Unlocking the Future: The Transformative Potential of AI and Big Data in Healthcare

As we navigate the complexities of modern medicine, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) promises to be more than a trend. It can be pivotal in the way we understand, diagnose, treat, and manage health conditions.
This article describes AI companies in healthcare that are reshaping the industry. We will also illuminate the possibilities and challenges in the industry. This way, we aim to foster AI software development for a healthier future.
Big Data and AI in Healthcare
Just a few decades back, surgical rooms were primarily mechanical. They depended heavily on manual processes, limited technological tools, and isolated data. Surgeons and medical teams relied on physical records, basic monitors, and their skills to conduct surgeries. Few considered using digital tech for surgical intelligence. It required collecting and integrating vast data. Consequently, the innovations in medical procedures faced significant constraints. That is why the adoption of AI in healthcare is going slower than expected.
A World Health Organization report says chronic diseases cause 71% of all deaths. This highlights the urgent need for better healthcare interventions. Enter AI: a tech that uses vast data, from genes to health records. It finds patterns that may elude human doctors. Also, we are nearing a digital age with 40 zettabytes of data. The solution to some of the world's toughest diseases might be in there. We just need to extract insights from this vast wealth of information.
Nota bene: when was AI introduced in healthcare? In 1971, scientists created INTERNIST-1. It used a solid algorithm to diagnose patients. In 1975, the NIH sponsored the first AI in Medicine workshop at Rutgers. (Apr 20, 2023, Cedars-Sinai Staff.)
Here are the top AI applications in healthcare:
- Increasing diagnostic accuracy.
- Identifying at-risk patients.
- Tailoring treatments to individual patients.
- Streamlining administrative processes.
- Facilitating remote patient monitoring.
- Simplifying drug discovery.
- Helping manage population health effectively.
This list is far from complete. Healthcare AI companies continue to innovate despite a decline in funding.
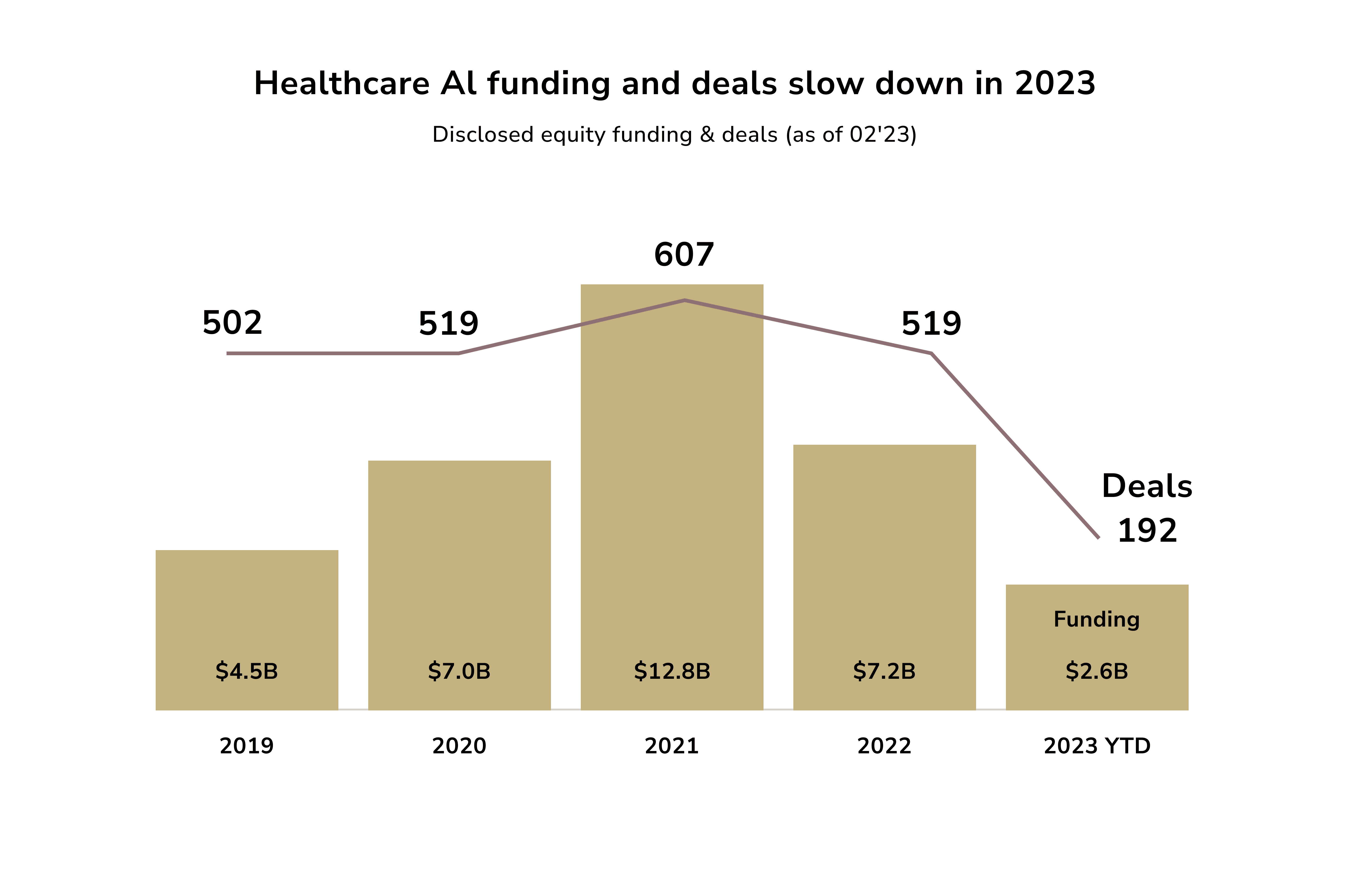
Healthcare experienced a remarkable transformation due to the integration of
- data warehouses
- data lakes
- machine learning
- artificial intelligence
- predictive analytics.
These technologies have changed many areas of healthcare. This includes preventive care, personalized treatment, and surgical room tech.

For EHRs, big data plays a particularly important role.
Electronic Health Records
Ask any healthcare professional about their biggest challenge. They will likely mention cumbersome electronic health records (EHR) systems. In the past, clinicians manually recorded observations and patient data, each using their own method. However, the process looks completely different with AI and deep learning. Speech recognition, interactions with patients, diagnoses, and treatment plans are all made more straightforward. Plus, AI documents this data more accurately and almost instantaneously.
Nota bene: Why are well-structured EHRs so important? The answer is - they could save lives. See, countless individuals have undergone cancer treatments. Each patient's experience generates massive amounts of digital data, often exceeding a terabyte. This data includes demographics, lifestyle, and medical history. It also has details about the disease and its treatment. Therefore, it is a valuable resource, ripe for analysis. Many initiatives aim to combine scattered data on cancer patients for a better study. Connecting doctors with this data lets them compare treatments and outcomes for similar cases. It will enable more effective, personalized therapies.
Preventive healthcare is a goal scientists aim for, and data plays a crucial role in reaching it. EHRs, medical devices, wearables, and admin systems create much healthcare data. This vast scale poses both challenges and opportunities for healthcare professionals.
Let’s focus on opportunities.
Combating Cancer
The cost to sequence the human genome is now as low as $2,000. So, industry pros can now test a person's DNA for cancer-related genetic markers. Also, digitizing medical records can help detect cancer symptoms faster. This can lead to more tests.
Big data analysis also uncovers global patterns. It helps identify high-risk groups and discover potential causes or treatments. Recently, a wide array of variables led to a surprising discovery. Desipramine, a common antidepressant, might treat small-cell lung cancer.
Combating Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are ever-evolving. Urbanization, climate change, and global travel drive this change. A rise in online searches for specific diseases may signal an outbreak. Social media can track an illness's spread across regions. With nearly four billion internet users, these platforms hold much potential. They are a rich source of data that AI can analyze. It can then detect patterns of behavior that indicate an epidemic.
The success of these methods has been mixed. Google Flu Trends (GFT) initially made significant advances in tracking flu outbreaks. However, the H1N1 pandemic caused a surge in global searches. This distorted local data and led to false findings, and operations ceased.
