EHR Summarization
Global electronic medical record provider MEDITECH has teamed up with Google Cloud to integrate an AI-driven search and summarization feature into its Expanse EMR. This enhancement allows healthcare teams to quickly locate critical information using Google's intuitive search functionality. MEDITECH's Expanse EMR is already renowned for its user-friendly interface and comprehensive functionality, but the integration of Google Cloud's AI technology promises to elevate the platform even further. By embedding advanced AI algorithms, MEDITECH will enable healthcare professionals to quickly access and summarize key patient information, thereby facilitating timely and informed decision-making in clinical settings.
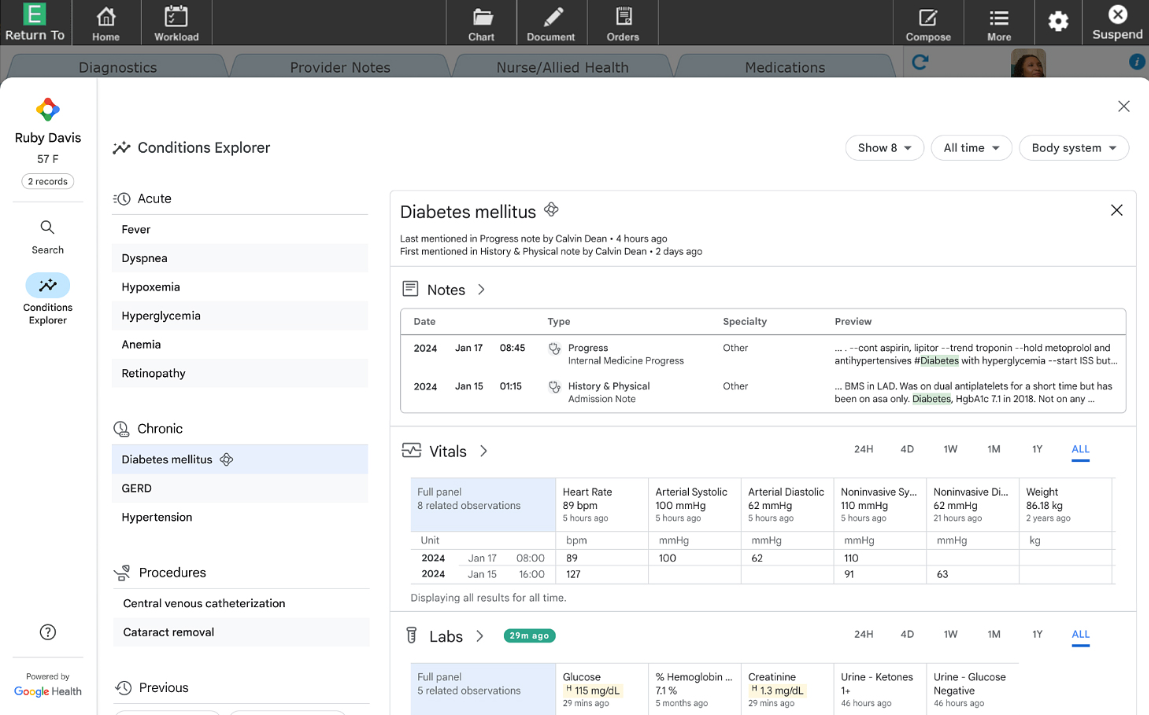
Source: MEDITECH
Leveraging Google Cloud's advanced generative AI and natural language processing technology, the tool employs a large language model to analyze medical records. It delivers relevant data in context, seamlessly embedding the information into users' workflows for improved efficiency.
The tool has already been tested at Mile Bluff Medical Center in Wisconsin, utilizing a cloud-based version of Expanse hosted on Google Cloud. It is now set to undergo trials on the on-premises version, with plans to roll out globally to MEDITECH users. The AI-driven search feature will utilize natural language processing (NLP) to allow physicians and clinicians to query patient records using conversational language rather than complex medical jargon. This intuitive approach means that healthcare providers can find critical data more efficiently, reducing the time spent navigating through extensive electronic records. For instance, a physician could simply ask, "What were the results of the patient's last blood test?" and receive a concise summary that highlights the pertinent details.
Additionally, the summarization feature aims to distill large volumes of patient data into actionable insights. By synthesizing information from various sources—such as clinical notes, lab results, and imaging studies—this feature will help clinicians grasp the most relevant information quickly, thereby enhancing their ability to provide personalized care. For example, during a patient consultation, the AI could present a synthesized view of the patient's medical history, current medications, and any potential drug interactions, all within seconds.
