Exploring the Potential of AI in Fintech

Ever since the COVID-19 pandemic, the world still can’t come to its senses. But it did speed up innovation in those industries that had to adapt to new demands. For instance, the financial sector saw a 72% surge in FinTech app use since the black swan entered the arena (Fintech Magazine, 2020). This change is not merely a response to a global crisis. It marks a seismic shift in how consumers use financial products, stretching the boundaries of innovation.
In this article, we’re looking at how fintech solutions development with AI is emerging at the forefront of this evolution.
AI in Fintech: Market Overview
AI in fintech is the use of artificial technologies to make financial services smarter and more secure. Business analytics and reporting hold a 34.1% market share (Dimension Market Research, 2024). They are key market drivers. And it's no surprise. Data analytics is crucial for businesses today. Companies rely on informed decisions. They use the four pillars of analytics: descriptive, diagnostic, predictive, and prescriptive. The end result is:
- better financial products
- more sustainable services
- improved resource use
This will lead to data-driven strategies.
A KPMG survey found that 46% of financial execs say their productivity expectations have been surpassed. And 45% of respondents say their employee happiness has improved more than expected. This might provide them a major edge in the current struggle for industry talent (KPMG, Issue #65, 2024).
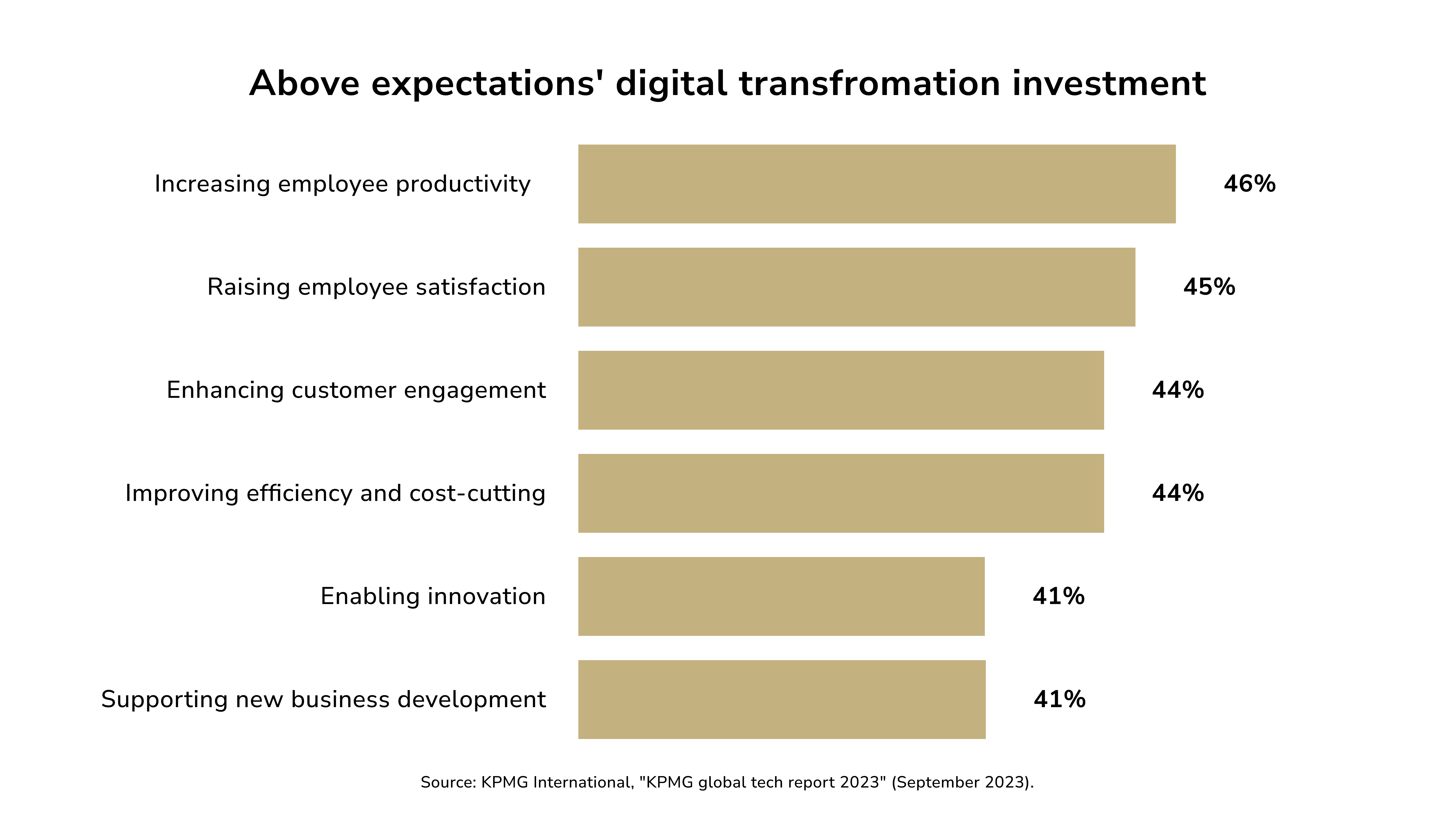
Financial enterprises have long been striving to automate processes. Both AI and ML help banks handle consumer data processing. For instance, monitoring for regulation compliance. This involves transaction and customer data analysis. AI systems help ensure that financial services comply with the law. This reduces the risk of penalties.
Other drivers for the AI and fintech merge include:
- mPOS, cryptocurrency, and mobile wallets have saturated finance. Now, more banks are using AI to improve security, efficiency, and customer experience.
- Users want fast, easy, advanced online payment solutions for small transactions. AI in fintech saves the day. It enables quick, secure, and user-friendly online banking.
- The mobile banking landscape is competitive. It fuels innovation in banking and finance. AI-powered mobile banking solutions increase customer loyalty, helping the market grow.
- R&D-driven tech helps companies improve their solutions. With more scrutiny on data privacy and usage, we expect more secure, user-friendly interfaces.
- AI integration improves services. Using AI in fintech speeds up problem-solving and personalizes customer experiences.
Market Statistics
The Future Market Insights says the global market of AI in fintech will grow from $13.5 billion in 2024 to $58.7 billion by 2034. That’s a 15.9% annual growth rate. Some key players include IBM, Intel, Narrative Science, and Microsoft.
The Fintech Futures’s study of AI possibilities in fintech holds important insights:
- AI solutions lead the type segment with a 78.1% market share in 2024. They succeed by using easy-to-apply tools. These include robotic process automation (RPA), machine learning, NLP tools, and predictive analytics. For example, RPA reduces the time to process mortgages and insurance claims.
- On-premise solutions lead the deployment segment. They help meet strict organizational requirements. They excel in security, regulatory compliance, compatibility with legacy systems, and customization.