These methods are still in development. But they can provide key insights for experts to explore.
Top Use Cases of AI in Healthcare
Below are real-world AI applications in healthcare examples.
AI in Radiology
AI algorithms have demonstrated remarkable proficiency in interpreting medical imaging. A striking example is deep learning algorithms. They can detect pneumonia in chest X-rays with accuracy similar to radiologists.
AI radiology examples:
- Viz LVO is an AI solution. It is clinically validated to automate detecting and managing LVO strokes. The FDA approved Viz LVO in 2018. It created a new category of medical devices: computer-assisted triage.
- An AI system from Google Health, tested on 100,000 mammograms, reduced false positives by 5.7%. It also decreased the number of false negatives by 9.4%. This improved breast cancer detection rates
AI in Disease Management and Patient Monitoring
Regular monitoring of patient health conditions is essential for prompt intervention. AI-driven technologies evaluate real-time health metrics and detect anomalies. It helps healthcare workers to act quickly in emergencies and avoid bad outcomes.
AI patient health monitoring examples:
- Biofourmis leverages algorithms to monitor patients' vital signs through wearable devices. Brigham and Women's Hospital used the solution to predict heart failure decompensation. It has led to timely interventions and reduced hospital readmissions by 30%.
- Stanford and Intermountain LDS Hospital have installed depth sensors in patient rooms. The sensors were empowered by ML. This technology successfully identified patient movements with an 87 % accuracy rate. The ultimate objective is to alert ICU staff when patients require immediate attention.
- Apple Watch AI-ECG algorithm achieved an area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of 0.89. This indicator is similar to medical screening and cervical cytology tests for cancer.
- Roche has received approval for its AI-driven continuous glucose monitoring system. Designed for adults with Type 1 or Type 2 diabetes, it helps manage their insulin doses.
- Sense.ly introduced Molly, the world's first digital nurse based on ML. Molly focuses on monitoring chronic illnesses and follow-up care through the mHealth platform.
AI and Robots in Healthcare
AI-powered robotics now assist surgeons in performing minimally invasive procedures with enhanced precision. Robots can help in many areas. Examples include surgical assistance, rehabilitation, elderly care, and social interaction. AI-assisted surgical robots are now common in operating rooms. They perform tasks without fatigue and reach areas human hands cannot.
Robot surgery examples:
- The da Vinci Surgical System helps surgeons perform minimally invasive surgeries. Surgeons can control robotic instruments with high precision. AI-driven analytics enhances the process by providing real-time feedback on the surgery.
- ROSA (Robotic Surgical Assistant): primarily used in neurosurgery, ROSA assists with brain surgeries. Its robotic arm is mounted on a mobile base and can direct surgical tools during procedures.
- At Maastricht University Medical Center, AI robots sew tiny blood vessels. Some are just 0.03 mm in diameter.
AI in Drug Discovery and Development
Transforming a drug from a lab concept to a patient medicine is often costly and slow. It typically averages $359 million and takes 12 years (California Biomedical Research Association.)
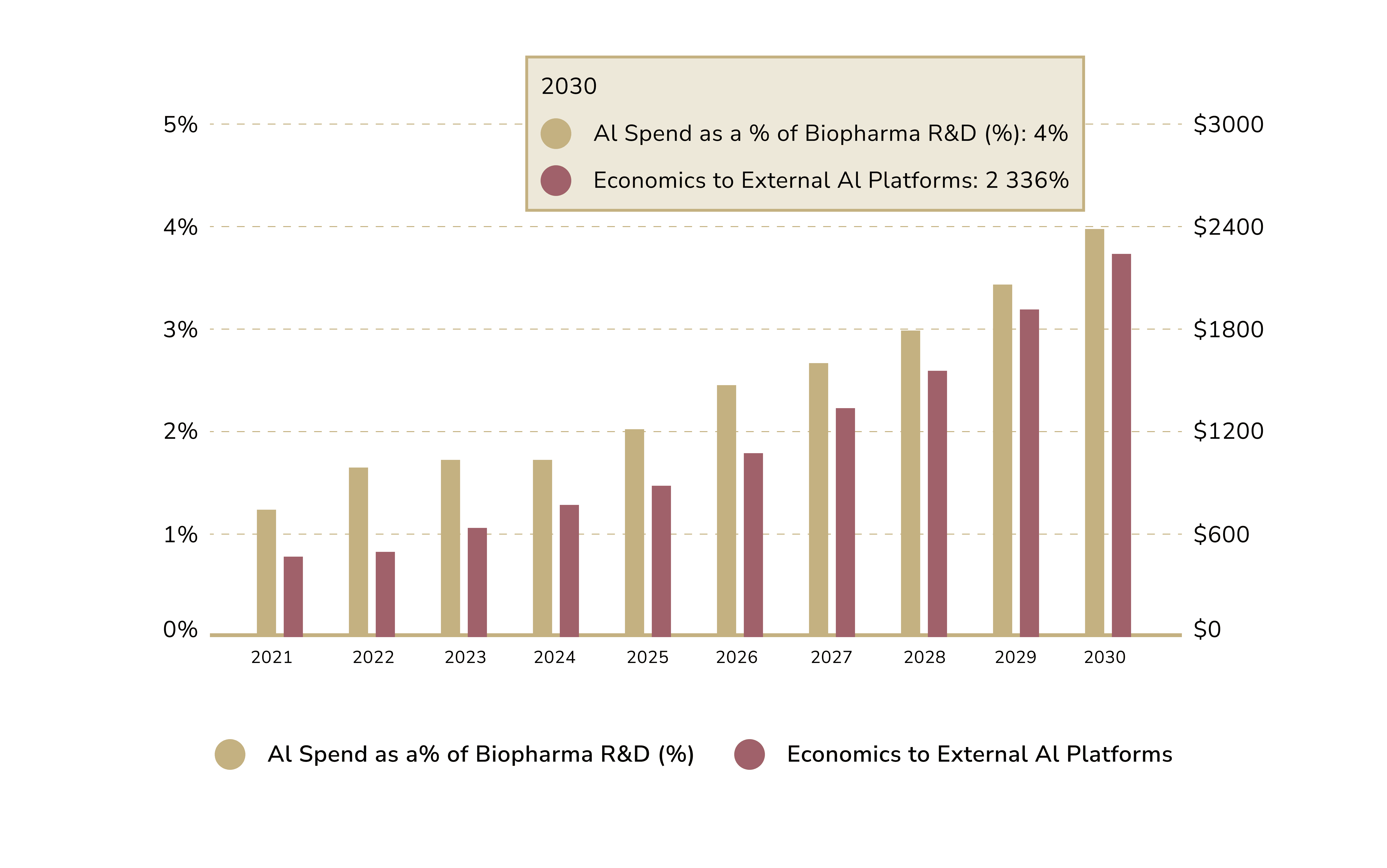
AI holds the promise of accelerating drug discovery by
- identifying potential new compounds
- predicting other uses for existing drugs
- simulating interactions with other chemicals or the human body.
Hospitals are now working with biotech firms using AI. The AI models simulate how different compounds interact with various biological targets. This approach has already shortened the drug discovery timeline from years to months.
AI drug discovery examples:
- In 2015, Atomwise used AI to find existing drugs to treat Ebola. This showcased the tech's ability to speed up drug discovery.
- Recursion Pharmaceuticals and Exscientia, two top AI drug firms, are merging. This merger builds on Recursion's efforts to use AI in drug discovery. This includes its high-profile partnership with NVIDIA. At the heart of this effort is BioHive-2. It's a leading supercomputer in the pharma industry. It is designed to tackle the complexities of biological research.
- PathAI leverages its native AI-driven pathology platform, AISight. The latter offers extensive capabilities for pharmaceutical research and clinical trials. PathAI uses ML to help researchers examine tissue samples. This leads to better identification and validation of biomarkers.
- NuMedii, a biopharmaceutical company, has developed AIDD technology. It uses AI to find links between drugs, diseases, and systems quickly.
- Eve, an AI robot scientist, helps reduce drug discovery costs.