Automated Document Generation at UCSF
The University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) Medical Center has emerged as a pioneer in the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) within healthcare, particularly in the realm of patient care documentation. By leveraging advanced AI-driven tools, UCSF has significantly enhanced the efficiency and accuracy of generating patient care summaries—critical documents that encapsulate a patient's medical history, treatment plans, and ongoing care needs.
One of the cornerstone technologies employed by UCSF is natural language processing (NLP), a subset of AI that enables machines to understand, interpret, and generate human language. This capability allows UCSF to seamlessly aggregate data from various sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), clinical notes, and diagnostic reports. By synthesizing this information, the AI tools create comprehensive and coherent patient care summaries that reflect the nuances of each patient's journey through the healthcare system.
The integration of these AI systems has led to remarkable improvements in clinical workflows. Traditionally, healthcare providers spent a considerable amount of time manually documenting patient information, which could detract from direct patient engagement and care. By automating the generation of patient summaries, UCSF has empowered clinicians to spend more time focusing on patient interaction and decision-making rather than paperwork. As a result, the efficiency of patient care processes has improved, leading to enhanced patient satisfaction and outcomes.
Automation of Medical Coding and Billing at Cleveland Clinic
The Cleveland Clinic has embarked on a transformative journey by integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) tools into its medical coding processes, a move that underscores the intersection of healthcare and technology. In an era marked by the relentless pursuit of efficiency and accuracy, the Cleveland Clinic's initiatives serve as a beacon for other healthcare institutions aiming to optimize their coding practices.
At the core of this initiative is the recognition that accurate coding is not merely a clerical task but a critical component of healthcare delivery that affects everything from insurance reimbursements to patient care quality. Traditionally, medical coders have relied heavily on their expertise and experience to translate complex medical documentation into standardized codes. However, this process can be labor-intensive and fraught with the potential for human error. In response, the Cleveland Clinic is leveraging advanced AI algorithms to enhance the coder's role, enabling them to focus on what truly matters: patient care.
The AI tools implemented by the Cleveland Clinic utilize natural language processing (NLP) to analyze voluminous patient records, extracting relevant data with remarkable speed and precision. These algorithms are trained on extensive datasets, including electronic health records (EHRs), clinical notes, and diagnostic reports, allowing them to understand medical terminology and the nuances of clinical documentation. By automating the initial coding suggestions, these AI systems can significantly reduce the time coders spend on each record, thus increasing overall productivity.
Note: the Cleveland Clinic's approach does not seek to replace coders but rather to augment their capabilities. By providing coders with AI-driven insights, the initiative fosters a collaborative environment where technology and human expertise coexist. Coders are empowered to validate and refine the AI's coding suggestions, ensuring that the final codes accurately reflect the complexity and specifics of patient cases. This hybrid model not only enhances the accuracy of coding but also elevates the role of coders to that of clinical informatics specialists, bridging the gap between technology and patient care.
Stanford Health Care Predictive Analytics for Resource Management
The predictive models developed by Stanford Health Care utilize a multifaceted approach to analyze vast datasets encompassing patient demographics, treatment histories, seasonal fluctuations, and even socio-economic factors. By employing advanced statistical techniques such as machine learning algorithms and time-series forecasting, these models can discern intricate patterns and trends that might elude traditional analytical methods.
One of the key aspects of this predictive modeling framework is its ability to integrate diverse data sources. Stanford Health Care taps into electronic health records (EHRs), claims data, and community health statistics, creating a comprehensive picture of patient flow dynamics. By analyzing these data points in conjunction, the models can identify correlations and causative factors affecting patient volumes, such as local disease outbreaks, demographic shifts, and changes in insurance coverage policies.
Moreover, the predictive models are not static; they are continuously refined and recalibrated as new data becomes available. This iterative process allows Stanford Health Care to respond proactively to emerging trends, ensuring that it can allocate resources effectively and anticipate surges in patient demand before they materialize. For instance, during peak seasons for respiratory illnesses, the models can forecast increased emergency room visits, prompting timely staffing adjustments and resource allocation.
In addition to historical data, the models also incorporate external variables, such as public health initiatives and regional healthcare access, which may influence patient behavior. By understanding how these factors interplay, Stanford Health Care can design targeted outreach programs and interventions aimed at managing patient volumes more effectively. This not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a more patient-centered approach, ensuring that individuals receive timely and appropriate care.
Johns Hopkins Medicine's Intelligent Workflow Automation
Johns Hopkins Medicine has increasingly embraced artificial intelligence (AI) to enhance operational efficiency, particularly in the onboarding process for new employees. By leveraging AI-driven platforms, the institution aims to streamline what can often be a cumbersome and time-consuming procedure, thereby fostering a more engaging and effective experience for newcomers to the organization.