- In 2024, business analytics and reporting apps will have a 34.1% market share, making them the top app segment. They help firms make smarter decisions, work more efficiently, and stay au courant with regulations.
- Regional analysis shows North America’s undeniable dominance. The region's fintech and AI firms drive faster, better innovation.
What Does AI Mean to Fintech?
AI fosters digitization by offering insights into innovation and the creation of new products and services. AI, by automating back-office tasks, boosts efficiency and cuts clerical costs.
Fintech solutions development with AI tackles different challenges. It can provide tailored financial advice, spot fraud, score credit, and automate tasks. It leads to benefits like higher efficiency and lower costs. AI also boosts accuracy, security, and customer experience.
Who Needs AI in Fintech?
With AI, banks and financial institutions can now tap into new data sources. They include utility bills, social media, and other data to assess creditworthiness. This means that those excluded from traditional finance can now be considered for loans and other financial products.
In addition to this, AI helps financial service providers cut costs via automation. For instance, ML improves KYC and CDD. It automates customer identity checks and provides precise risk assessments. This leads to lower fees and interest rates, making financial services more affordable and inclusive.
AI tools help with budgeting, saving, and investing. They help users make smarter financial decisions. These tools are beneficial not only for end-users but also for financial advisors.
Here’s a short list of who in fintech and fintech-related fields needs AI and how they can benefit from it:
- financial Institutions for fraud prevention and better customer support
- investment firms and asset managers for algorithmic trading and sentiment analysis
- insurtech companies for claims automation and predictive analytics
- regulatory bodies for real-time monitoring and risk assessment
- consumers for robo-generated advice and personal finance management.
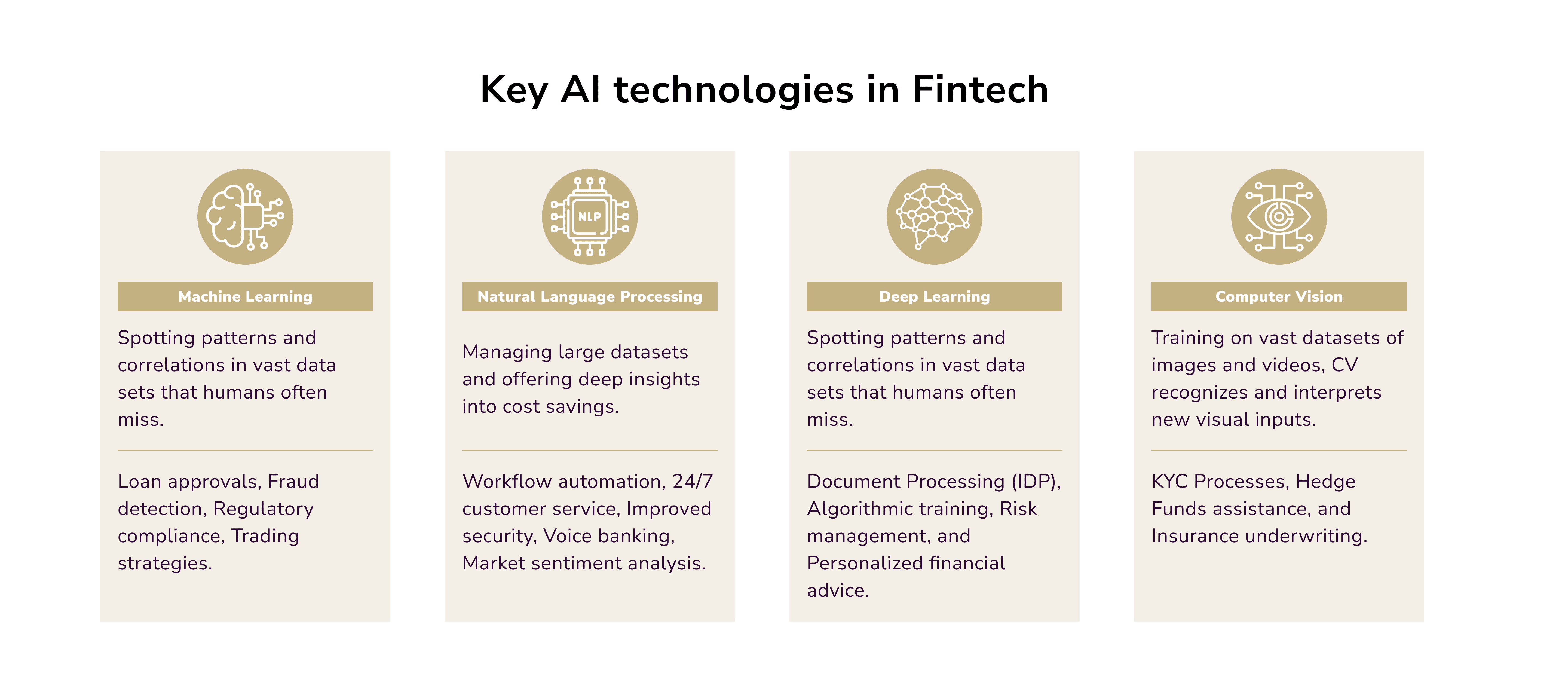
Key AI Technologies in Fintech
Let’s uncover the four important AI subsets are what they bring to the table.
Machine Learning in Fintech
ML algorithms excel at identifying patterns that humans often overlook. The technology finds links in vast sequences and events. It extracts crucial information from large data sets. This helps fintech companies to spot new business opportunities and develop sounder strategies.
The top three uses of ML in fintech include:
- Loan approvals: traditional models use FICO scores and income data. ML looks at more factors, like social media activity, utility payments, and even health records;
- Fraud detection: ML analyzes transaction data in real time. It can detect fraudulent activities and continuously update its models;
- Regulatory compliance: cloud-based platforms equipped with ML can automatically track regulatory changes. They then ensure that all transactions meet the latest standards.
Natural Language Processing in Fintech
In Fintech, NLP primarily serves to understand human speech and meaning extraction. This further entails discovering purpose and developing a suitable claim response. By means of pattern recognition (text mining), NLP transforms unstructured data in databases and texts into structured data. It then generates pertinent insights.
The top three uses of NLP in fintech include:
- Workflow automation: NLP fosters tasks like document processing, data entry, and data validation. It also speeds up customer onboarding by verifying their info and identities;
- 24/7 customer service: NLP-powered chatbots and virtual assistants provide unstoppable client support. They handle routine queries and assist with simple questions;
- Improved security: by quickly spotting fraud, banks can protect their customers and themselves.
Deep Learning in Fintech
At its core, DL uses layers of connected “neurons.” They process input data just like human neurons transmit signals. These networks are trained to automatically learn representations and features from raw data. Unlike experience-dependent ML approaches, they avoid manual feature extraction.