AI in Precision Medicine
AI and precision medicine create a powerful synergy. It makes therapies effective and tailored to each patient's unique genes and environment. This customization could reduce side effects and improve treatment success. For example, machine learning in genomics can find disease-related genetic mutations. Some hospitals use AI to recommend personalized medications. This improves treatment and reduces side effects.
AI precision medicine examples:
- IBM's Watson suggests personalized treatments based on a patient's allergies and medical history.
- Tempus uses AI and genomic sequencing to create personalized cancer treatments.
- 23andMe exemplifies the use of AI in personalized healthcare diagnostics and DNA analysis. The company analyzes a saliva sample. It provides insights into how a person's genes may affect their reaction to certain drugs.
AI in Diagnostics
AI algorithms can diagnose some conditions, like diabetic retinopathy and skin cancer. Their accuracy matches or exceeds that of human specialists. This shows AI's precision. It shows its potential to democratize healthcare in underserved areas with few specialists.
AI diagnostics examples:
- Moorfields Eye Hospital uses AI to identify eye diseases. It has 94% accuracy, based on data from over 15,000 patients.
- Google's AI can detect diabetic retinopathy in retinal images. It can help screen in low-resource areas. For rare diseases, diagnosis can take years and cost a lot. The 3billion algorithm, developed in 2019, can test for up to 7,000 DNA-based conditions. It may cut diagnostic time and costs for patients worldwide.
- Zebra Medical Vision uses AI to analyze medical images. It enables faster, more accurate diagnoses. Their platform, which scans X-rays, CT scans, and MRIs, has been used in hospitals across the globe.
AI in Predictive Analytics
AI's potential extends beyond diagnostics. Predictive analytics can forecast patient admissions to optimize staffing and manage supply chains. This reduces inefficiencies and improves resource use. A study in Health Affairs found that AI can cut patient wait times by 30%. This improves the patient experience.
AI shows its value by using data and global travel patterns to predict epidemics. A remarkable example is Blue Dot's AI. It predicted COVID-19 before any official announcements.
Another great example is how AI makes heart care more anticipatory and preventive. A recent study highlighted the forecasting abilities of deep learning models. It predicted the short-term risk of atrial fibrillation from 24-hour Holter monitor readings. This shows how AI can improve patient care by enabling earlier intervention.
However, Deloitte warns that predictive analytics bears both benefits and risks for healthcare.
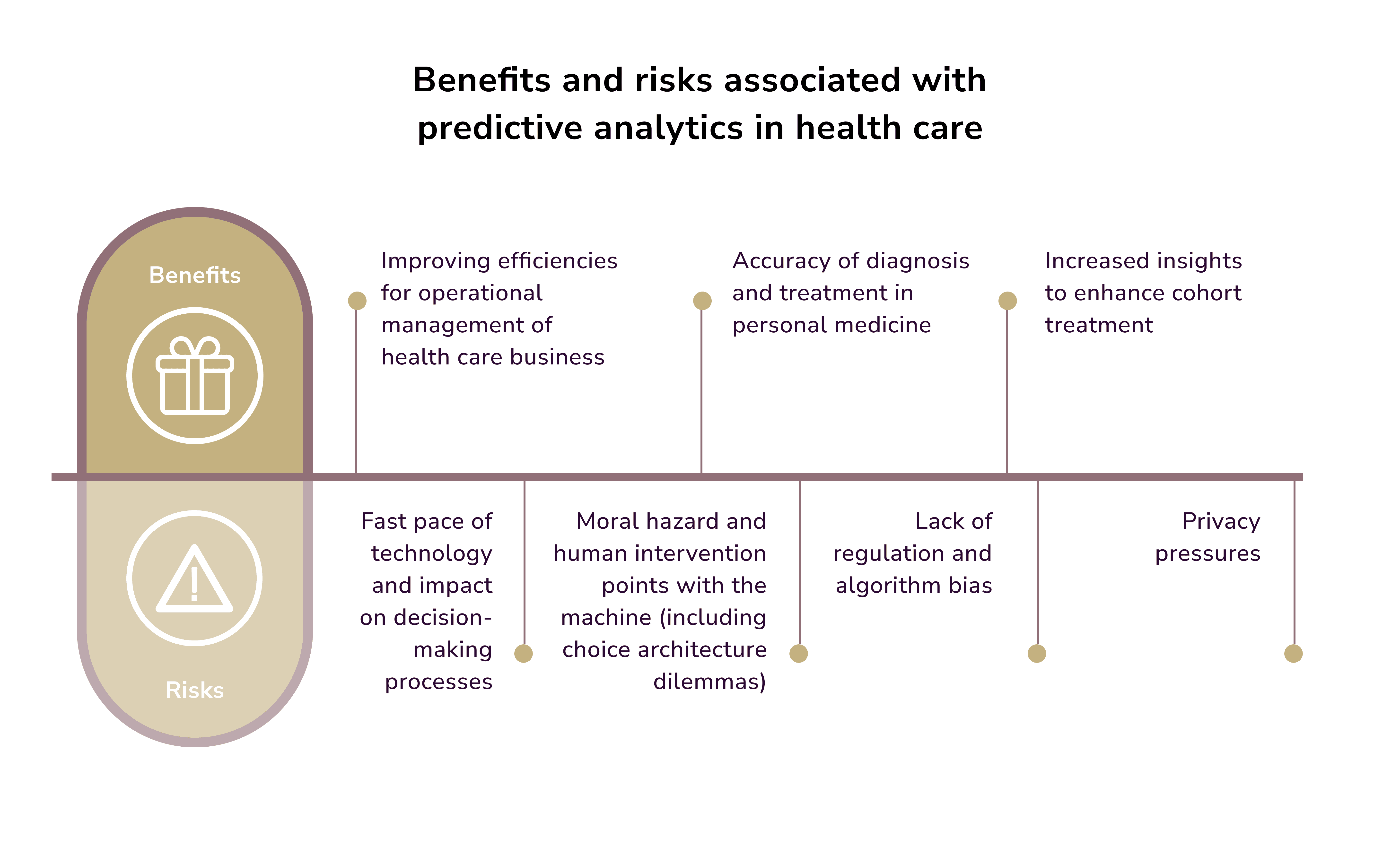
AI predictive analytics examples:
- The University of California found that AI could help forecast sepsis. Their AI model predicted sepsis with a 90% accuracy 48 hours before a physician did.
- Epic Systems utilizes AI-driven predictive analytics to enhance patient treatment outcomes.
- Researchers at Cedars Sinai trained a computer with 900 coronary CTA images. However, experts assessed these images prior. They thus enabled the AI to recognize and measure plaque levels.
AI in Mental Health
AI chatbots have emerged as a promising solution. They offer a mix of speed, anonymity, and scale that traditional mental health services often lack. These digital companions use advanced natural language processing. They engage users in empathetic dialogue. They guide users through emotional issues like anxiety, depression, stress, and low self-esteem.
A national US 2021 survey by Woebot Health 2021 revealed insights into mental health chatbot use.