One of the key advancements in their onboarding strategy involves the implementation of AI chatbots. These chatbots are designed to assist prospective employees by providing real-time answers to frequently asked questions regarding policies, benefits, and the onboarding timeline. This capability not only reduces the burden on human resources personnel but also ensures that new hires receive consistent and accurate information, facilitating a smoother transition into their roles.
Additionally, Johns Hopkins Medicine utilizes machine learning algorithms to analyze candidate profiles and match them with departments that best suit their skills and career aspirations. This data-driven approach not only enhances job satisfaction but also contributes to higher retention rates, as employees feel more aligned with their positions from the outset.
The Permanente Medical Group (TPMG)
The Permanente Medical Group, which is part of the Kaiser Permanente health system, has embraced the use of ambient AI scribes to enhance clinical documentation practices. Ambient AI scribes operate seamlessly within the clinical environment, leveraging advanced natural language processing and machine learning algorithms to transcribe and contextualize patient interactions in real-time. This shift not only alleviates the burdens of manual documentation but also allows clinicians to devote more attention to their patients during consultations. TPMG has recognized that these AI-driven tools can improve not just productivity but also the overall quality of care delivered.
One of the key innovations introduced by TPMG is the integration of ambient AI within their electronic health record (EHR) systems. This integration enables the AI scribe to capture conversations between physicians and patients without requiring explicit commands or interruptions, allowing for a more natural and empathetic dialogue. The AI scribe documents relevant clinical details, medical histories, and treatment plans, ensuring that the EHR is updated in real time and reflective of the most current patient data.
By integrating Natural Language Processing (NLP) capabilities, the AI can discern key clinical information, such as symptoms, diagnoses, and treatment plans. One of the standout features of TPMG's implementation is its seamless integration with electronic health record (EHR) systems, enabling clinicians to reduce time spent on documentation significantly. This technology not only alleviates the burden of administrative tasks but also fosters a more patient-centered experience, allowing physicians to focus on direct patient care rather than being tied to screens and keyboards.
Speech Recognition Technology at Frimley Health NHS Trust
Frimley Health NHS Trust, located in the UK, has implemented advanced speech recognition technology to improve the efficiency of clinical documentation. Through this implementation, clinicians can dictate notes directly into their EHR systems, allowing them to generate comprehensive patient records quickly. The speech recognition software employed at Frimley Health is designed to understand medical terminology and context, thereby enhancing its accuracy in transcription. The use of this technology has led to a reduction in the time healthcare professionals spend on documentation, allowing them to allocate more time to patient care.
Additionally, the trust has observed an increase in the completeness of clinical records, as the immediacy of speech-to-text documentation ensures that information is accurately captured during patient encounters. By improving data accuracy and reducing the administrative burden, Frimley Health's use of speech recognition technology exemplifies the role of AI in enhancing the quality and efficiency of healthcare services.