The top three uses of DL in fintech include:
- Intelligent document processing: DL creates synthetic documents. They closely mimic real ones in structure and content. Being robust and adaptable, DL models manage a wide array of document types and scenarios;
- Using synthetic data to train models: it allows for safe, thorough testing of financial apps. It also helps IDP systems to continuously evolve and adapt to new document formats;
- Adaptive algorithms for continuous improvement: these enhance fraud detection and risk management. Researchers improve their precision and effectiveness as they process more data.
Computer Vision in Fintech
Computer vision helps machines understand and interpret media files like photographs and videos. Using images from cameras and DL models, machines can recognize and categorize objects. Then, they can respond to what they “see.”
The top three uses of CV in fintech include:
- KYC: companies can let users register via selfies or video calls, bypassing lengthy verification;
- Digital codes: CV allows for a cardless ATM experience using machine vision. This innovation helps mitigate fraud risks associated with card theft;
- Assisting hedge funds: CV uses old images and economic trends to make accurate forecasts.
The Benefits of AI in Fintech
A KPMG poll of bank technology leaders found that AI and automation boost employee satisfaction. So the market of fintech solutions development with AI primarily focuses on automation. Most banks see this as their biggest benefit. KPMG professionals spoke with staff. They are happy about the AI-enabled, automated customer service. Others claim working on higher-value projects and jobs inspires them.
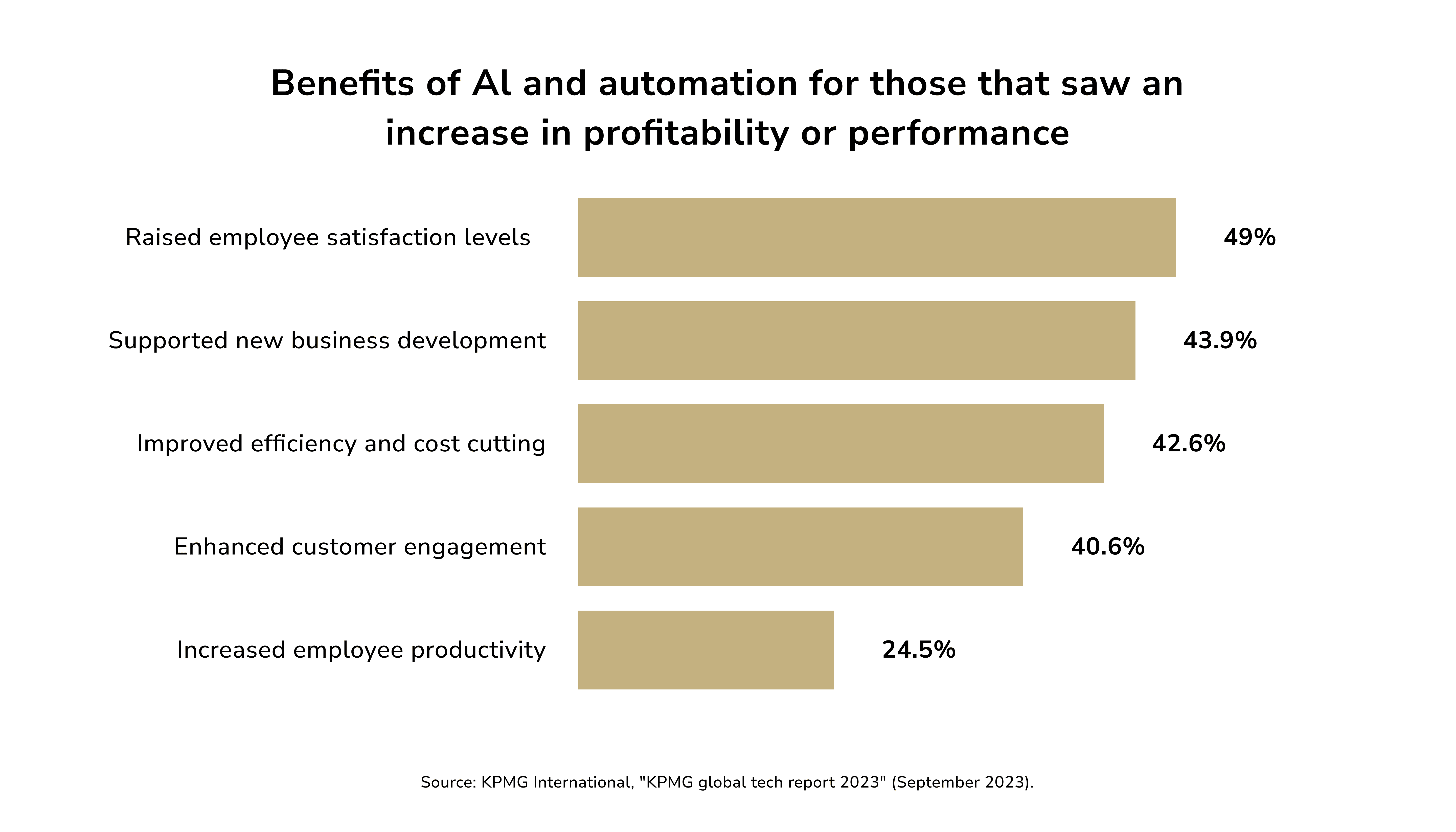
AI improves fintech on many levels. We will discuss the most evident ones.
More Accessible Financial Services
Traditional credit scoring models label 1.5 billion people “unbanked.” This is due to static variables and historical data. Traditional models use these to define a borrower’s creditworthiness. AI analyzes data like total income and credit history. It also looks at transaction patterns, work experience, and other factors. The statistical model processes data, resulting in personalized scoring. This can potentially enable more individuals to access financial services.
Better Fraud Detection Strategies
As of today, fintech AI development services primarily focus on fraud detection. AI systems use RNNs to detect anomalies. They monitor transactions and user activities, flagging any deviations from normal behavior. This includes changes in location, transaction frequency, amounts, and payee details. Advanced AI models integrate techniques like neural networks, fuzzy logic, and Bayesian filters. They use hundreds of risk indicators. These include IP addresses, device fingerprints, and user behavior traits. All to accurately identify potential fraud. Also, AI reasoning helps detect fraud, assess credit risk, and optimize trading strategies by analyzing financial patterns and predicting outcomes.
Note: RNNs, like feedforward and CNNs, learn using training data. What sets RNNs apart is their “memory” capability. They use information from previous inputs to affect later inputs and outputs. Unlike traditional deep neural networks, RNNs’ outputs depend on earlier inputs. The networks treat inputs and outputs as independent.