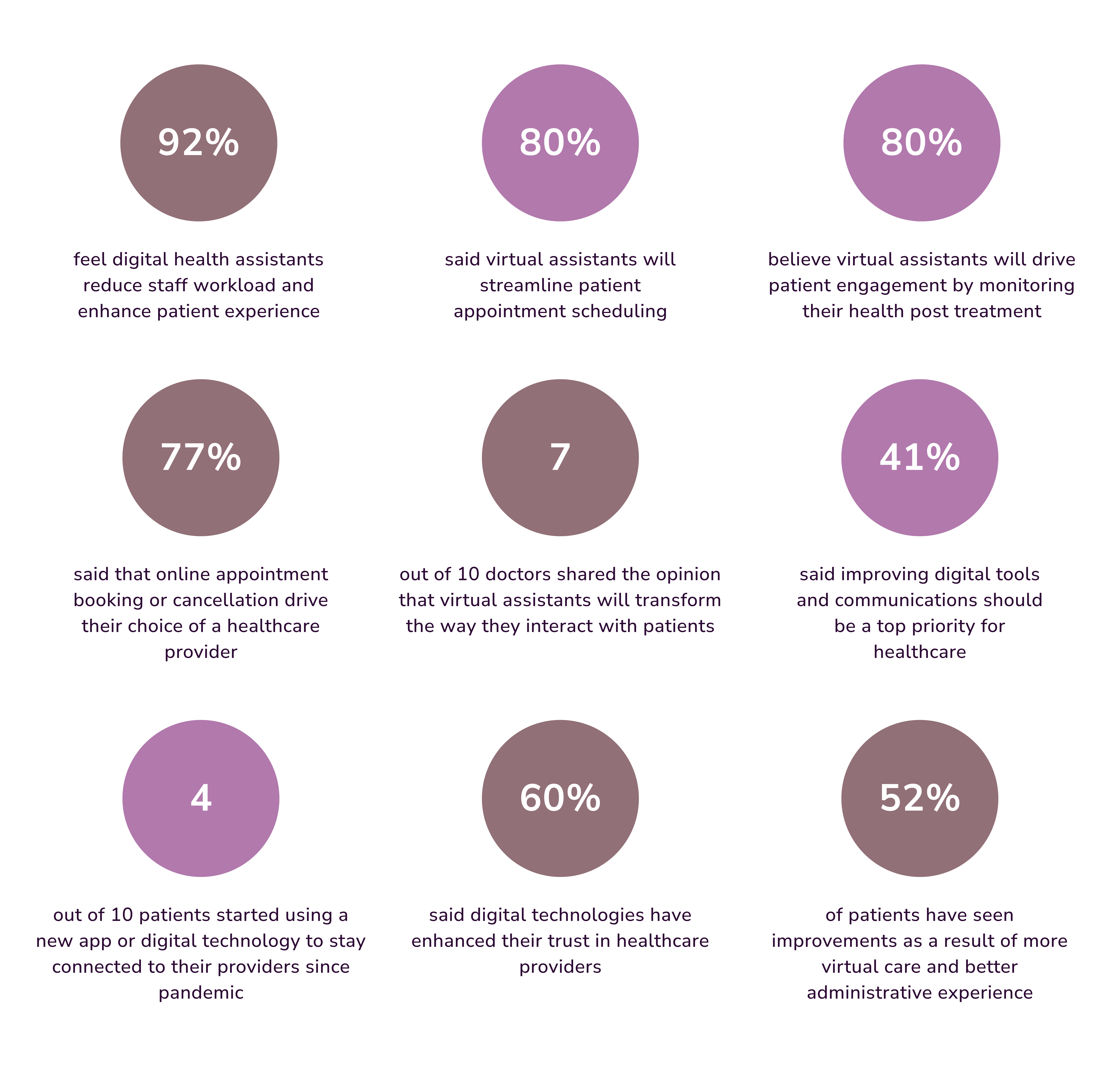
AI mental health examples:
- Ginger.io provides on-demand behavioral health analytics to deliver mental healthcare.
- Ellipsis Health uses AI to analyze vocal biomarkers for mental health assessments.
- Talkspace uses AI analytics in its online therapy platform.
AI in Gene Editing
Advancements in AI have led to the creation of blueprints for tiny biological tools capable of altering DNA. So, a future where scientists can cure diseases more quickly is possible today. This innovation leverages methods similar to those powering ChatGPT.
Also, AI-driven techniques could reduce a major concern in gene editing: unintended off-target effects. These unexpected changes can have harmful effects. They raise ethical and safety concerns. AI's power lets scientists refine their methods. They can now target exact genomic locations and reduce risks. It boosts therapy's effectiveness and public trust in these new technologies.
AI gene editing examples:
- IBM's health division developed Watson for Genomics. It uses AI to scan scientific literature and genomics databases. This offers clinicians a curated list of treatment options based on a patient's DNA.
- CRISPR Therapeutics is at the forefront of utilizing AI for gene editing. CRISPR-Cas9 lets geneticists modify, remove, add, or change parts of the DNA.
AI in Fraud Detection
Combining machine learning and AI for healthcare can help detect fraudulent activities. This will facilitate assigning risk scores to insurance claims. It can analyze claims data to identify suspicious patterns that may suggest fraud. Then, it promptly flags potentially problematic claims before disbursing payments. This helps insurers avert financial losses and reduces the time spent on investigations.
AI use cases in health insurance and fraud detection examples:
- Change Healthcare AI algorithms scan millions of transactions to identify anomalies. They have helped hospitals reduce fraudulent losses by up to 40%.
- Harvard Pilgrim Healthcare uses Codoxo's AI solution to detect fraud. It effectively complemented its existing internal system.
- Healthcare Fraud Shield (HCFS) recently introduced FWA360Leads to identify fraud, waste, and abuse.
AI in Alert Management
Research at Mount Sinai Hospital found that AI alerts improved patient care. Care teams were 43% more likely to respond quickly to deteriorating patients. This led to a lower mortality rate. The AI alerts beat manual methods, like the Modified Early Warning Score, at predicting patient decline.
AI alert management examples:
- Philips IntelliVue is a top-notch patient monitor. It uses AI to manage alarms in hospitals. With machine learning and AI for healthcare, critical and non-urgent alerts can be distinguished. Hospitals that implemented IntelliVue reported a 60% reduction in false alarms.
AI in Improving Population Health
AI can analyze vast datasets to solve complex health problems. For instance, digital twins can simulate crisis scenarios to enhance preparedness and management. Scientists can create digital duplicates of the entire healthcare facility and its operations. This can help tackle various issues troubling hospitals today, including but not limited to
- rising patient numbers
- increasing clinical intricacies
- outdated facilities
- space constraints
- longer waiting times.
Digital twinning can also work in human-related studies.
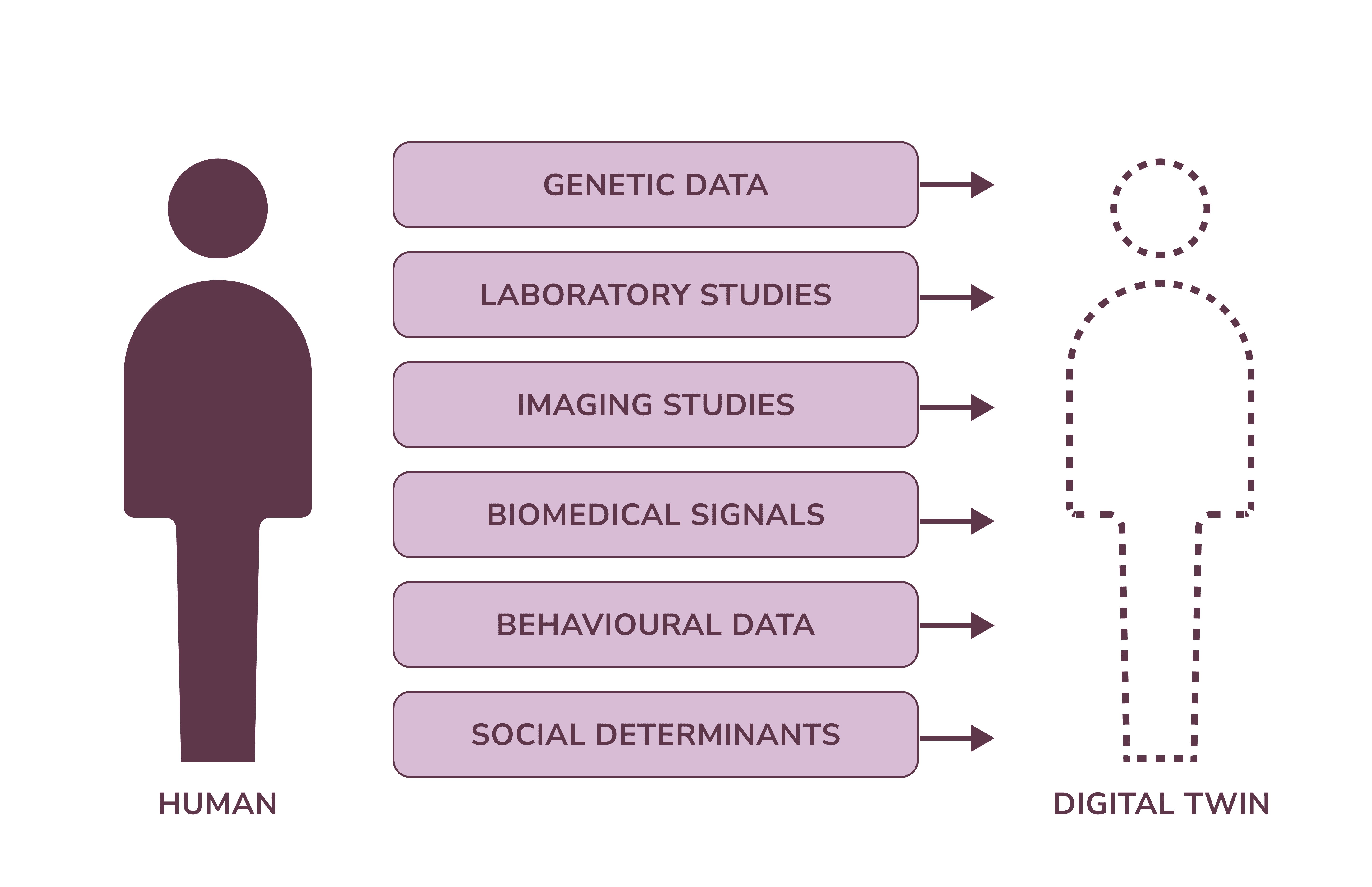
AI population health examples:
- Linguamatics, located in Cambridge, MA, employs NLP to sift through unstructured patient data. It finds key lifestyle factors and predicts patients at higher disease risk.