Find out more amazing examples of GenAI transforming business operations across industries.
Risks of Generative AI in Healthcare
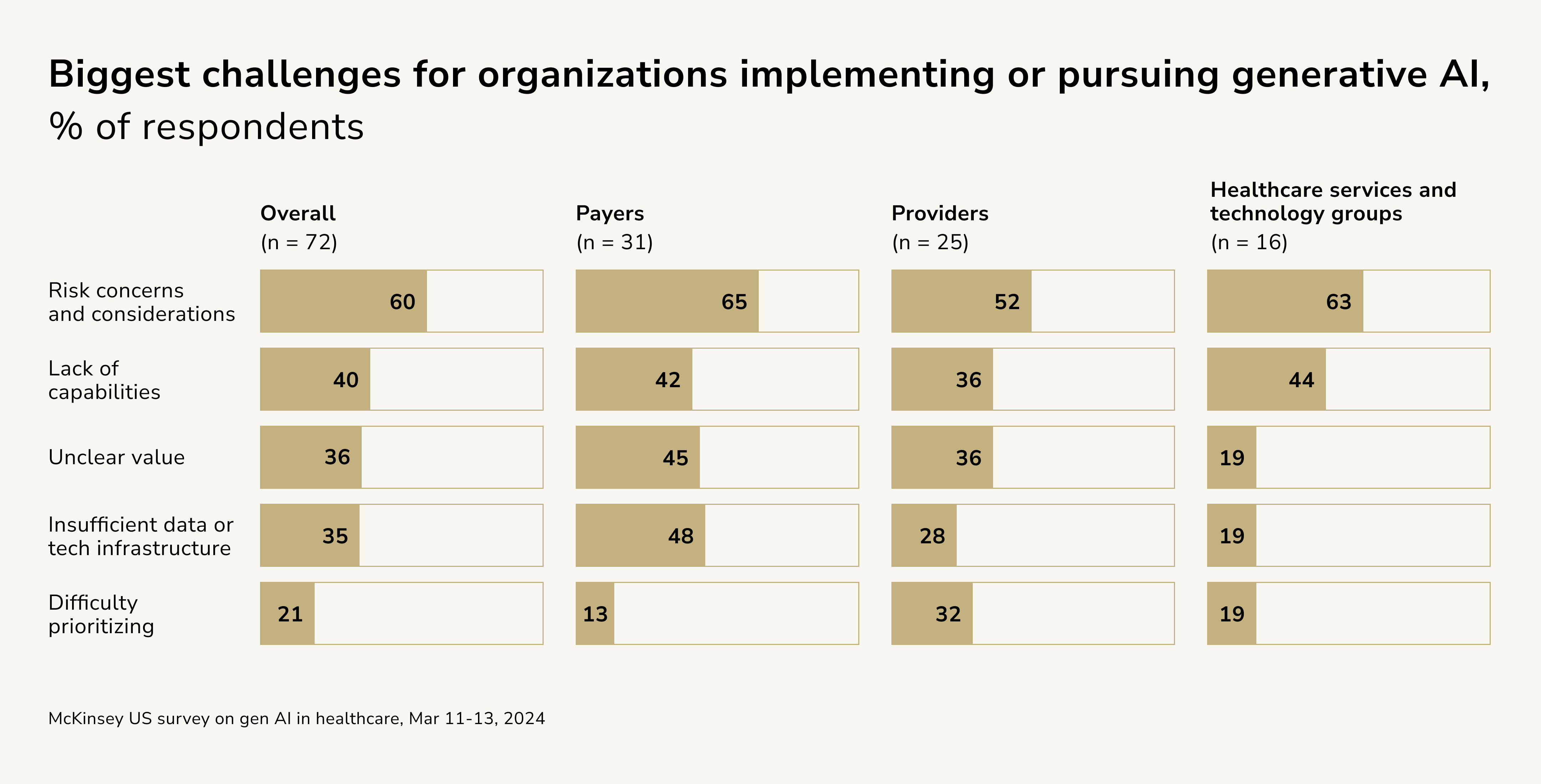
Challenges related to risk management are consistently reported as a top concern for leaders across payers, providers, and HST companies when scaling operations. This concern is largely driven by the unproven nature of generative AI technologies, the substantial investments required to enhance organizational capabilities, and the ambiguity surrounding evolving regulations. These factors emphasize the critical need for robust governance frameworks and risk mitigation strategies to address issues such as data privacy, clinical outcomes, and regulatory compliance while ensuring high standards of care delivery.
Beyond risk, respondents identify other significant barriers, such as limited organizational capabilities, underdeveloped data and technology infrastructure, and challenges in proving value. These issues highlight the inadequate technological readiness among many healthcare organizations, both in terms of implementing generative AI solutions and validating their efficacy.
Automating medical documentation through generative AI offers clear benefits, but misconceptions and concerns around its adoption persist. A prevalent worry is the potential for job displacement among healthcare professionals. However, generative AI is designed to assist—not replace—healthcare providers.
The partnership between Google Cloud and HCA Healthcare, one of the largest healthcare systems in the US, illustrates the potential of generative AI. By integrating AI into HCA hospitals, healthcare professionals have been able to spend more time with patients as time-intensive documentation tasks are streamlined. Physicians and nurses now focus on delivering tailored, empathetic care, forging stronger relationships with their patients, and addressing each individual's specific needs more effectively.
Another critical area to address in implementing generative AI for medical documentation is data privacy and security. Healthcare organizations must rigorously safeguard patient data and meet regulatory requirements. Measures such as robust encryption, secure data storage, and access controls are essential. Google Cloud, for example, deploys advanced security protocols to protect sensitive health information, ensuring compliance with pivotal regulations such as HIPAA. These secure practices establish Google Cloud as a trusted partner for healthcare institutions, providing a reliable platform to store and manage patient data with scale and efficiency.
Future Outlook of GenAI in Healthtech
The potential of AI and Big Data in healthtech is immense; the market leaders just need to find the right ways to implement it. Paired with machine learning, this technology can analyze vast datasets like medical imaging and lab results to identify patterns that might elude human clinicians. This capability aids faster and more accurate diagnostics while enabling real-time disease forecasting for proactive interventions.
GenAI also improves data integration and interoperability, creating a seamless flow of comprehensive patient information across healthcare systems. This fosters better collaboration among healthcare teams and supports public health initiatives, such as chronic disease management.

Victoria Melnychuk
Other articles