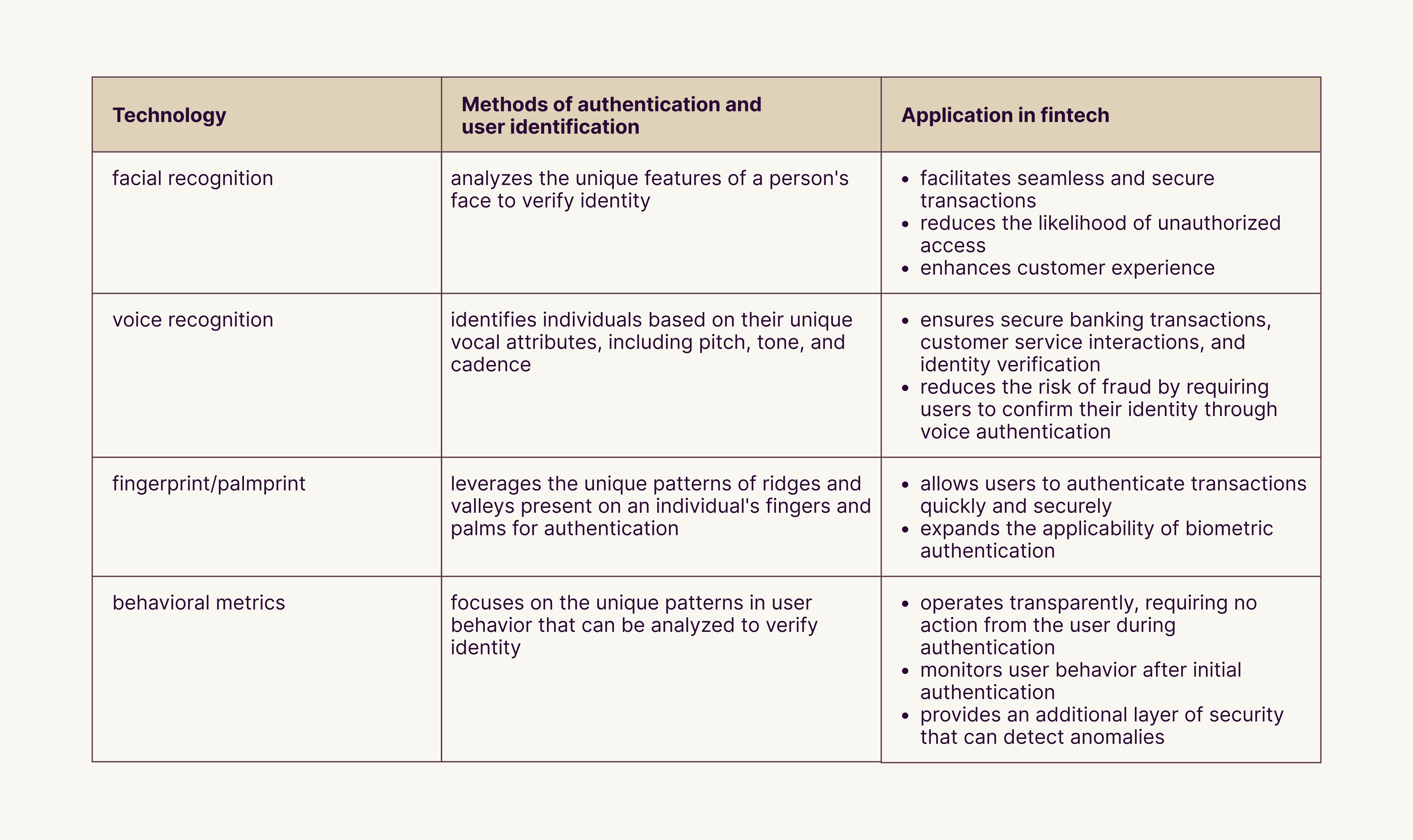
AI is also pivotal in developing biometric security solutions within the financial sector. See the table below to understand how biometric technology works.
Automated Customer Service
Utilizing chatbots has become the norm, and not only within financial services. These AI-based digital assistants provide unstoppable expert-level support. They may help navigate banking services, optimize user data, and offer personalized CTAs. AI chatbots fintech companies use save time and money while improving the quality of customer service.
Note: Bookkeeping and accounting tasks involve a lot of data. Plus, they are prone to human error. By automating these processes, AI can ensure more accuracy. This, in turn, gives employees more time to concentrate on other tasks. See the table below to understand the AI value for each separate process.
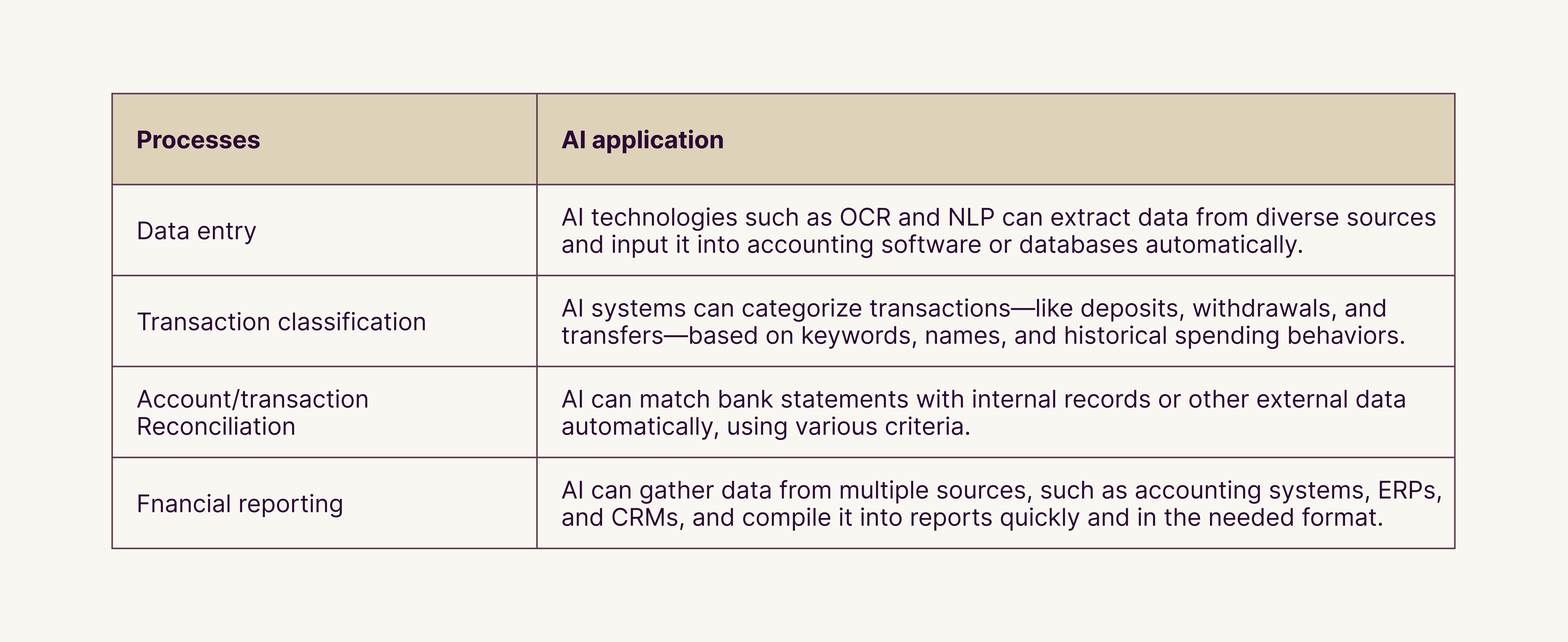
Faster User Behavior Analysis
AI provides deep insights into customer data through AI APIs. For instance, if a customer requests their monthly expenses, the tech expects follow-up questions. It then delivers comprehensive responses in a single interaction. This analysis cuts system load and boosts customer satisfaction by speeding up data retrieval.