- Hortonworks assists in organizing and integrating billions of records. It enables pharmaceutical companies to conduct more effective clinical trials.
Virtual Assistance
Hospitals face rising patient volumes, staff shortages, and a need for cost-effective solutions. This is where AI-driven virtual assistants come into play. They offer a promising avenue to ultimately elevate the quality of care. One striking example is human-machine interfaces (HMIs). They interpret facial expressions, helping individuals with disabilities operate robotic vehicles and wheelchairs.
AI virtual assistance examples:
- Cedars-Sinai Hospital in Los Angeles uses Alexa robots. This virtual nursing assistant performs routine tasks.
- Sensely, a virtual nurse uses NLP and medical devices, like blood pressure monitors. It assists with self-care, offers clinical advice, and manages appointments.
- AI robots, like Paul, assist medical teams during patient rounds. They analyze records and quickly deliver needed information.
- Another robot, Maria, directs patients to hospital appointments using their medical ID cards.
- RUDO, an ambient intelligent system, helps blind people. It lets them work in fields like computer science by pairing them with sighted people.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Healthcare Systems
There’s often a belief that AI is ready for adoption, but that’s not necessarily the case. It may be fine for tasks like weather prediction. But, its use in health care can have life-altering effects. In 2016, Geoffrey Hinton, known as the "godfather" of AI, made an interesting statement. He predicted that radiologists would become obsolete, like typesetters and bank tellers. He claimed that people should stop training radiologists. Within five years, he predicted, deep learning will do that better.
Yet, over five years later, radiologists are still being trained to read scans. Medical experts say AI has not met its high hopes. Health systems are not ready for such technology. Furthermore, the government's regulatory response is still developing.
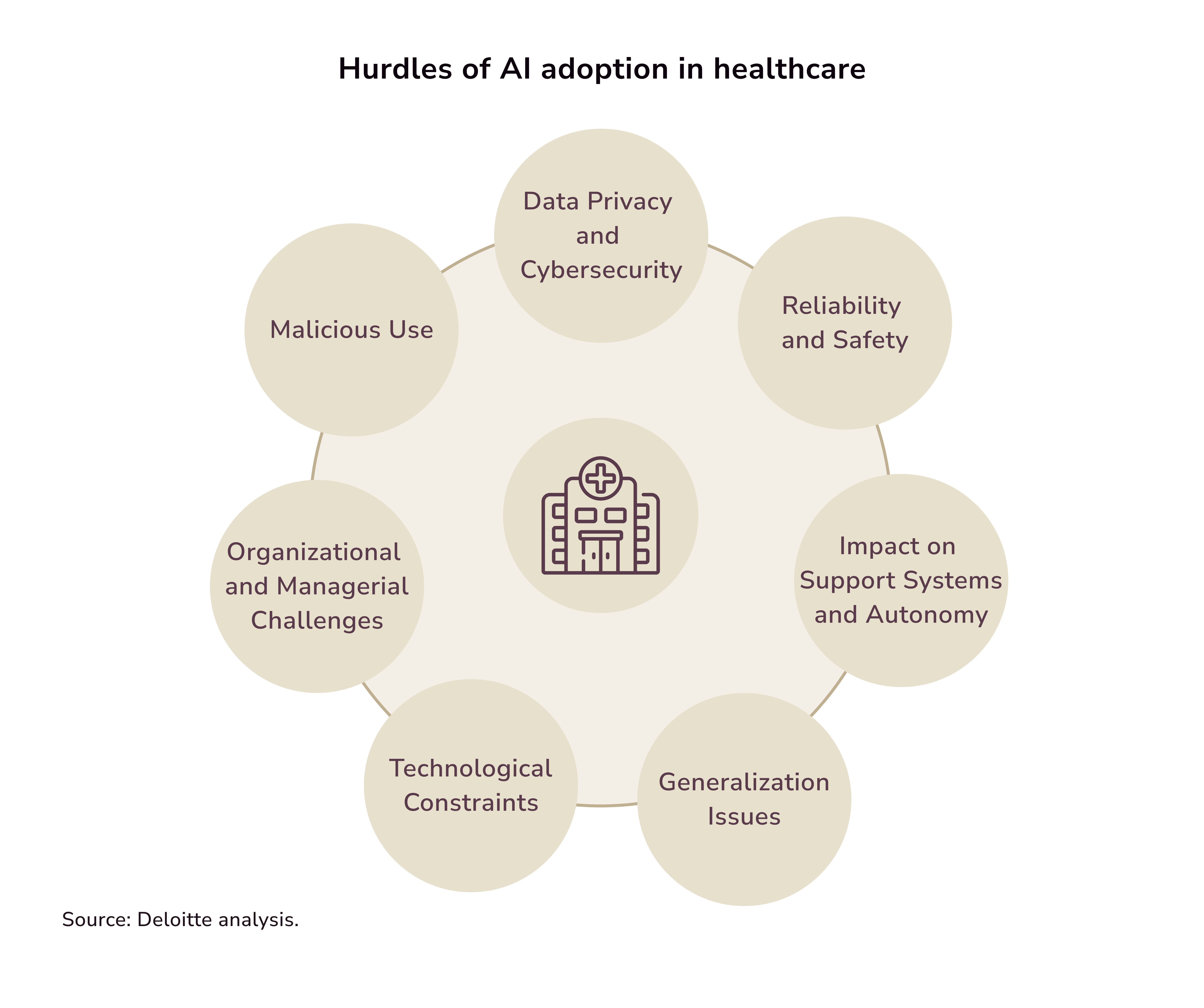
Ethics Issues with AI in Healthcare
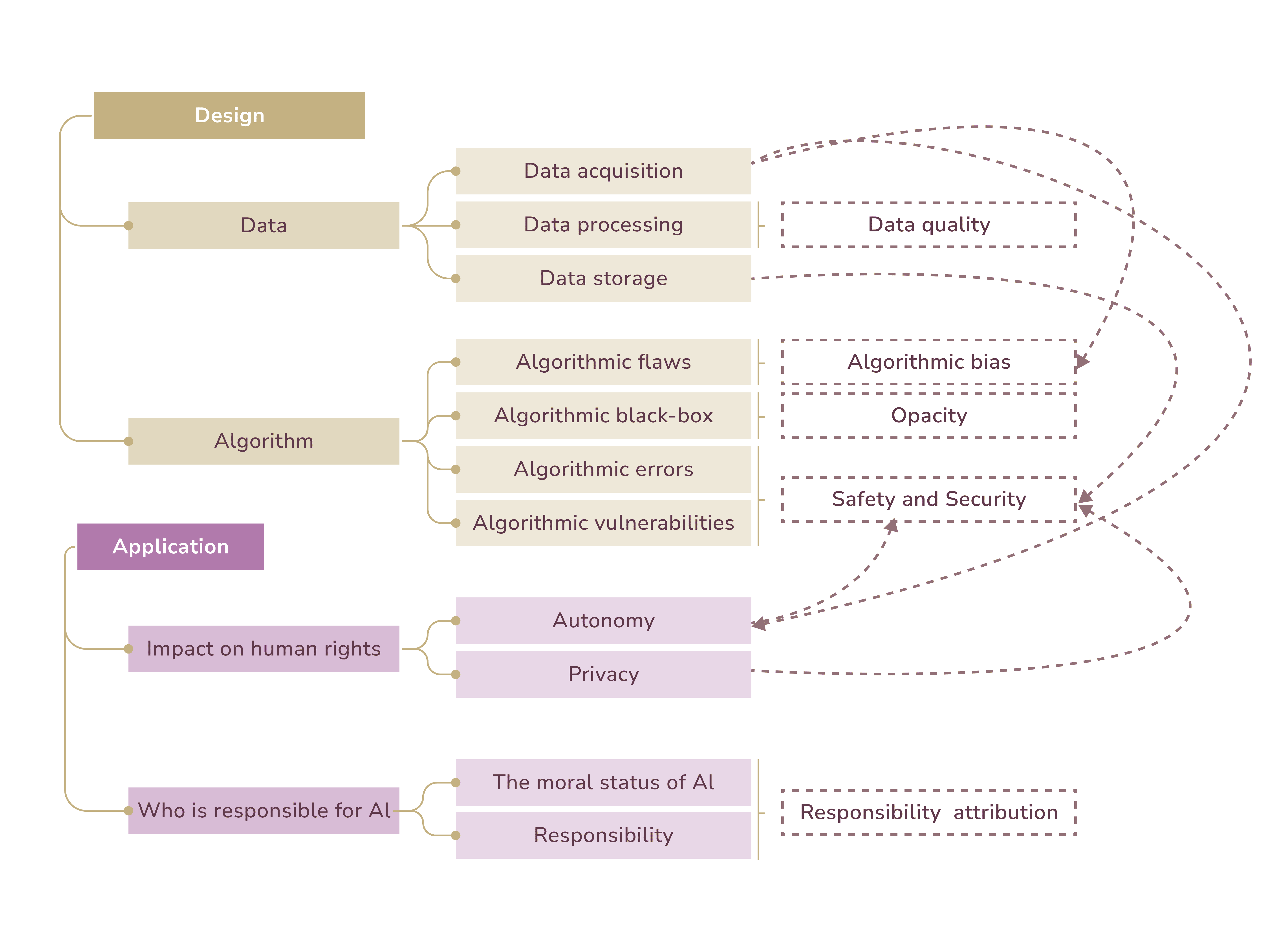