More Precise Financial Forecasting
ML helps predict market indicators, asset prices, and consumer demand. All are vital for strategic decisions.
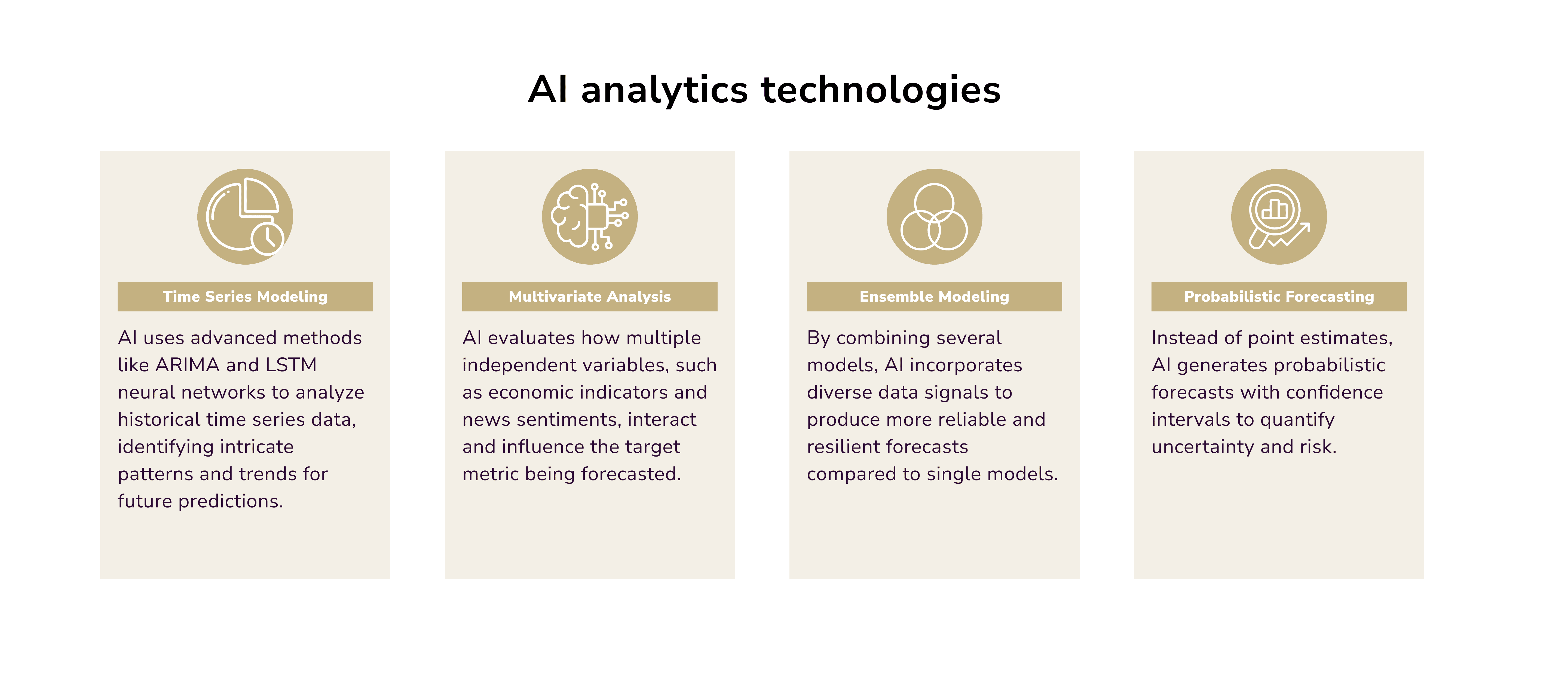
For instance, Upstart uses advanced ML models to find links in borrowers’ data. This includes unusual ones, like their education, field of study, and GPA. It uses these to evaluate creditworthiness. This approach enhances credit accessibility for everyone and ensures fair pricing.
Similarly, ZestFinance utilizes AI to analyze alternative data, focusing on thin-file borrowers. The technology develops customized underwriting models. These can identify the creditworthiness often overlooked by traditional scoring models.
The Challenges of AI in Fintech
AI still faces certain growth restraints despite its undeniable importance to financial institutions. The most pressing ones are:
- data privacy: 2024 marks the rising awareness among consumers about their data privacy rights. AI’s impact on privacy is now in the spotlight. It forces companies to adapt to stricter regulations;
- fairness and bias: these issues extend societal inequalities and minority discrimination. Yes, Google AI shares best practices. IBM’s “Fairness 360” framework helps too. But, AI’s black box still puzzles stakeholders. Besides, biases in data used to train the model also lead to AI hallucinations;
- small talent pool: a Reuters study points out a 50% hiring gap for AI-related positions in 2024. The lack of AI specialists is considered to be a major business threat. It also slows down AI innovation and implementation. To address this skill gap, companies start to train new employees to use AI in their daily workflow.
- integration challenges: legacy systems and data silos often stay in the way of AI adoption. Scalability is another common block. Businesses should be equipped with robust infrastructure to manage the complexity and volumes of AI data.
Top 5 Examples and Use Cases of AI in Fintech
AI has almost limitless potential. But, we want to highlight five vivid examples of its use.
1. Fraud Prevention as a Service (FPaaS)
Cybercrime rates rise along with digital adoption. KPMG’s 2022 fraud outlook report says 77% of customers saw a rise in fraud. FPaaS can help firms deal with this issue. Utilizing predictive and prescriptive analytics, AI/ML models assess the riskiness of transactions.
A case worth noting is Vectra, which created Cognito — technology designed to detect and track cyber threats. The software leverages automation to:
- identify threats
- uncover hidden attackers
- accelerate event investigations
- detect compromised data.