As we near this tech revolution, we must view AI in healthcare with a socially conscious lens. BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making study examines problems with AI in healthcare. The study outlines values, principles, and norms for deploying AI in healthcare.
The study highlights five key areas that affect the trustworthiness of medical AI:
- Data Quality: AI effectiveness depends on high-quality data from trustworthy sources. These may include medical literature, clinical trials, and smart devices. IBM's Watson for Oncology faced criticism for using hypothetical training data. Because the company used bad sources, their treatment recommendations were unsafe.
- Algorithmic Bias: Biases can enter AI systems from human input. Developers may inadvertently embed personal biases, which can be amplified over time.
- Opacity: Opacity arises from trade secret protection, employee knowledge gaps, and inherent complexity.
- Safety and Security: AI in healthcare still raises many concerns. These primarily relate to errors, cybersecurity threats, and lack of rigorous testing.
- Responsibility Attribution: AI's role in healthcare shifts traditional patient-doctor dynamics, complicating ethical responsibility.
To eliminate the disadvantages of using AI in healthcare, WHO proposes to follow these principles:
- Safeguarding Human Autonomy: Ensure humans control healthcare systems. Prioritize privacy and require patient consent.
- Advancing Well-being and Safety: AI developers must comply with safety and accuracy regulations.
- Ensuring Transparency: Publicly document AI information prior to design or deployment.
- Encouraging Accountability: Stakeholders must ensure AI is used correctly.
- Promoting Inclusiveness: Develop AI for fair access across demographics.
- Fostering Sustainability: Regularly evaluate AI for environmental efficiency.
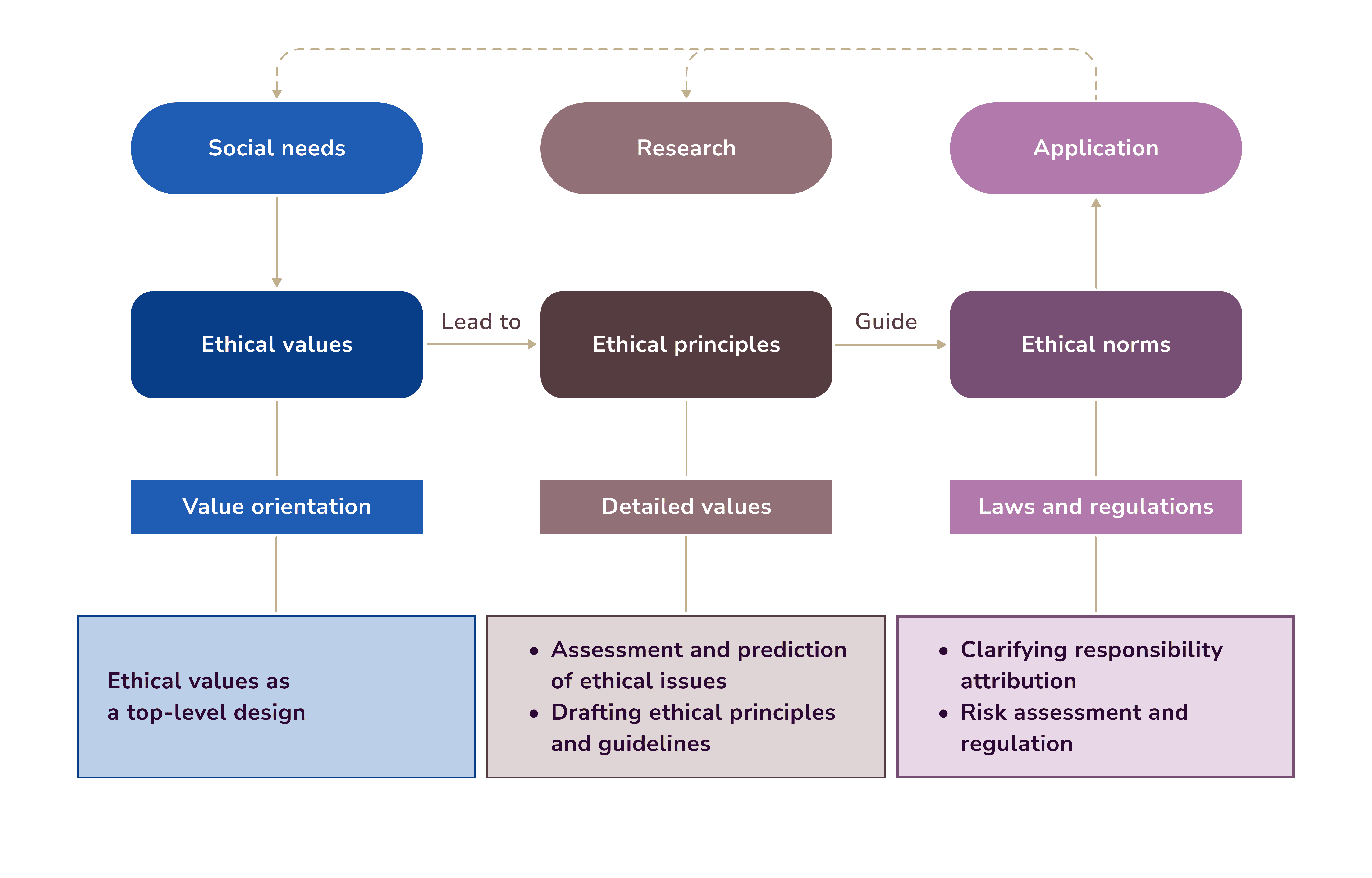
The ethical governance system by BMC looks as follows:
Top AI Healthcare Companies
The market cap of AI medical AI startups and investments peaked in 2021. It is projected to rise from USD 15.1 billion in 2022 to an estimated USD 355.78 billion by 2032.