Note: monitoring and preventing money laundering is a vital responsibility for financial institutions. AI can link seemingly unrelated entities and transactions, revealing complex money laundering networks. NLP helps match entities and identities across data sources. It works even with different spellings or aliases. This helps to detect criminal connections. AI screens customers and transactions against global sanctions lists in real time. It prevents interactions with bad actors. For example, HSBC used Google Cloud’s AML AI. It trained the AI on customer data. This improved its ability to detect suspicious activities better than manual systems. This AI has found 2-4 times more suspicious activity than the old system. It cut the number of alerts by 60%.
2. AI-Powered Chatbots for Customer Support
According to Juniper Research, chatbots in banking saved $7.3 billion in 2023. Here are two great examples of how they’re used in fintech customer support:
- Automated investment platforms, such as Betterment, leverage AI to supervise investments. These platforms review data and adjust asset procedures based on the financial objectives you set.
- Kasisto has introduced KAI, a conversational AI platform to improve banking experiences. Customers can enjoy self-service options and solutions. Meanwhile, banks reduce the volume of inquiries to contact centers. Meanwhile, AI-driven chatbots provide financial advice, promoting informed decision-making.
Generative AI in fintech is also gaining traction due to virtual assistant deployment. Notable AI in banking examples are Bank of America’s Erica, Capital One’s Eno, Wells Fargo’s Fargo, and Zara from Zurich Insurance.
3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
Fintech and banking organizations have always struggled with routine back-end tasks. RPA can automate and streamline these processes using “smart” chatbots.
Common tasks automated by RPA include:
- automating document verification
- KYC process
- information collection
- enhanced screening.
JPMorgan Chase’s virtual assistant simplifies global money transfers for corporate clients. It works with both routine payroll operations and large-scale mergers and acquisitions. The chatbot completed 360,000 hours of finance work in seconds, the company states.
4. Biometric Security
Methods like PINs, passwords, and security questions are vulnerable to hackers. AI can enhance security and authentication for tasks like onboarding and logins.
HSBC’s Voice ID is one of the best AI in banking examples. It allows access to phone banking through voice recognition. The system uses advanced voice tech. It authenticates users by their unique vocal traits. Meanwhile, Seven Bank plans to replace its ATMs. They will use ones that offer biometric authentication and QR code reading.
5. Personal Finance Management
AI uses algorithms to assess financial goals and risk tolerance. It then gives tailored advice. This makes advanced wealth management accessible to more people. This democratizes investments. It lets individuals improve their strategies. Many can now use methods once reserved for wealthy clients.
Wealthfront is one of the best examples of fintech companies that employed AI just right. The company uses AI for custom investment strategies and financial planning. Its minimum account requirement is just $500, which makes it highly accessible. The fees start at just 0.25% for most accounts, with no charges per transaction.
Top 5 AI Fintech Startups
Many AI fintech companies gained remarkable outcomes after they incorporated the technology. Seven of those caught our eye. Let’s plunge into their use of AI in finance.
1. Axyon
Axyon AI showcases the profound impact of AI on investment strategies. By focusing on DL, the firm provides advanced models. They help asset managers and traders make better investment choices. Axyon can process huge datasets to forecast market trends. This enhances clients’ understanding of the fast-changing finance sector.
2. Forwardlane
Forwardlane’s AI platform consolidates financial data and news. It delivers personalized investment insights and recommendations. This significantly enhances client engagement and satisfaction for wealth managers and financial advisors. It simplifies the investment process and delivers objective-specific advice.
3. Adyen
Adyen is a digital bank. It offers payment processing, point-of-sale services, card issuance, and analytics. The company uses AI for revenue, insights, and risk management. Clients like McDonald’s, Uber, LinkedIn, and Booking benefit from its all-in-one platform.
4. FlowFi
FlowFi uses advanced tech and a network of finance pros. It provides personalized financial services and advice. The platform uses AI and workflow automation to enhance efficiency. FlowFi serves over 50 venture-backed and traditional businesses.
5. Angle Health
Angle Health unifies fragmented healthcare benefits systems into one platform. It streamlines processes from instant broker underwriting to personalized care navigation for members. Angle Health’s application of AI in finance lies in real-time pricing and operational optimization.
What Fintech Niches Are Still Open for New Players?
The fintech products landscape has absorbed a myriad of opportunities from AI pioneers. Still, several niches remain ripe for disruption by new AI players. Prominent avenues for exploration of AI use in finance include:
- Many insurtech firms still use traditional systems for claims and fraud. AI risk assessment tools can analyze customer data. They can predict claims and offer personalized policies. AI can also streamline customer service with chatbots and automated claims submissions.
- RegTech solutions still depend on manual checks and rule-based systems. AI can automate compliance checks. It can spot suspicious transaction patterns. It can also predict regulatory changes. This helps financial institutions better manage compliance complexities, minimizing risks and operational costs.
- Community banks and credit unions use outdated systems. Their non-traditional banking services have seen little tech upgrade. AI can help these institutions. It can personalize banking services. It can automate back-office tasks. It can use data to improve customer engagement.
- P2P payment platforms in developing markets often act as basic transaction processors. AI can enhance these platforms. It can improve fraud detection, credit scoring, and user engagement. It can also tailor services using alternative data and behavioral analytics.
- Real estate crowdfunding platforms often rely on manual evaluations and paperwork. AI can transform this by using machine learning. It will analyze market trends, property values, and investment risks in real-time. Automated valuation models (AVMs) and predictive analytics enhance decision-making and streamline operations.
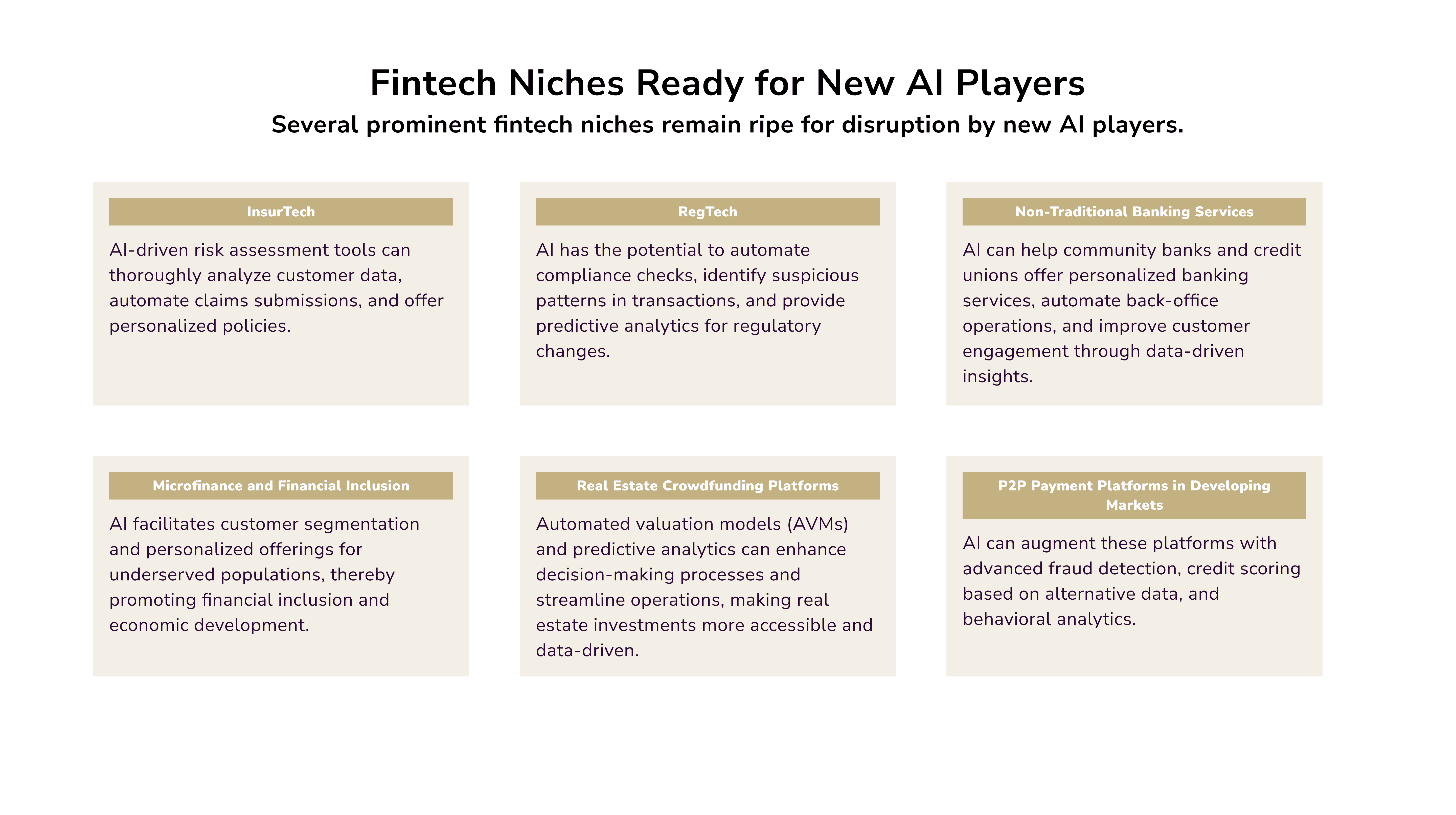
The Future of Fintech with AI
AI has granted fintech a perfect opportunity to evolve financial services. However, noteworthy innovations appear fast, so firms have to stay in the know. With LLMs, autonomous agents, and edge AI, we can anticipate further groundbreaking changes.
Key Trends to Watch
Here are the most vital trends to follow:
- autonomous finance where AI manages end-to-end decision processes with minimal human involvement
- hyper-personalized banking where AI assistants cater to individual contexts and needs
- AI-native fintech that alters traditional business models and makes financial services more accessible
- AI-driven predictive risk analysis and dynamic pricing tailored to individuals
- AI co-pilots enhance human expertise and skills across various financial roles.
Generative AI in Fintech
Generative AI (or GenAI) is the application of sophisticated ML models to produce new data sets, insights, or forecasts grounded on current financial data. These models can create synthetic data, automate client support, and improve decision-making procedures.
Note: fintech GenAI refines trading plans for high-frequency trading. High-frequency, low-latency trading strategies rely on workflows that run in milliseconds. They exploit tiny market inefficiencies to boost profits. Renaissance Technologies is in the spotlight for algorithmic trading. Its premier fund has a 66% annual return since 1988.
As per KPMG, AI contributions are most evident in corporate banking and risk analysis. Meanwhile, Gen AI could add $2.6 to $4.4 trillion a year. This is across 63 applications in various industries. The banking sector could gain $200 billion to $340 billion annually. This would be due to higher productivity. The increase equals 9% to 15% of the industry’s operating profits.
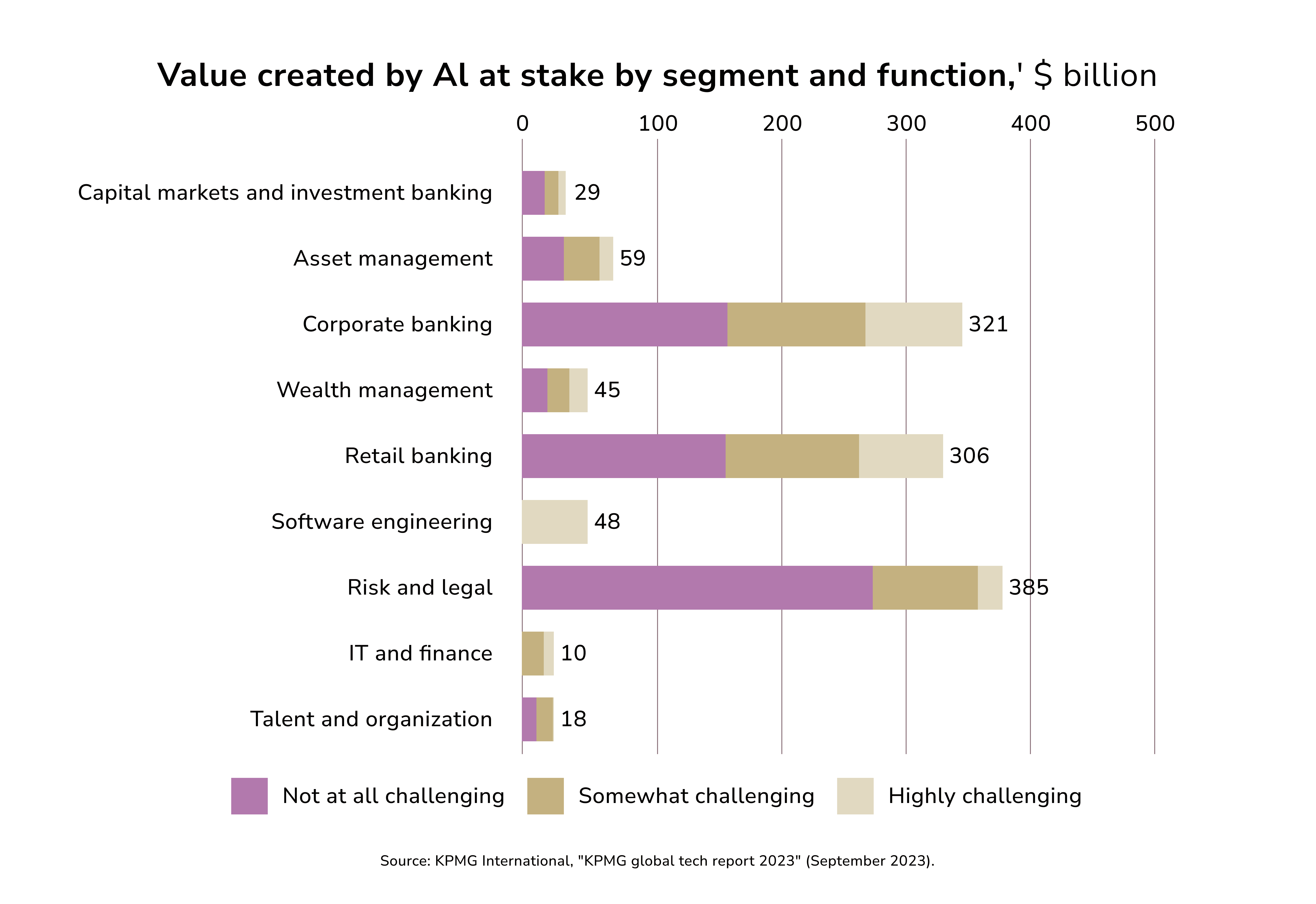
Gen AI Benefits for Fintech
The drive for AI innovation is not merely for its own sake. Businesses, particularly small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), face significant macroeconomic challenges. By improving payment experiences, SMEs can generate revenue that might otherwise be unattainable.