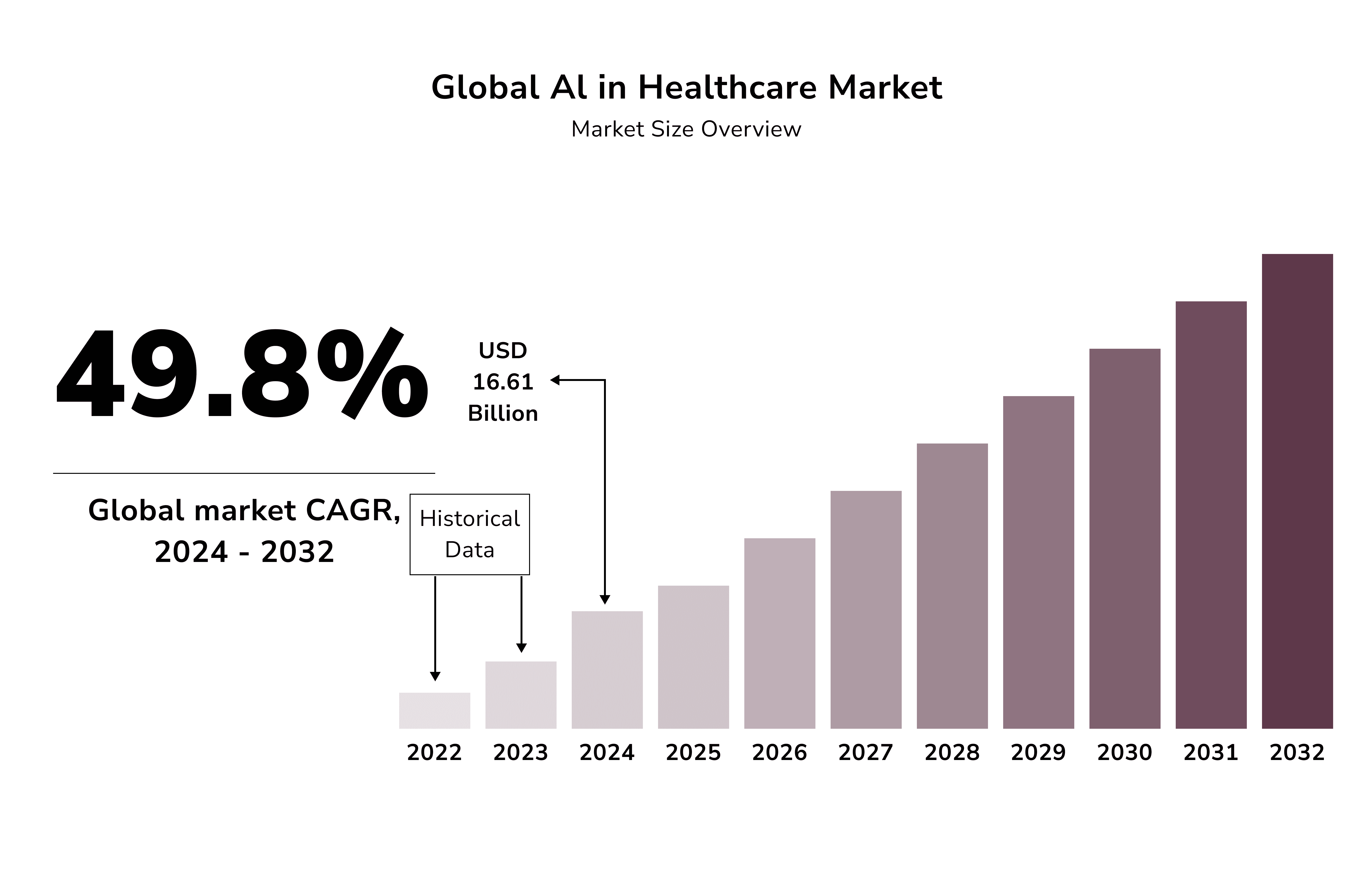
Let’s showcase the sector's vibrant and innovative spirit. Here are some of the leading healthcare AI companies.
- H2O.ai. With the University of California, H2O.ai has developed powerful AI algorithms. They can manage the 1.4 million patient referrals and documents. UCSF’s health system receives this data annually.
- PathAI created PathExplore. It delivers high-resolution tumor microenvironments from H&E whole-slide images. PathAI has also partnered with FNIH to advance mucosal healing research using AI.
- Viz.ai. Viz.ai uses a vast library of scans to compare a patient's brain image against a database. It identifies patterns and provides insights to detect early stroke signs. Medical professionals can access these images via AI-powered mobile apps.
- Healthcare Fraud Shield (HCFS). The new FWA360Leads tool helps health insurers. It provides insights to find risky cases and save costs.
- NVIDIA for Healthcare. In 2024, NVIDIA launched 25 microservices in its AI Enterprise software. These tools enhance medical imaging, natural language understanding, and drug discovery.
Harnessing big data and AI is critical in healthcare. The application market is predominant in the following industries:
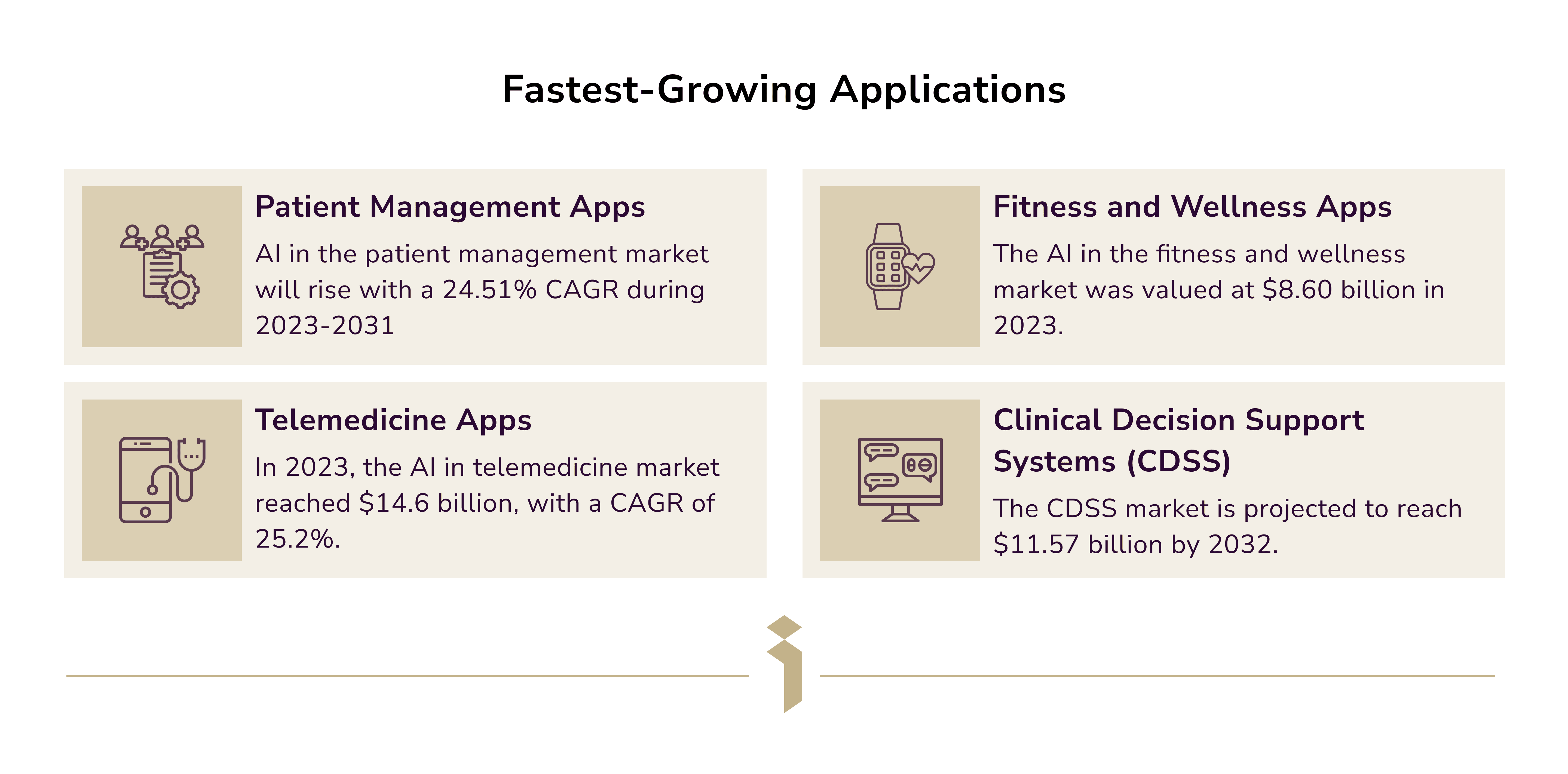
As we can see, proactive AI development in healthcare is on the rise.