Gen AI can use data to improve payment experiences. It can recommend payment methods, update status, detect fraud, and boost loyalty.
In paytech, banks are increasingly embracing Gen AI. Especially those that use multi-cloud and hybrid multi-cloud models. This, in turn, gives companies that offer fintech AI development services a great push. Composable architecture lets payment firms innovate and go to market faster. It provides a flexible, agile tech stack. As SaaS-based composable architectures grow, the market expects a surge in payment innovation. Initiatives like the ISO 20022 migration and CBDC pilots are driving innovation. So are instant payment services.
Note: The main drive of AI in financial software development is to improve business operations. This is possible by creating more efficient and user-friendly payment methods. Merchants must build strong customer loyalty. It's key to boosting revenues and entering new markets. This loyalty comes from fast, seamless, and secure payments. They must cater to their preferences.
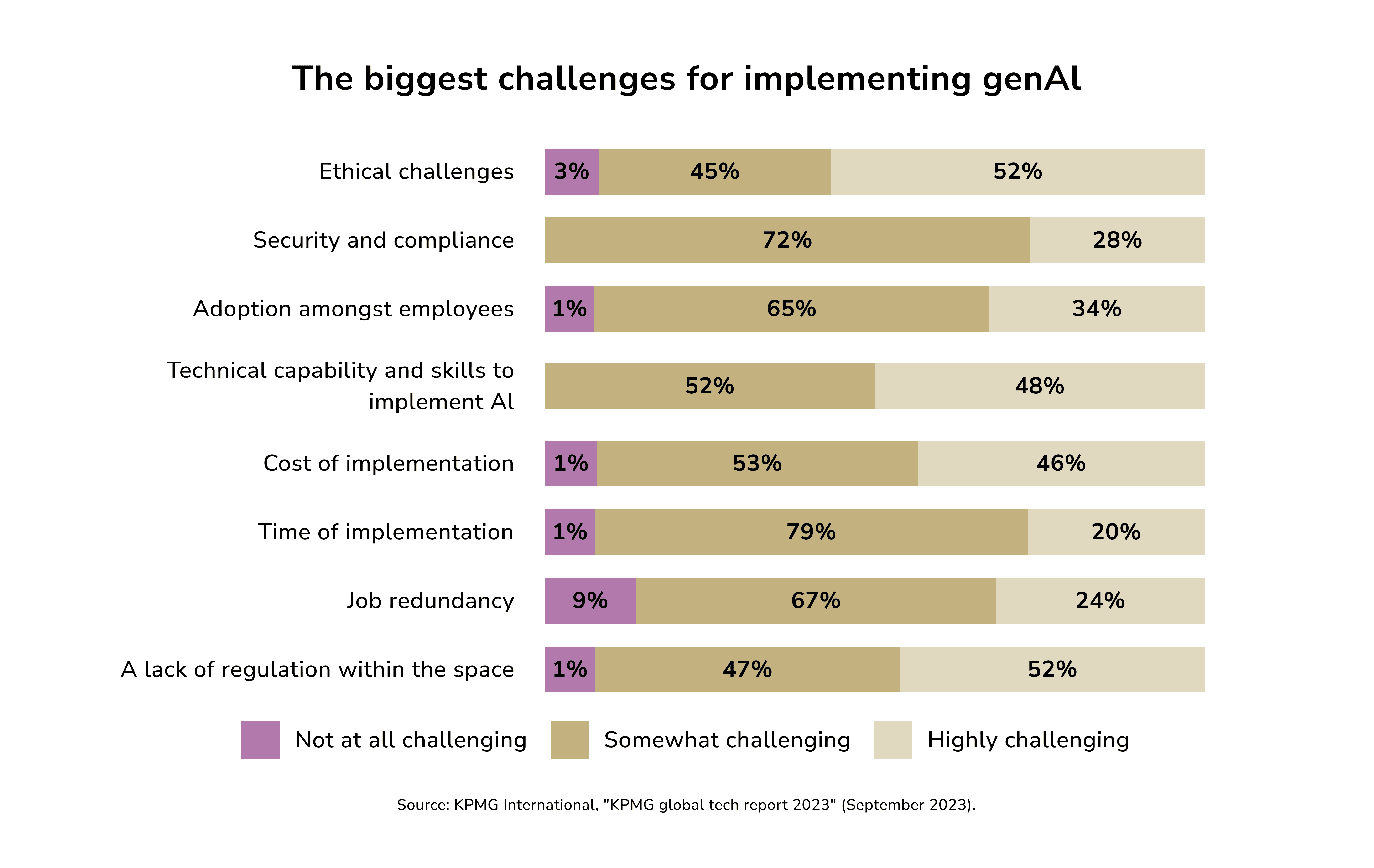
Gen AI Challenges
Every new technology carries risks and obstacles. KPMG research shows that CEOs are clearly aware of the challenges that hinder the great promise of AI.
AI: Redefining the Future of Fintech
AI has furnished the financial sector with a range of benefits. Fintech can keep innovation going further by exploring the multifaceted AI potential. Clients can enjoy top-notch services while AI takes care of their safety. Fintech companies worldwide use AI to make their operations safer and more effective. They share a common objective: increasing the productivity of fintech firms. Employing AI automation tools can help them achieve just that.
Despite these advancements, there is still a shortage of qualified AI developers. Consequently, banks are referring to fintech AI development services. Are you seeking a team of AI developers in the fintech space? Contact us, and we will assist you in harnessing the power of these cutting-edge technologies.

Roman Zomko
Other articles