Examples of Leading Healthcare Organizations Using AI
Radiology is where AI shines. The Mayo Clinic is testing an algorithm in a clinical trial. It aims to simplify the complex task of planning surgery for intricate head and neck tumors. Oncologists and physicists are involved in this work. According to John D. Halamka, president of the Mayo Clinic Platform, this algorithm can reduce human effort by 80 %. This technology gives doctors a plan to review and adjust. They don't need to do the basic physics themselves.
There are other notable successes as well:
- Ochsner Health in Louisiana made an AI model. It detects early signs of sepsis, a severe reaction to infection. To encourage nurses to use the system, they formed a response team. It would monitor alerts and act on them.
- In the UK, Alder Hey Children's Hospital uses AI virtual assistants. They answer parents' questions and provide real-time updates on their child's condition. This reduces anxiety during hospital stays.
- In the US, Mount Sinai Health System uses AI to improve its emergency department workflow. AI analyzes patient data and predicts arrivals. It helps manage staffing and resources, ensuring timely care.
- Meanwhile, Zhongshan Hospital in China has used AI-guided robots for surgery. They help surgeons do complex procedures with precision. This minimizes risks and improves recovery times.
- Cleveland Clinic uses AI chatbots to improve patient interactions. They answer questions and schedule appointments quickly. It improves the patient experience and saves healthcare professionals' time.
- IBM Watson Health works with hospitals worldwide. They develop AI solutions for drug discovery and disease management. They aim to use AI to speed up research. This will bring life-saving treatments to market faster.
FDA-approved AI Algorithms
On October 19th, the FDA released its 2023 list of authorized AI medical devices. This year saw an addition of 171 new devices, marking a 33% increase over the past year. Despite a growing interest in using generative AI in medical tools, no FDA-approved devices currently use GenAI or LLMs.
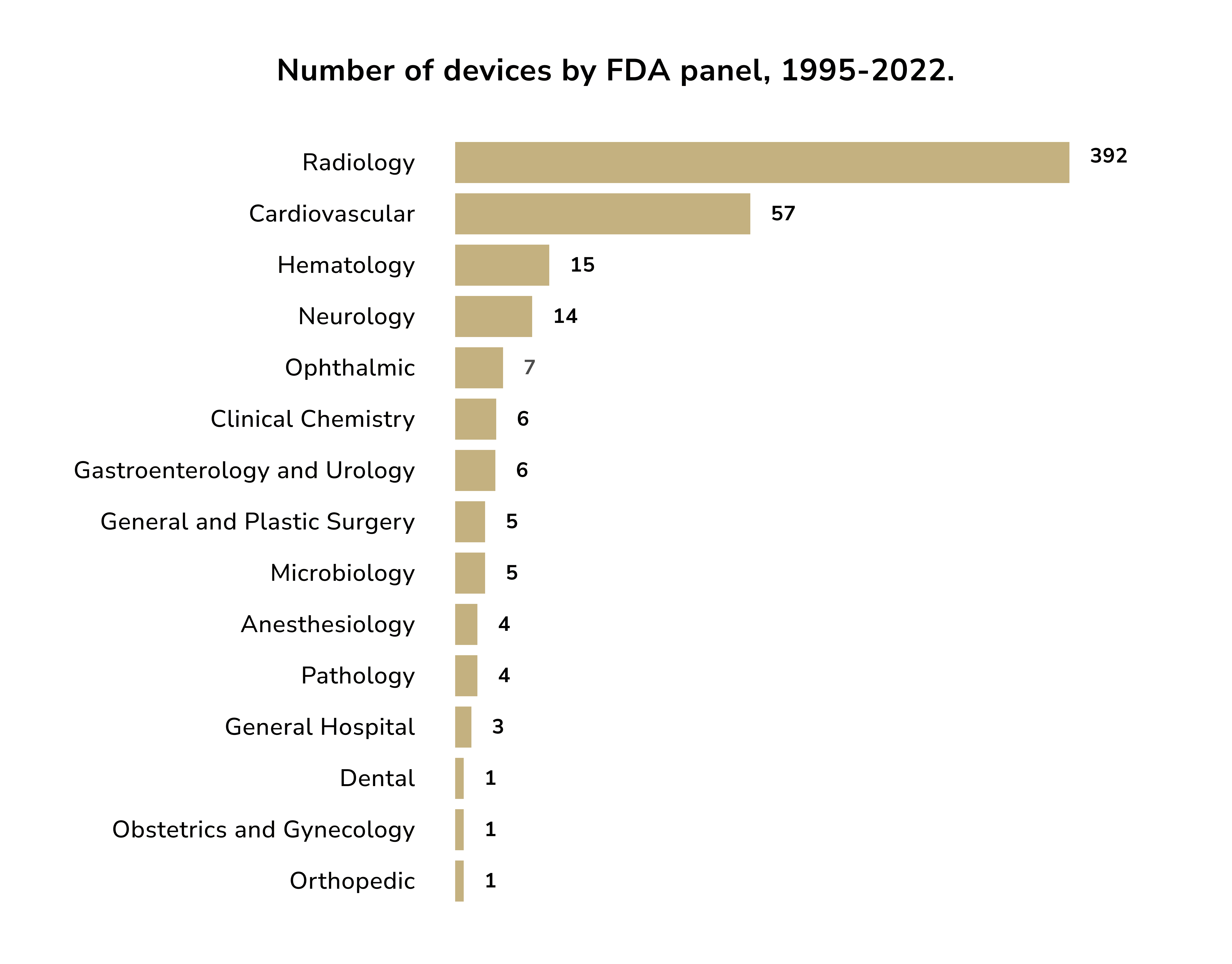
The FDA list includes 692 devices:
- Radiology: Comprising 77% of the list with 531 devices.
- Cardiovascular: Making up 10% with 71 devices.
- Neurology: Accounting for 3% with 20 devices.
- Hematology: Representing 2% with 15 devices.
Nota bene: FDA-authorized devices likely are a small portion of AI tools for healthcare. This is because most automated learning applications don't necessitate regulatory review. For instance, predictive tools, including some computer vision models, don't require FDA approval.
Clinical Validation
Researchers at the UNC School of Medicine analyzed data on 500 AI medical devices. They found that nearly half of the FDA-authorized tools lacked public clinical validation data. Despite claims by manufacturers, AI tools for healthcare are untested. Their clinical efficacy has not been evaluated using actual patient data.
The implications of these findings are manifold. First, it’s clear that mandatory clinical validation studies need to go public before FDA approval. It would build trust in AI among healthcare providers and patients. This research also urges the medical device industry to account for their product claims. AI healthcare startups can boost the integrity of their devices by rigorously validating them. Making the results public would be a big plus.
In short, healthcare startups should aim toward creating a culture of evidence-based practices.
What is the Future of AI in Healthcare
The future of AI in medicine is undeniably intertwined with a shift in patient care. As AI improves, it will play a bigger role in preventive care, diagnosing, and treatment. The ongoing trend toward cloud connectivity pushes collaboration between AI companies. This will help set clear guidelines for smart data processing to further foster AI acceptance. These advances have deep implications. They can improve health and promote health equity.

Victoria Melnychuk
Other articles